The truss and truss beam are the structures used for the installation of the roofing system. All structures of the bearing type belong to the sub-rafter and rafter elements. Rafter systems cover the span and serve as the basis for the roof deck.
Under-rafter structures, covering 12 and 18-meter spans between columns, are intermediate supports for truss structures with a 6-meter step.
Values of structural truss elements

According to the nature of the perception and distribution of internal and external forces, roof structures are divided into truss beams and trusses.
The beam is a single-element structure that takes the load along the entire length of the span.
In its sections, the bending moments cause different normal forces, which are the largest for the extreme fibers.
roof truss is a bar structure that is loaded exclusively at the junction points of the bars. Normal unambiguous forces caused by the nodal load in the rods make it possible to use their cross section in full.
For prefabricated reinforced concrete, the most rational recently recognized bezraskosnye trusses with a circular outline of the upper belt. With approximately inverse ratios in height in the middle of the span, the own weight of the truss is 1.5-2 times less than the weight of the beam.
Rafter beams made of reinforced concrete
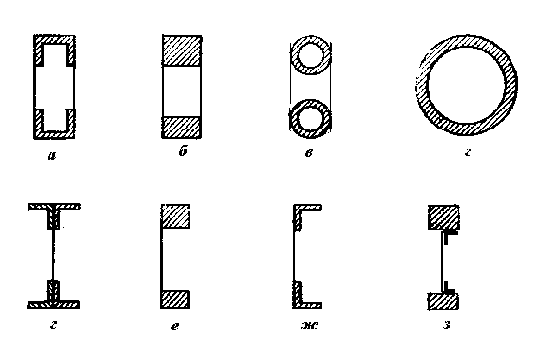
Types of beams by profile type
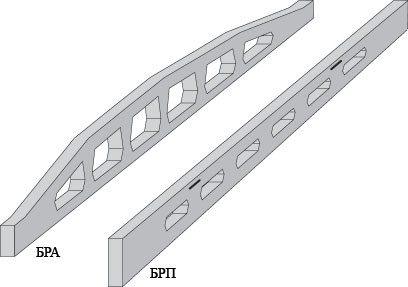
Reinforced concrete truss beams are used to cover spans of 18, 12, 9 and 6 meters. When spans from 24 meters are overlapped, beams are inferior to trusses in terms of technical and economic indicators. Beams 6 and 9 meters long are mainly used for roofing extensions, and beams 12 meters long - as longitudinal and transverse crossbars of the coating.
Beams 18 meters long are used as transverse crossbars, on which 3x12 or 3x6 slabs are laid.
According to the type of profile, the following types of beams are distinguished:
- Shed with lower broken belt or parallel belts;
- Trapezoidal gable, having a constant slope of the upper belt;
- With an upper curvilinear and broken belt.
Different types of beams are used in the construction of various types of coatings:
- Usually single-pitched beams are used for roofing with a slope in one direction, for example, roofs of extensions.
- Reinforced concrete truss beams with parallel chords are easy to manufacture. Reinforcing cages in them have a constant height. Such beams are used in the construction of horizontal roofs.
- The most widespread on gable roofs are beams with a constant slope of the upper belt, equal to 1:30 for roofs with a small slope and 1:12 for pitched ones. Their main disadvantage is the need to make reinforcing cages having a variable height.
- When it becomes necessary to skip engineering communications at the level of coverage, gable beams with a span of 18 and 12 m are used.
- Beams with the outlines of the upper chord in the form of a curve or a broken line are characterized by the most favorable distribution of materials along the span than gable beams, which have a constant slope for the upper chord. But such beams were not widely used due to the complex technology of their production.
Beam section selection
The selection of cross sections and reinforcement for reinforced concrete beams has its own characteristics:
- The most economical form for the cross section of the crossbars is an I-beam with a wall of 60-100 mm. The wall thickness is selected mainly based on the conditions of placement of reinforcement cages, compaction and placement of concrete in a vertical position.
The wall thickness of the V-shaped supports gradually increases to ensure the strength and resistance to cracking of inclined sections, turning into a trapezoidal or rectangular section on the support, having a width that is equal to the width of the shelves. The T-section can be taken for beams with a length of 6 and 9 meters.
Advice!
In the general case, in the middle of the span, the height of the section of the crossbars is assigned 1/10-1/15 of the span. In addition, for gable beams in the middle of the span, the section height is determined by the typical beam height (900 or 800 mm) and the slope of the upper chord.
- The width of the upper shelf, for reasons of stability during installation, transportation and reliable support of roofing slabs, is taken in the range of 1/50-1/60 l, which, as a rule, is 200-400 mm.
The width of the lower flange is determined depending on the compressive strength of the concrete of the flange, the placement of prestressing reinforcement (taking into account the diameter of the clamps of the tensioning devices), and the required length of the support platform on the beam column.
