 Each newly minted developer invariably faces the question of how to make a roof. It is this complex protective structure that becomes the main barrier to the penetration of moisture and cold into the house. The term and quality of service of the entire building as a whole, coziness and comfort in the rooms below depend on how competently the roof is built. In this article, we will consider the basic principles of roofing, highlight how you can achieve a solid and durable construction.
Each newly minted developer invariably faces the question of how to make a roof. It is this complex protective structure that becomes the main barrier to the penetration of moisture and cold into the house. The term and quality of service of the entire building as a whole, coziness and comfort in the rooms below depend on how competently the roof is built. In this article, we will consider the basic principles of roofing, highlight how you can achieve a solid and durable construction.
How to ensure the durability and proper functioning of the roof
Before you make a roof, you should understand the main aspects of its functioning.
One of the most important conditions for the service life of a roof structure is the absence of moisture accumulation in the form of steam and water, and this can only be achieved with properly installed ventilation and good insulation.
This condition is especially important when constructing attics or simply insulating the attic.
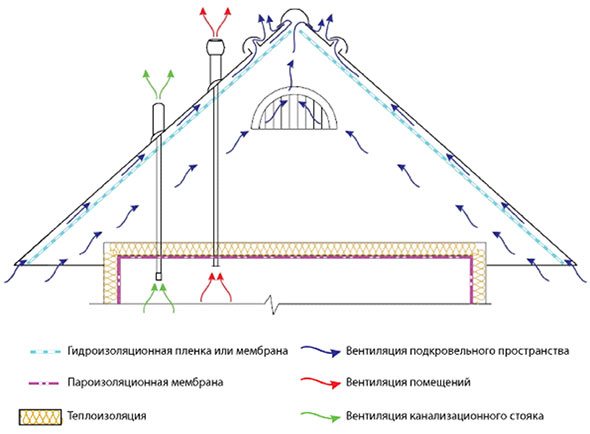
A cold roof, as a rule, already implies the presence of ventilation, however, its installation will require compliance with the installation technology.
So, the moisture contained in the air is, perhaps, the main enemy of the structure. Daily and seasonal fluctuations in temperature are conducive to the formation of condensate on metal and other types of roofing.
This also applies to other parts of the structure. In addition, in the coldest time, with a temperature difference in the insulation reaching tens of degrees, the air contained in it releases moisture, which then settles there.
Also curious is the fact that the lower the temperature, the stronger the pressure on the under-roof space of water vapor from the room.
Cold air at the same time is able to hold a small amount of steam. This can lead to the fact that the moisture-saturated insulation simply ceases to perform its function due to an almost twenty-fold increase in thermal conductivity.
In addition, moisture adversely affects the condition of structures that are prone to corrosion.Sources of moisture, among other things, can serve as melt and rainwater.
Advice! During installation, special attention must be paid not only to protection from rain, but also from precipitation in the form of snow, capable of penetrating into any slightest gap.
In other words, making a roof with your own hands, designed for a long service life, must provide for ventilation, and this requires air circulation.
How to ensure roof ventilation:
- Hemming of the roof eaves should provide free access of fresh air around the perimeter of the entire roof. For example, this can be achieved by installing perforated spotlights or lining with provided gaps between the planks.
- As usual, the movement of air occurs from the eaves to the ridge by heating the roof with the sun's rays and the warmth of the house. This implies the possibility of air escaping from under the ridge. If the roof slopes are large enough and are more than 7-10m in length, additional ventilation outlets should be installed.
- When sealing the roof, the use of mounting polyurethane foam is not recommended, since after hardening it loses its elasticity, and the elements of the roof structure change their dimensions and shift relative to each other under the influence of temperatures over time. It is necessary to use special seals.
About the roof base

The most common material for the construction of load-bearing structures for pitched attic roofs is softwood.
This category of structures involves the use of semi-dry or air-dry wood with a moisture content of not more than 20%. The material used must be free from defects such as cracks, knots, wormholes, oblique, heart-shaped tubes.
Wood roof frame must meet all the requirements for calculating the bearing capacity and deformation that does not interfere with normal operation, taking into account the duration of action and the nature of the loads.
The durability of such structures, as a rule, is ensured by constructive measures and protective treatment, which implies their protection from biodamage, fire and moisture.
Roof insulation device

The arrangement of a cold-type roof assumes the presence of thermal insulation based on the insulation of the attic floor.
In order to ensure reliable thermal protection of the attic floor, it is required to lay a vapor barrier layer on the inside of the insulation to protect it from moisture vapor in the indoor air.
