 For any pitched roof, a system of load-bearing elements is necessary. Otherwise, the roof will either not hold at all, or will collapse in the very near future. That “corset”, which takes on the load from the coating material itself, and the loads acting on it, is called truss structures. About why they are needed, and how they are calculated - later in the article.
For any pitched roof, a system of load-bearing elements is necessary. Otherwise, the roof will either not hold at all, or will collapse in the very near future. That “corset”, which takes on the load from the coating material itself, and the loads acting on it, is called truss structures. About why they are needed, and how they are calculated - later in the article.
You can choose a very high-quality and beautiful roofing material for your home, but without a proper frame it will not be possible to install it. This frame is called truss system, and it is being built for any type of pitched roof.
Even if the roof has only one slope, the coating is attached to the supporting structure, which, as a rule, in this case is represented by horizontal layered rafters resting directly on the walls of the facade.
Important information! The truss system is a set of load-bearing elements of the roof that perceive the weight of the roofing material and atmospheric loads on it, and transfer these forces to the supporting structures of the building. It consists of rafters, connecting and reinforcing elements, sub-rafter structures and battens.
Since the roof structure will take on not only the weight of the roofing material, but also wind loads, and in winter - the mass of lying snow, these effects are immediately included in the calculation of the required power of the supporting elements.
In general, from the factors that determine the structure of the truss system, we can distinguish:
- roofing material
- Normative snow load for a given area
- Compliance with fire resistance requirements
- Roof pitch
- span length
- Durability Considerations
- Features of the architectural solution
- Material selected for system device
- The presence of an attic
The material used for the supporting structures of the roof is very important. After all, everyone roof material has its own strength characteristics, weight, corrosion resistance, which cannot but affect the design parameters.
The manufacture of the truss system is made from:
- tree
- metal
- Reinforced concrete
- Combinations of wood and metal

Reinforced concrete structures have not found much use in residential construction due to their large dead weight, installation difficulties and the lack of flexibility in architectural solutions.
As a rule, structures of reinforced concrete truss systems are used in the construction of industrial and public buildings of a large area, and reinforced concrete slabs are used as a coating.
Metal systems are increasingly used, especially for roofs with complex configurations. It is easier to give them almost any shape, they are durable and have great strength.
Their disadvantages include:
- The need for special equipment on site, or fabrication in the factory
- Big weight
- Relatively high cost
The most common material for the manufacture of load-bearing roof structures is still wood. It allows you to meet all the requirements for the roof, and problems arise only in the case of a particularly broken shape, or excessive weight of the coating material.
Since rafters have been made from lumber for centuries, the properties of this system are well studied and predictable, and the manufacturing technology has been worked out to the smallest detail.
In private housing construction, wooden truss structures are used in the vast majority of cases.
Mixed metal-wood structures are also a rarity in the construction of individual housing due to the difficulties in manufacturing and installation.
As a rule, the upper part of such structures, working in compression, is made of wood, and the lower part, subject to tensile forces, is made of metal.
As a rule, this type of system is used in the construction of large structures with a significant span (15-20 m) - swimming pools, industrial and agricultural enterprises.
Terms denoting various elements of the truss system:
- The rafter leg is the main element of the roof, which takes the load from the roofing material and transfers it to the supporting structures of the building - walls or columns. Serves for fastening the crate on which the coating is installed
- Mauerlat (rafter beam) - a wooden strapping that runs along the top of the walls of the building, on which the rafters rest
- Strut - a strut between the upper and lower chords of the truss system, working in compression
- Rack (support) - a power element through which the truss structure transfers pressure from the rafter legs to internal load-bearing structures (walls or columns)
- Run - a beam laid along the racks, on which the rafter legs rest, including - and in those places where there are no racks
- Lying - a bar laid along load-bearing internal walls or columns, taking the load from the racks, including in those areas where there is no capital structure (in the case of columns)
- Strut - an element that works in compression, and prevents collapse and shift inward of the struts and racks
- Puff (crossbar) - an element that perceives the load of the rafter legs in a horizontal plane