Usually the width of the bottom shelf is 200-280 mm. The transition to the vertical wall from the shelves is carried out with the help of haunches with an inclination angle of about 45 °. - Trellised gable reinforced concrete truss beams have a cross section of 200-280 mm. These beams are easier to manufacture and very convenient when passing various kinds of communications.
- For the production of gable beams, concrete of classes B25-B40 is used. As prestressed longitudinal reinforcement, rod reinforcement of classes A-V and A-IV, high-strength wire of class Bp-II, ropes of class K-7 are used.
With the help of class A-III fittings, longitudinal structural rods of the upper shelf, shelf clamps and wall frames are made.
In the supporting parts of the crossbars, in which there are large forces from the preliminary compression and reactions of the supports, it is necessary to install additional reinforcement in the form of vertically arranged rods and meshes.
- At the stage of compression in gable beams having an I-section, initial cracks may occur in the upper flange. In this regard, it is also advisable to reinforce such reinforced concrete truss beams in the upper part of the crossbar with structural prestressing reinforcement.
The installation of such reinforcement helps to reduce the eccentricity of the compression force and, accordingly, to reduce the tensile stresses in the upper flange. - The calculation scheme of crossbars for roofing is taken as a freely supported beam on two supports. Taking into account the details of support on the beam columns, the calculated span is taken. The load on the beams from snow and the own weight of the coating is transferred to the supports in the form of concentrated forces through the ribs of the panels.
In the case of five or more concentrated forces, the actual load is replaced by a uniformly distributed equivalent one. Loads from suspended loads, suspended transport and a lantern are taken into account as concentrated. - The calculation of resistance to cracks and deflections, the selection of transverse and longitudinal reinforcement is carried out as for a simple bending element of a rectangular, I-beam or T-section for all stages of the structure.
At the same time, it must be taken into account that the dangerous normal section in gable beams is not located in the middle of the span, but is 0.35-0.4L away from the support. - When exposed to a uniformly distributed load, with the slope of the upper shelf equal to 1:12, the location of the dangerous normal section is at a distance of 0.37L from the support.
- In beams with parabolic curvilinear and parallel outlines of the upper chord, the normal design section is located at a uniformly distributed load in the middle of the span.
Beams from a bar
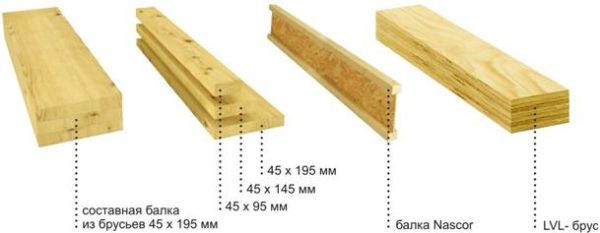
Glulam rafters, or glued beams, are a technologically advanced modern building material created using advanced technologies. Glued rafters are widely used in the USA and Europe due to their high performance.
For example, in the United States, approximately half of interfloor floors are installed using structural glued beams. This figure in the EU countries is about a third. Structural timber is also used in load-bearing structures.
The most bending-resistant beam is a beam with an aspect ratio of 7:5.
A round log is able to withstand a greater load than a beam that is hewn from it, but it has less bending strength. Often, beams bend under pressure from the weight of people, furniture, floors, and backfill. Basically, the deflection does not depend on the width, but on the height of the beam.
The connection of two identical beams with dowels and bolts allows this design to withstand a load 2 times greater than these two beams, which will simply be laid side by side. But there is a limit in reducing the width. If the glued rafters are too thin, they may bend to the side.
Advice!
Beams for attic and interfloor floors must have a thickness of at least 1/24 of its length.

Rafter beams
Under-rafter beams, which are used in coverings with beam structures of rafters, and under-rafter trusses, used in coverings with truss trusses, have the following features:
- They are made with beam reinforcement only prestressed.
- The rafter beam and truss are attached to the frame columns with bolts or welding of steel embedded parts.
- Beams of subrafter structures come with non-parallel and parallel belts.
- The rafter beam is calculated according to the scheme of a single-span beam loaded with a distributed load from its own weight and in the middle of the span with a concentrated force (support reaction rafter beam).
- Trusses or beams of sub-rafter structures have steel tables or reinforced concrete consoles to support the supporting structures of the coatings.
- Trusses and truss beams are attached to the frame, as are the main roof structures, the support of which on the truss structures is the same as their support on the frame columns.
- The upper belts of the beams of the sub-rafter structures are untied with a solid disk of profiled decking.
The reliability of the entire roof structure depends on the correct choice of rafter and rafter beams, therefore, the calculation of their cross section must be approached with all responsibility.
Did the article help you?
