 This article will discuss wooden rafters, layered and hanging, their main pros and cons, and the installation of a wooden rafter system.
This article will discuss wooden rafters, layered and hanging, their main pros and cons, and the installation of a wooden rafter system.
For the manufacture of load-bearing elements of pitched roofs, the following materials are usually used:
- Wood being the most popular material;
- Rafter reinforced concrete systems;
- Reinforced concrete truss trusses - diagonal truss elements;
- Large concrete panels.
The choice of a specific design depends on a number of roof parameters:
- span size;
- Tilt angle;
- Requirements for the durability of the roof;
- fire resistance;
- Thermal performance, etc.
For the manufacture of wooden rafter systems, round wood (logs), beams and boards are used. There are two types of wooden rafters: layered and hanging rafters.
Rafters
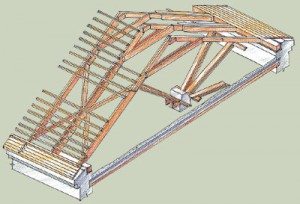
Laminated wooden rafters are a spacer structure used to span small spans.
When installing a load-bearing middle wall, they can be used to cover spans whose width does not exceed 18 meters. In the case of pitched roofs, the maximum width of the overlapped span is 7 meters.
Rafters must have high strength and stability, as well as withstand maximum wind and snow loads and the weight of the roof itself.
During the construction of gable roofs, the lower ends of the layered rafters are supported by a mauerlat (rafter beam), and the upper ends are supported by a system of racks, girders and struts, through which the load is transferred to the walls. The rafters of shed roofs rest on a mauerlat laid along the walls.
The purpose of the rafters is to distribute the load created by the rafters on the walls. When laying the rafter beam on the wall, waterproofing material should be laid under it, and after laying, treat the beam with an antiseptic.
hanging rafters
Hanging wooden rafters are a system of elements consisting of a series of rafters connected with nails, bolts or cuts. There are asymmetric and symmetrical systems of hanging rafters, as well as single-pitched and gable.
Hanging rafters include two pairs of rafter legs connected by a puff, which perceives the thrust.
If the span is less than 18 meters, stiffness should be increased and the deflection of the legs of the rafters should be reduced with the help of crossbars. truss system assembled on cuts and fastened with staples.
When connecting the elements of the rafters to each other, all mates should be precisely adjusted. For the manufacture of parts such as rafter legs, crossbars and struts, coniferous wood is most often used in the form of beams, boards or logs.
Useful: the truss system of factory-made houses is created from plank rafters equipped with struts and racks. The cross section of the rafters is 100x50 mm, and the cross section of the crate is 50x50 mm.
The main advantages of wooden truss systems are:
- Low weight design;
- Quick and easy installation of the system;
- Low system cost rafters in relation to other materials, the cost of erecting the entire roof is correspondingly reduced.
The main disadvantages of wooden rafters include:
- Small compared to other materials, the length of the legs of the rafters;
- Shorter service life than for reinforced concrete or metal structures;
- The need to use additional means to protect wood from fire.
Installation of wooden rafters

Before proceeding with the installation, a site should be organized on the site on which the elements of the rafters will be marked and processed.
Mauerlat is most often made solid and is a log hewn into two ropes.
Consider the main nuances of installing a wooden truss system:
- Mauerlats of external walls and beds of load-bearing internal walls must be treated with an antiseptic and roofing felt before installation for additional protection;
- The ends of the legs of the rafters of wooden houses rest on the outer walls;
- In the case of a small span, not exceeding 6.5 m, the installation of layered rafters can be performed without using an intermediate support.With a span width of 10 to 12 meters, one should be used, and with a width of up to 15 m - two intermediate supports;
- The installation of the rafter system is carried out from the bottom up, starting with intermediate supports with underlay boards or beds.
- Support bars, Mauerlats and backing boards, the cross section of which is usually 100x50 mm or more, are attached to wooden corks treated with an antiseptic. Corks should be laid in masonry, and their step should be 400-500 mm. Fastening is carried out using K4x100 nails.
- The height of the Mauerlat above the upper edge of the attic floor should be at least 40 cm.
- After laying and fastening the elements of the supports, the racks are installed on the beds using a notch with a hidden spike, after which they are additionally nailed to the supporting elements.
- The racks are aligned on a plumb line and two fastenings are equipped. The first is done with the help of temporary board fights, and the second - by nailing diagonal anti-wind permanent ties with the help of light portable scaffolds.
Important: ties are called cross-mounting of racks, for which boards with a section of 100x50 mm are used. These fastenings prevent the racks from folding in case of a strong wind flow from the front side of the building. To fasten the ties to the posts, nails are used, the distance between which along the fibers is at least 60 mm, and across - at least 20 mm.
- A run is laid along the ridge along the upper part of the racks. In the absence of wood material of sufficient cross section, the run is made of two boards, the thickness of which is 50 mm. The fastening of the boards is carried out with nails, the pitch of which is 200 mm.
- Perform alignment of the stacking of runs, after which they are unfastened with metal brackets.If the Mauerlat is the lower support of the legs of the rafters, then the run is made the upper support. However, in some projects it is allowed to rest the upper ends directly on the posts.
- The lower parts of the rafter legs are connected by a notch to the Mauerlat, additionally fastening with nails.
- Mauerlat, using a twist of two 4-mm wires, is tied to ruffs embedded in the walls during masonry. In the case of chopped walls, the leash is fastened with large nails.
- Counter rafters in the ridge are connected with overlays.
- Layered rafters made of round wood are knitted together in half a tree or on an open single spike, after which they are seized with a wooden dowel or bolt. For this, corresponding cuts are made in the leg and run.
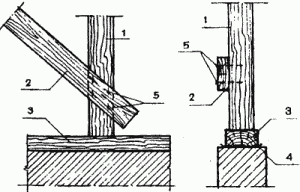
1. Rack:
2. Communication from boards with a section of 50x100 mm;
3. Board lining;
4. Roofing felt in two layers;
5. Fastening with K4x100 nails.
First, the installation, alignment and unfastening of the two extreme pairs of rafter structures is carried out. It is important that their upper part is horizontal.
In accordance with the verified designs, the rest are installed, after which you can proceed to the implementation of the crate.
Important: in the case of large spans, ordinary plank rafters are replaced by truss trusses, or the flat rafter system is replaced by three-dimensional structures that can significantly reduce wood consumption.
The crate is carried out almost simultaneously with the installation of the rafters, since it begins immediately after the first ordinary rafters are mounted.
This allows you not to bother using a large number of temporary connections when attaching the rafters.
Depending on the type of roof, the design of the lathing also changes significantly, which ensures the fastening of the roofing and the resistance of the loads of the snow cover, people performing work on the roof and various tools for these works.
Solid battens are the most versatile, but in many cases it is sufficient to equip the batten with gaps.
It is clear that the greater the distance between the rafters, the greater the cross-section of the sheathing beams. The batten is fastened to the rafters with nails, the length of which should be at least twice the thickness of the beams.
Important: in the most vulnerable places of the roof, such as the ridge, roof ribs, valleys and overhangs of cornices, it is imperative to mount a continuous crate.
That's all I wanted to talk about wooden truss systems and their application and installation.
Wood is the most popular material for making rafters, but for the greatest reliability and efficiency of the rafter system, the various rules and requirements described in the article should be followed.
Did the article help you?