The rules for laying thermal insulation material are as follows:
- To ensure competent thermal protection at home, the material is laid continuously, without breaks and thereby forming cold bridges.
- When insulating the attic floor, the insulation is also placed vertically on a section of the outer wall, thereby blocking the insulating layer located horizontally.
- When arranging the attic, all vertical, horizontal and inclined surfaces are subject to insulation.
- Insulation plates are laid on the base tightly to each other, ensuring the same thickness in each layer.
- I lay the thermal insulation in several layers, provide for the separation of the seams of the plates.
- Attic insulation involves laying a vapor barrier membrane on the inside of the insulation material, after which the room can be sheathed with clapboard, boards, drywall and other finishing materials.
- In order to protect the base of the roof and the thermal insulation layer from moistening with steam penetrating from the premises, the vapor barrier must be laid hermetically.
- To prevent heat leakage, thermal insulation boards should be installed to the ceiling and walls of the attic as tightly as possible, and when laying the material in several layers, also to each other, while preventing the plates from deforming.
- It is very important that the thermal insulation is initially dry and does not fall into the rain during installation. To do this, a waterproofing film is often installed first, especially in large houses, the terms of work in which are usually long.
A sign of poor-quality installation or simply insufficient thermal insulation of the roof is the formation of condensate on the inner walls, as well as vapor barrier.
The correct roof for the climate of the middle lane should have a thickness of insulation of at least 150 mm. The thickness depends on the insulation material, installation recommendations from the manufacturer and wall thickness.
Accordingly, the further north construction is carried out, the thicker the thermal insulation layer should be, and the further south - the thinner (in the south, the insulation layer can be only 50 mm)
The size of the insulation is selected so that the slab can be held tightly between the rafters, while the air is not able to circulate between them.
To finally fix the plates across the rafters, additional thin slats are mounted under the insulation.Insulating material fills all the space provided for it. In the thermal insulation layer, the formation of depressions and cavities for the passage of air is prevented.
In order to avoid the formation of cold bridges during the construction of the interface between the coating and the wall, the following errors must be avoided:
- Coincidence of horizontal and vertical seams of various structural parts.
- Curvature and curvature of the beams and frame supports, which create air channels for the passage of cold air in the thermal insulation layer.
- Loose pressing of the insulating material to the warm surface of the coating.
- The formation of a gap between an additional vertically installed wall thermal insulation layer and a coating insulation layer.
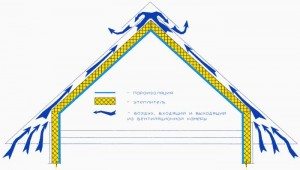
Roof ventilation devices
Before you properly make a roof, you should study the criteria for ensuring proper roof ventilation:
- must be provided with unobstructed roof penetration air flow from the eaves to the ridge.
- The required height of the ventilated air layer above the thermal insulation is determined based on the calculation of the drying effect of the layer over a period of operation of 1 year. In this case, it should be at least 50 mm. The area of supply and exhaust openings is arranged no less than the cross-sectional area of the ventilation layer.
- Exhaust openings must be located at the highest point of the roof.
Advice! A non-ventilated air layer in the roof of the building is allowed above the premises, the relative humidity of which does not exceed 60%. When installing non-ventilated coatings, the use of wood and heat-insulating materials based on it is prohibited.
The thickness of the ventilation layer depends on the angle of inclination and the length of the slope: the smaller the angle and the longer the slope, the wider the gap should be.
The general purpose of such ventilation is as follows:
- reducing the influx of heat that occurs under the roof sheathing under the action of sunlight;
- removal of steam penetrating upwards from interior spaces such as a kitchen or bathroom;
- ensuring uniformity of temperature on the entire roofing surface to avoid the appearance of ice over the heated surface due to snow melting.
Roof waterproofing device
Roof waterproofing is usually arranged using rolled waterproofing materials on top of the counter-lattice under the roofing itself.
Before laying, the rolled materials are placed at the installation site, and the placement of the sheets of rolled waterproofing materials must ensure compliance with the values of their overlaps during fastening.
As additional moisture insulation, lining materials such as a bituminous waterproofing membrane based on polyester and a self-adhesive SBS-bitumen membrane with a polymeric protective layer can be used.
With a slope of up to 30 degrees, an additional lining layer is laid over the entire roof area in rows parallel to the eaves with a longitudinal and transverse overlap of 10 and 20 cm, respectively.
