 The truss system of the house is a supporting structure that, along with the roofing, accepts the entire list of external loads, including the weight of its own elements, transfers forces to the walls and internal supports of the building.
The truss system of the house is a supporting structure that, along with the roofing, accepts the entire list of external loads, including the weight of its own elements, transfers forces to the walls and internal supports of the building.
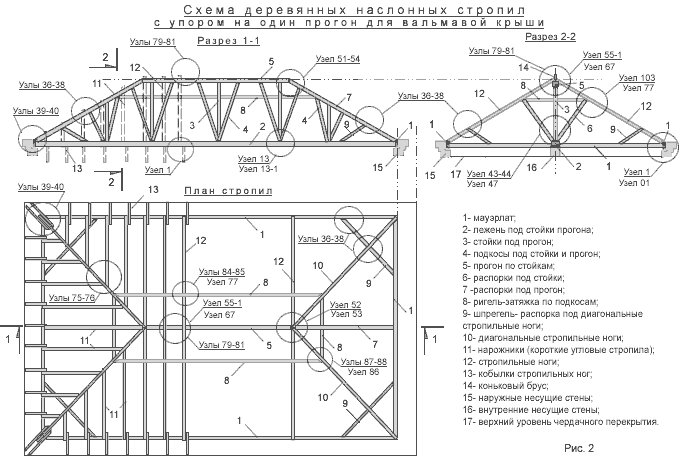
The main elements of the supporting structure of the roof are rafters, mauerlat and crate. In addition, there are such additional fastening elements in the roof structure as racks, crossbars, spacers, struts, etc.
Components of the truss system and their device
Before you make a roof truss system, you need to understand its structure.
The roof support system consists of the following set of elements:
- Sloping and / or hanging rafters.
- Mauerlat.
- Side and ridge runs.
- Braces, struts and diagonal ties that serve to stiffen the truss truss.
Such roof details, connected to each other, form roof trusses, which are based on one or more triangles, which are the most “rigid” geometric figure.
The rafters serve as the basis for the supporting structure of the roof. The assembly of the truss system is carried out at an angle in accordance with the angle of the slope of the roof slope.
By laying from a Mauerlat bar longitudinally laid on the walls, necessary for even weight distribution roof truss system on the walls, the lower ends of the rafter legs rest on the outer walls.
At the same time, the upper ends of the rafters are supported on intermediate runs or a ridge beam, which are designed to transfer the load to the internal walls of the bearing type using a system of racks.
The rafters are located in increments of 0.8-2 m, depending on the selected section of the rafters, the type of roofing material and other kinds of conditions. Thanks to them, the roof can withstand not only the weight of the roofing, but also the pressure created by wind and snow.
Rafters are of two types:
- Hanging - based on only two extreme supports, for example, without intermediate supports, only on the walls of the structure. Hanging type rafter legs work on bending and compression. Among other things, the design creates a significant bursting horizontal force transmitted to the walls.You can reduce such an effort by tightening (metal or wood) connecting the rafter legs. It can be placed at the base of the rafters (in this case, it can serve as a floor beam at the same time - the most commonly used option in the construction of mansard roofs) or higher. The higher its location, the more powerful it is made and the more reliable the fasteners for the rafter system should be.
- Layered - installed in houses with an average load-bearing wall or columnar intermediate supports. Their ends rest on the outer walls of the building, and the middle part - on supports or an internal load-bearing wall. As a result, the elements of such rafters work similarly to beams - only in bending. With an identical width of the structure, the roof of the layered rafters will be lighter, moreover, it will require less lumber and, accordingly, is more profitable from an economic point of view. When installing a single roof structure over several spans, hanging and layered trusses can alternate. In places where there are no intermediate supports, hanging-type rafters are used, in places of presence - layered. The latter are mounted when the length between the supports is no more than 6.5 m. With an additional support, it is possible to increase the width of the overlap with layered rafters up to 12 m, and with two additional supports - up to 15 m.
To ensure the strength of the connection, it should be fixed with a bolt, bracket and dowel. To connect the component parts of the puffs, a tooth, metal linings and bolts are used.
One of the purposes of a roof is to protect the walls of a building from the damaging effects of snow and rain.In order for this function to be implemented, a cornice overhang is used, the length of which should not be less than 55 cm.
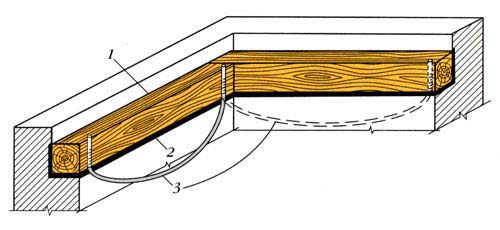
Mauerlat device
Rafter legs, as a rule, do not rest on the walls themselves, but use a Mauerlat for this purpose, which is a support beam, usually of a large section. Mauerlat can be placed both along the entire length of the building, and placed only under the rafter legs.
