 In comparison with other structural elements of the house, the roof is most exposed to atmospheric precipitation. Along with the basement and foundation, the service life and reliability of the structure depend on it, therefore, it is necessary to perform roof overlapping with great care, observing all the necessary technological conditions.
In comparison with other structural elements of the house, the roof is most exposed to atmospheric precipitation. Along with the basement and foundation, the service life and reliability of the structure depend on it, therefore, it is necessary to perform roof overlapping with great care, observing all the necessary technological conditions.
In this article, we will consider the types of roof slabs, as well as the conditions and technologies for their construction.
Overlapping with asbestos-cement materials
Asbestos-cement roof slabs are the most common in the construction of country houses, since they are relatively cheap, easy to install and very durable.
The main types of asbestos cement roofing materials are as follows:
- wavy sheets, often called ordinary slate;
- flat slabs.
However, corrugated sheets are often preferred, since they are easier to mount, they are more reliable in operation, and less wood is needed for the crate under the sheets. More often slate roof laid with a slope of 25-33 degrees.
Rules for the installation of floors from asbestos-cement sheets:
- When the roof is covered, corrugated sheets of asbestos cement of a conventional profile are mounted on a crate made of wooden beams with a section of 50 * 50 mm with a step between the rafters up to 1.2 m, and also - 50 * 60 mm with a step of up to 1.5 m.
- As for the crate, boards 120 * 40 mm or poles 70-80 mm in diameter are used for it, which are hewn into two edges. The step between the bars of the crate should not exceed 525 mm.
- When overlapping the roof of the veranda, the slope of the roof of slate sheets can be reduced to 10 degrees, however, in this case, the longitudinal and transverse joints (overlaps) of the sheets should be sealed.
- Each of the corrugated sheets should rest on three boards or timber. To ensure a snug fit of the sheets to each other and the crate, the eaves beam is lifted with linings measuring 6 * 8 mm, and the subsequent even beams - with the help of a 3 * 70 mm plank. In the ridge, grooves, on the overhang and around the roof openings, the crate is replaced with a flooring of 2-3 boards.
- The sheets are laid from the bottom up in rows (from the cornice to the ridge) parallel to the cornice, while aligning their position along the cord. Each stacked sheet should overlap the adjacent one by one wave. Adjacent rows are laid with an overlap of 120 mm with a roof slope of 33 degrees, 200 mm - with a slope of 25 degrees.
- Rows of sheets are also stacked in a run.The amount of run-up is selected depending on the method of their installation. The first method involves shifting the even rows relative to the odd ones by one wave. In this case, the goal is to prevent the concentration of the corners of four sheets at the same time at one point, since this will lead to a break in the sheets, as well as the appearance of significant gaps in the roof. The second method involves laying sheet rows without a run-up with preliminary cutting of the corners of the sheets.
- With a slope of the roof slope of more than 33 degrees, the sheets are laid dry, and the gaps in the places of overlaps from the side of the attic are sealed with a cement-sand mortar with fiber filler. If roof pitch angle less than specified, the sheets are laid in places of overlap on a layer of mastic or a similar solution. Mastic is prepared from bitumen, fluff lime, diesel oil and slag.
- Sheets are fastened to the crate with galvanized nails or screws with washers made of roofing material or galvanized steel with dimensions of 35 * 35 mm put on them. After the mastic dries, the nails are painted.
Advice! Holes for screws or nails on the crests of waves in the sheets are drilled during operation or in advance using an electric or hand drill.
- Each of the sheets of the eaves row is attached with three nails: two - to the second wave from the edge from the overlap side, one - to the fourth wave to the cornice beam. The remaining extreme sheets on subsequent rows are attached with two nails.
- For fastening the navigation bridges on the ridge beam, the hooks are strengthened with a step of 2 m. The ridge and ribs of the roof are covered with semi-cylindrical asbestos-cement fittings. If there are no shaped parts, boards knocked down at an angle can be used.They must be painted with aluminum paint, which is bred on bitumen, or red lead.
- With a roof slope of less than 35 degrees, roofing felt or roofing material can be placed under asbestos-cement sheets. The purpose of the underlayment is to prevent rainwater from getting under the sheets and flowing into the attic.
- When the roof is covered with corrugated asbestos-cement sheets, dormer windows, chimneys and grooves are lined with sheet steel. To connect the sheets, double lying folds are used or sheets are overlapped by 150 mm. In this case, a strip of burlap smeared with bitumen or minium is laid between the sheets. Under the groove, a continuous flooring of boards is arranged and roofing material is laid.
Tiling
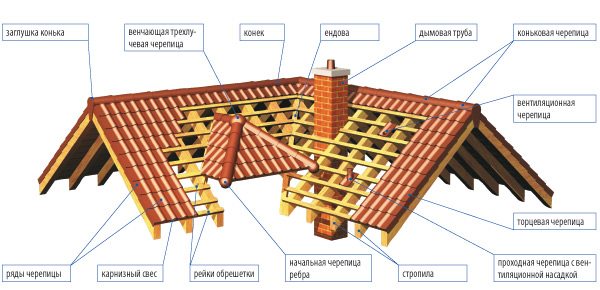
Tiled roofs are famous for their strength, fire resistance and durability, but this roof material has been of little use lately. Repair of such a roof is reduced to the replacement of individual, failed tile tiles.
The disadvantage of a tiled roof is its large mass, which requires additional strengthening of the rafter and sheathing structure.
The slope of such a roof should be at least 30 degrees to ensure operation without leaks.
There are several types of tiles:
- groove tape;
- groove stamped;
- flat tape.