If the slope exceeds 30 degrees, waterproofing PVC roofing membrane it is enough to mount it in the valleys, around the chimney, skylights, ventilation shafts, along the eaves and in other places where snow can accumulate.
Roof framing installation
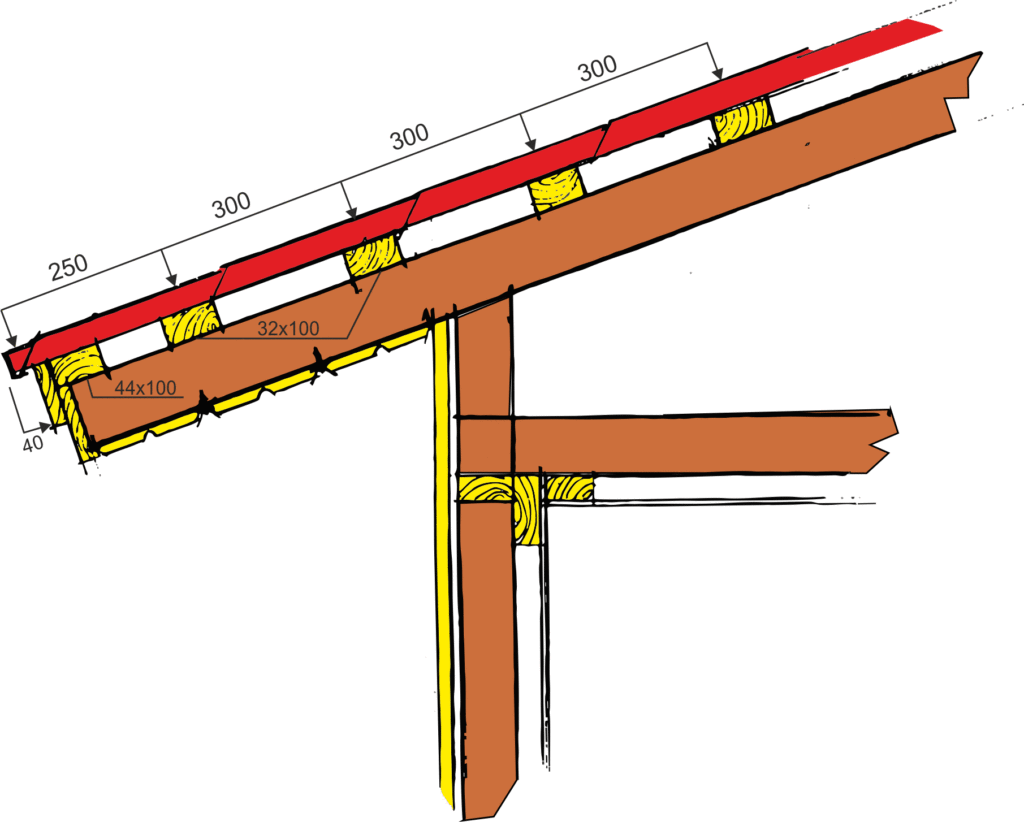
Before laying the roof, you need to take care of the arrangement of the crate.
When arranging a wooden crate for roofs made of piece materials, a number of requirements should be observed:
- the joints of the crate must be placed apart;
- the step between structural elements must be observed in accordance with the project;
- in places of shelter of valleys, grooves, cornice overhangs, as well as under the roof of small-piece elements, a solid base should be arranged.
When installing, for example, bituminous tiles, a smooth, clean and dry base is equipped, made of moisture-resistant plywood at least 9.5 mm thick, edged, tongue-and-groove boards from 25 mm thick, OSB, reinforced concrete slabs, etc.
The maximum allowable height differences, as well as the gaps between the parts of the base, do not exceed 2 mm.
Drainage device
Roof drainage can be both external and internal, and in any case, water is removed by special drainage systems. There is also an unorganized drainage system, in which water flows from the cornice overhang to the adjacent territory, although this option is applicable only to low-rise structures located in the middle of block development.
External drainage is applicable in buildings no higher than 5 floors. The organization of external drainage from the roof by means of gutters, funnels and downpipes requires a preliminary calculation.
An important component for the implementation of roof repair work is GOST on safety for roofers and strict adherence to its instructions.
It is mandatory for installers to wear safety harnesses before climbing onto the roof. For comfortable movement on the roof, ladders should be provided at least 0.3 m wide with slats for foot rest.
You should not perform roofing work in ice, fog, thunderstorm or wind, because you will agree that it is better to finish the work with a slight delay than to regret the accident later.
Did the article help you?
