 When erecting the roof of a country wooden house, such a structural element as a sliding support for rafters plays a rather significant role. This article will talk about what it is, how it is used and how this element is installed.
When erecting the roof of a country wooden house, such a structural element as a sliding support for rafters plays a rather significant role. This article will talk about what it is, how it is used and how this element is installed.
The sliding support for the rafters is required in order to compensate for the distortions of the truss structure resulting from the shrinkage of the wood during operation.
With the help of a sliding support, the rafters are attached to the bearing beam, as a result of which a self-balanced structure is formed.
In addition, this element can be used in many other cases where several sliding elements need to be connected to a fixed base.
In addition to strengthening the structure of the rafters, the sliding support has a number of advantages, which include ease of installation that does not require special skills and tools.
In addition, the sliding support reduces the amount of manual labor involved in the construction of the roof, as it eliminates the need to manually balance the elements of the roof structure.
When manufacturing a sliding support, it should be taken into account that it is subjected to intense influence of various negative external factors, the most significant of which is the environment.
Therefore, the sliding supports of the rafters are coated with zinc melt, which is additionally alloyed with other elements to increase strength and reduce corrosion, which improves the load-bearing capacity of the structure.
The sliding bearing itself is made by cold forming from a material having sufficient strength and ductility, such as 08 ps semi-quiet mild steel.
The carbon content in this grade is 0.08%, which makes it possible to stamp this material well. To balance its strength characteristics, the deoxidation method is used.
Purpose of sliding supports

Sliding supports for rafters are designed for their fastening to the mauerlat during the construction of timber and log buildings.
The effectiveness of this perforated fastening is proved by practice: the sliding fastening of the rafters allows you to avoid the "hanging" of the roof and the bursting of the walls of a wooden house.
All buildings made of solid wood, which include rounded and chopped logs, as well as profiled timber, are characterized by natural shrinkage.
Shrinkage of the rafter system of a wooden house can cause weakening and distortion of the structure. Floating rafters made with sliding supports help to solve these problems.
The sliding support consists of a metal bracket and a corner with a loop.
It is mainly characterized by standard sizes:
- Thickness - 2 mm;
- Width - 40 mm;
- Height - 90 mm;
- The length can vary between 90 and 160 millimeters.
The rafter system must withstand quite serious loads, so the fasteners used during its installation, including sliding supports, must be made of reliable and durable materials.
In accordance with GOST 14918-80, for the production of perforated sliding bearings, low-carbon steel grade 08 PS is used, which is characterized by a rather high strength.
In addition, since the roof of any building is subject to various negative atmospheric influences, the material of the blanks is additionally galvanized to reduce the corrosive effect.
It should also be noted that the process of roof installation using the technology of sliding rafter supports is rather low laboriousness, since it is enough to use only a screwdriver to fasten them to the required structural element.
Characteristics of the sliding support for rafters
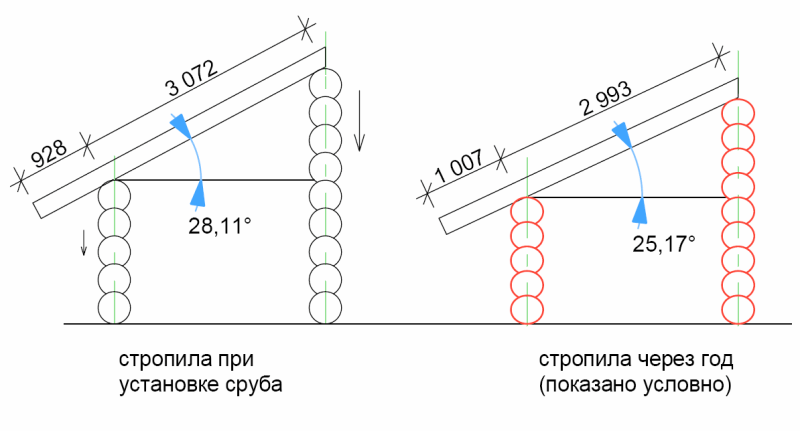
Wooden houses shrink during the first years of operation, after which their geometric shapes and sizes gradually change under the influence of changes in humidity and temperature.