In the case of hanging rafters, two more elements are added to the structure: screed 2, which prevents the rafter legs from “running apart” under the weight of the roof, and headstock 4, which looks like a rack, but works on a different principle.
Struts 5, under the action of the weight of the roof, stretch the headstock, and it, in turn, transfers this force to the screed, while compensating for the stretching of the latter.
Rafters
There are two generally accepted schemes for organizing the truss system of a pitched roof. The first of these is a layered truss structure.
It is used when organizing roofs for relatively small buildings, with span dimensions (distance between supporting structures):
- up to 6 m - without installation of internal supports (racks)
- up to 12 m - with the installation of one rack on the supporting structures (moreover, the rack is not necessarily installed exactly in the center of the truss system - it can be displaced asymmetrically to one of the walls)
- up to 15 m - with the installation of two supports
This type of rafters is called layered, since they are superimposed on top of the Mauerlat, and also, if there is a ridge beam (run) - a longitudinal element that connects the tops of all truss trusses.
Farm - a single element of the system, consisting of a pair of rafters and supporting / connecting elements between them. This system is mounted in buildings of small width, or with load-bearing structures inside.
A characteristic feature of the layered rafters is the low weight of the structure and the low consumption of lumber.
Also, they (especially in the absence of racks) are convenient for organizing the attic floor, since they do not have elements running parallel to the ceiling at a low height.
ADVICE! Do not use layered rafters (in any case, in a “pure” form) for roofing made of heavy coating materials, in particular mineral ones (tiles, asbestos-cement sheet, slate). This will necessitate the use of large-section timber and boards, as well as the installation of powerful slopes, racks, crossbars.
hanging rafters

The second type is a hanging rafter structure.It is so named because the ends of the rafters rest only on the external load-bearing walls, without intermediate supports inside the building.
Since, under the action of the weight of the roof on the rafter legs, bursting loads occur on the walls of the building, the rafters are supplied with a coupler, which compensates for the resulting force.
If necessary, auxiliary elements are used - struts, grandmas and racks. With the help of hanging rafters, spans up to 20 m long and even more can be created.
Combined options
In cases of a particularly complex shape of the roof, or the use of heavy coating materials, combined truss structures are used - special trusses.
They can be made in the form of a single type of construction (layered or hanging), or they can include a combination of both in different parts of the farm.
There are also roofs where “clean” hanging and layered trusses alternate: layered ones are used in those places where the supporting structure goes under the roof, and hanging ones - at those points where it does not exist.
This allows you to evenly distribute the load and create slopes of the required size and length, while not going beyond the selected roof shape.
Important information! When organizing a gable roof, without fail, trusses of any design are connected along the roof with runs along each row of rafters, or by diagonal dressings of neighboring trusses.
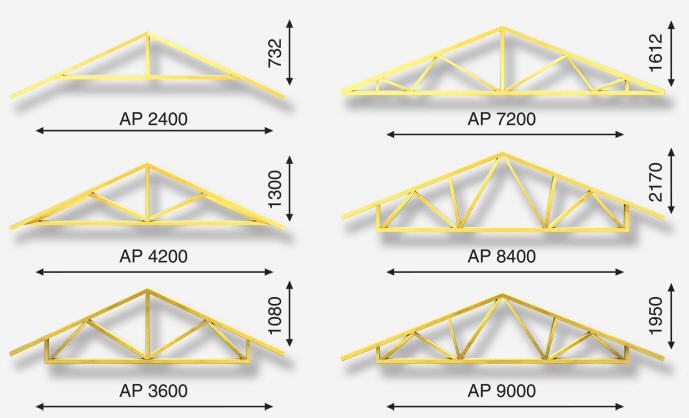
It is possible to manufacture truss structures on site, directly during the installation of the truss system, assembly on the ground, followed by lifting to the roof, or in factory production.
The last two options are attractive due to the achievement of the geometric accuracy of all blocks, but installation in place allows you to take into account all the nuances of this particular roof.
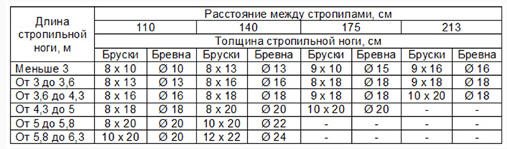
The pitch of the rafters is essential - the distance between adjacent trusses. It varies between 0.8–2 m, and depends on the type of truss, rafter section and roofing material, and is determined by calculation.
The following table may help in determining the step:
The tree needs protection
Since lumber has a relatively low biological stability, is hygroscopic and prone to decay and damage by pests, and is highly combustible, it needs protection.
Subject to simple rules, you can be sure that the repair of the truss structure will not be required for the entire period of its operation (according to the standard - 50 years).
Protecting the roof from premature aging consists of the following measures:
- treatment with antiseptics, hydro- and fire-retardant impregnations
- installation of waterproofing gaskets at the points of contact between wood and metal or wall materials
- roof leak prevention
- maintaining the safety of hydro and vapor barrier layers of the roof
- ensuring proper ventilation of the under-roof space
The supporting frame of the roof is the most important element of the building. Both the atmosphere of the interior and the life of the structure itself depend to a large extent on its reliability.
Therefore, whether classic wooden truss structures are chosen for the house, or more exotic metal, the roof requires careful calculation and no less high-quality installation.
Did the article help you?