The installation of rafters on a log house implies the support of the rafter legs on the upper crowns of the building. As for brick walls, it is laid flush with respect to the inner surface of the wall (outside, the timber is lined with brickwork).
Between the brickwork and the mauerlat, a waterproofing layer is always required. As such, you can use roofing material. Mauerlat is placed along the entire wall of the building or laid only under the rafters.
When using rafter legs with a small section width, over time this can lead to their sagging. To avoid this, it is necessary to use a special lattice consisting of a rack, crossbar and struts.
Advice! Remember that before starting roofing work, according to the requirements of SNiP - the truss system requires compliance with all points related to safety.
Installation of ridge run, braces, braces and diagonal braces
At the top of the truss system, a run is organized that is necessary to connect the truss trusses to each other. It is on this element that the roofing ridge will subsequently be arranged.
In places where there are no load-bearing walls, the heels of the rafters can rest on the side runs - powerful longitudinal beams, the dimensions of which depend on the load acting on them.
If the truss trusses themselves provide rigidity in the rafter plane, then in order to qualitatively withstand wind-type loads that act, for example, from the side of the gable (tongue), each roof slope requires the installation of the required number of diagonal ties.
Boards 30-40 mm thick can be used as them, which are nailed to the base of the outermost rafter and approximately to the middle (or slightly higher) of the adjacent one.
Advice! The slope of the roof slope is determined by the developer, taking into account the type of building, the purpose of the under-roof (attic) space, while not forgetting that the slope angle directly affects the choice of roofing. The recommended slope angle for a rolled roof is 8-18 degrees, for a coating of asbestos-cement sheets or steel sheets - 14-60 degrees, for a tiled roof - 30-60 degrees.
Mansard roof truss construction

For mansard roofs, as a rule, layered rafters or a combination of layered and hanging rafters are used. The walls and the lower slope of the attic are always layered, while the ceiling and the upper slope can be fixed to both hanging and layered rafters.
A mansard roof using a combination of two types of rafters is arranged according to the following rules:
- In the lower slope, the layered rafters look like a right triangle.
- In order to increase resistance to loads, contractions are provided in the lower and upper parts of the rafters.
- The upper slopes of the roof are mounted on hanging rafters. At the same time, the tightening of such rafters serves to suspend the ceiling. Her work is in tension and bending, but since the loads are small, the material may be of a small section.
- Rafters for the attic they are made from materials of a large section, since their goal is to cover the entire span and form a full-fledged roof.
- To eliminate deflection of the puff from the weight of the ceiling, it is suspended on the headstock.
- Rafters on the upper slopes may have additional fastening in the form of attendants, crossbars and struts. The elements of the truss system must withstand the calculated loads.
- Installation of rafters of the lower slope of the mansard type roof can be carried out both with struts and without them.
- Depending on the method of fastening (this can be a sliding rafter system for log cabins or a fixed one for stone buildings), the rafters are fixed using hinged-fixed fasteners or using sliders.
Racks of the lower rafters are supported by floors. When using reinforced concrete floor slabs, additional calculations are not required.
In the role of a support for the racks, a bed is laid, which can be placed directly on the waterproofing with a flat surface of the floors, or on leveling pads.
As for wooden floors, they require a tie-in into the ceiling beam, which will require calculation for a concentrated load at the support points of the racks.
If the design of the truss system involves the construction of a large cornice overhang, then the installation of a Mauerlat in this case is not required. Here, the installation of the attic truss system is carried out using beams.
The attic truss system with the device for the lower stop of the rafters outside the outer wall is carried out according to the following rules:
- Under rafter without fail, a strut is mounted, and the racks are cut into the wooden floor beams to a depth of not more than 1/3 of the depth of the section of the beams.
- The lower rafters are usually designed for compression, since the slopes in this case are steeper, and the main load comes from the wind and the upper slopes.
- To prevent the roof from being blown off by the wind, the rafters are additionally fixed with anchor joints and wire twists.
- Unloading of floor beams is possible due to racks installed at the intersection of rafter legs and struts, and the lower ends of the racks should abut above the outer wall against the floor beam.
- Additional stability of the roof is given with the help of contractions, which connect the layered rafters on the lower slopes, and support bars are arranged along the bottom of the puffs of the hanging rafters on the upper slopes.
The rafter system of the attic from the layered rafters is assembled in the following order: first, the frame is knocked down in the shape of the letter “P”, after which runs are laid on it.
It is the attic frame that will bear the main load here, while less weight will fall on the rafters. Because of this, they can be made with a smaller cross section.
Even a complex truss system will be successfully erected subject to all design calculations, reliable fastenings and a competent approach to business.
Did the article help you?