In this case, the height of each beam or log changes, as a result of which the height of the entire wall also changes, consisting of changes in the height of each individual element.
From this we can conclude that the higher the wall, the more it shrinks during operation. The wall located under the ridge has the greatest height, therefore its draft is also maximum.
The walls supported by the rafters located at the edges of the house settle less, which leads to a change in the angle of the roof over time.
This makes it necessary to take into account these geometric changes when fastening the rafters and giving mobility to the joints:
- rafters, located in the ridge, are made rotating relative to each other, fixing them on both sides with metal plates on studs.
- Lower ends do-it-yourself rafters represent a particularly difficult case, since in the process of shrinkage, not only their rotation occurs, but also a shift relative to the wall. Therefore, a rigid and immovable fastening of the rafter leg to the wall will cause it to bulge after shrinkage.
It should be possible for the rafter legs to slightly, but tangibly rotate and shift along the wall, without reducing the strength of their fastening.
Previously, twisted annealed wire was used for this, with the help of which the upper log was tied to the leg of the rafters, which provided both a movable and reliable fastening.
Modern technologies have made it possible to find a more effective replacement for this method, which turned out to be a sliding rafter support. This mount is more convenient in terms of installation, meets various requirements and allows you to securely fix the leg of the rafter on a log or Mauerlat beam.
Useful: in the case of using glued beams in the rafter system, this method is the only one that simultaneously provides the required mobility in combination with reliability.
The fastening is located along the displacement of the beam, for which the wood of the upper beam is ground down.
In this case, a platform is formed on which the fixed lower part of the support is fastened. During installation, the support should be positioned so that its shear reserve is as large as possible.
It is recommended to fasten the support on both sides of the rafter leg, although with a slight slope of the slopes and a low roof height, one fastening is enough.
Important: the rafter leg, which has intermediate supports between the Mauerlat beam and the ridge, should also be fastened with a sliding support.
Installation of sliding rafters
Installation of sliding rafters is performed when the gables of the house are made of timber or logs, and the ridge run is attached to the body of the gable. This is necessary to prevent the walls from bursting as a result of a change in the angle of the roof slope after shrinkage.

Wherein do-it-yourself roof rafters they are placed on top of the ridge run and fastened there with the help of a hinged connection, in which it remains possible to change the angle at which the legs of the rafters are connected.
For the manufacture of such a connection, perforated plates are used, connected with studs, or the upper parts of the legs of the rafters are superimposed on each other and connected with studs with nuts and washers.
In this case, the following conditions are met:
- Mauerlat, which is the upper crown of the log house, is connected to the rafter legs with the help of sliding supports. They are made from 2mm thick galvanized carbon steel. Usually sliding supports are made in sizes 90x90x40, 120x90x40, 160x90x40 and 270x90x40 mm. Their length is selected in accordance with the expected displacement of the legs of the rafters.
- During installation, the guide rail of the sliding support should be fixed parallel to the leg of the rafter, and the corner should be installed in the upper part perpendicular to the leg to allow sliding at the maximum shrinkage length.
- The rafter legs are laid on the Mauerlat either from above or by cutting into the body of the Mauerlat. The depth of such a tie-in does not exceed ¾ of the diameter of the Mauerlat beam or log.
- For the manufacture of rafters, boards with a section of 200x50 or 150 mm are used.
- All elements that make up the rafter system should be treated with special bioprotective and fire retardant preparations.
Summing up all the above, we can conclude that sliding supports are the most important element in the construction of the roof of a wooden house.
In addition to increasing the rigidity of the rafter structure, this element allows you to compensate for the natural shrinkage of wood in the first years of the building's operation.
Did the article help you?