Grooved tiles are made from clay or cement-sand mixture. Ridge tiles are used to cover roofing ridges.
The most common is the grooved strip tile, which, in comparison with other types, is lighter in weight. It has grooves (flanges) into which, when overlapping, the protrusions of neighboring tiles are placed.
Slotted stamped tiles have an eye with a hole through which they are tied to the crate. As for the tape tile, it has a hole in the spike for this purpose.
Rules for laying roof tiles:
- Laying grooved stamped and strip tiles is carried out in one layer, and flat strip tiles - in two layers using a scaly or conventional way.
- In order to evenly distribute the load on the rafters and walls, the roof is arranged simultaneously on opposite slopes.
- Tiles are laid from right to left, maintaining an overlap in a row of 20-30 mm and an overlap between rows of 60-70 mm. If the tiles do not fit snugly in places of overlap, such places are additionally compacted with a cement-sand mixture. Tiles are attached to the crate with wire through a row or each, depending on the roofing slope.
- Flat strip shingles can be laid both from right to left and from left to right with overlapping rows and spaced seams. To ensure the expansion of the seams, each odd row is made from whole tiles, and the even row is started from halves. Such tiles are attached to the crate by means of cleats.
- Depending on the amount of precipitation, the presence of conditions for the occurrence of significant ice on the roof and the type of tiles, roofs of this type are arranged with a slope of 30-40 degrees.
- A tiled roof made of flat strip and grooved tiles is usually laid on a crate made of 50 * 50, 60 * 60 mm beams or poles with hewn edges, which provide a tight laying for the tile rows.
- When installing a roof overhang, it is imperative to ensure a smooth transition between the overhang and the slope. The first row of tiles on the overhang is laid directly on the overhang boards.For this reason, they are laid 25 mm higher in comparison with the main plane of the crate.
- In rare cases, in order to avoid blowing snow into the cracks, the tile roof is laid on a roofing sheet laid in one layer. At the same time, instead of the crate, a solid boardwalk is performed. The flooring is covered with a layer of roofing, then the bars are stuffed in the form of a crate, after which they lay a tiled roof, while clinging the tiles to the bars, in other words, they lay a continuous crate and a solid flooring.
- To prevent excessive consumption of timber, instead of a continuous flooring, as well as a roofing layer flooring, it is sometimes limited to puttying the joints between the tiles with a setting mortar. However, the practice of using gap-filled tile roofs indicates that the grout does not adhere well to the tile, which soon causes it to lag behind and fall off the roof in pieces.
- The crate is nailed to the rafters with nails in a length equal to at least two thicknesses of the beams. The slopes of a tiled roof are arranged by laying tiles in rows on each of the opposite slopes, starting from the bottom. If they take place, trim the overhang, ridge, ribs, grooves.

Part of the tile tiles, located on the slopes (every 8-10 pieces) in a checkerboard pattern, are attached to the crate using annealed wire 1.4-1.8 mm in diameter, using special spikes on the tile, as well as roofing nails, which attach the wire to the crate.
- The overhang is trimmed and frontal boards are sewn under the overhang, which, along with the eaves, protect the lower tile rows from being blown away by the wind and, in addition, increase the rigidity of the overhangs, which are the most critical parts of the roof slopes.
- The ridge of the tile roof is covered with grooved tiles laid on lime mortar and tied to the rafters or battens. Such tiles cover the upper rows of ordinary tiles by 40-60 mm. If there is a significant gap between the upper bars of the crate of two slopes converging at the top, the gap is preliminarily sealed with a rail.
Advice! If there is no ridge tile, then the roof ridge can be covered with two boards, which are knocked down at a certain angle and attached to the crate with nails.
- Tiled roofing is best suited for covering single and gable roofs. Roofs of a more complex shape have ribs and grooves, and their lining greatly complicates the installation process, and also reduces the quality of the roof.
- The tiled roof is completed with the finishing of ventilation and chimneys. At the same time, it is important to prevent the possibility of water leakage near the pipe into the attic space, and from there further into the room. If the tiles fit snugly to the pipe, they are limited to coating with cement mortar around the pipe. In other cases, a roofing steel scarf is made around the pipe.
Sheet steel ceiling

The advantage of such roofs is the ease of work when constructing complex roofs that have sinking corners, curvilinear outlines, different slopes, protruding volumes and other difficulties. However, sheet steel is quite expensive and also requires systematic maintenance during operation.
The use of non-galvanized roofing steel requires its processing before laying with hot bitumen coating twice on both sides.
Sheet steel coating is performed on a crate of 50 * 50 mm bars with a step between them of 200 mm. In some cases, a continuous crate with flooring over roofing material or roofing is performed to insulate attic spaces and extend the life of the roof.
The sheets are connected by means of folds: on the short side - recumbent, along the length - standing.
The roof is fastened to the crate with clamps, nailed with 50 mm long nails to the side of the crate. Clamps are placed at each location of the ridges with a step relative to each other of not more than 0.6 m (along the length of the ridge) and at least 3x per 1 sheet.
Cornice overhangs are arranged on crutches, gutters on the walls are mounted on hooks, drainpipes are hung on stirrups.
When covering the roof slopes, sheets with folds and edges are laid out in rows perpendicular to the ridge, after which the sheets of each row are connected with recumbent folds. The sheets are laid in place and fastened with clamps to the crate.
Next, the subsequent strips are assembled in the same order, after which they are connected to each other with standing folds. On the ridge there are strips of roofing slopes with a double standing seam.
At the end of the finish of the ridge, the ordinary coating is fastened to the wall gutter using a double lying fold.
Did the article help you?
