 The basis of any pitched roof, which subsequently serves as a support for the mounted roofing pie, is a truss structure. Floor beams and rafters must withstand the weight of the roofing and easily cope with snow and wind loads. As usual, the vast majority of the elements of the truss system are made of coniferous wood with a moisture content of up to 20%.
The basis of any pitched roof, which subsequently serves as a support for the mounted roofing pie, is a truss structure. Floor beams and rafters must withstand the weight of the roofing and easily cope with snow and wind loads. As usual, the vast majority of the elements of the truss system are made of coniferous wood with a moisture content of up to 20%.
In this article, we will determine how to calculate the truss system, and also describe in detail the subtleties of its installation.
Calculation of the truss system
First you need to find out what a rafter is.These are the supporting structures of a pitched roof, made of rafter legs, which are placed under a slope, inclined struts and vertical ones.
If necessary, they can be “tied” from below with rafter horizontal beams.
The loads perceived by the truss system are temporary and permanent. The former include such phenomena as the exit of people to the roof for repair or maintenance of the roof, snow and wind loads, as well as special loads, such as seismic vibrations affecting the building.
Permanent loads are the weight of the roof structure as a whole.
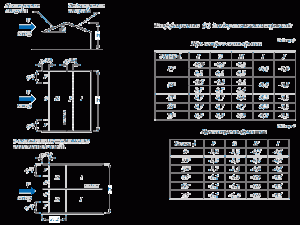
The calculation of the load indicators on the truss system is performed as follows:
- The snow load index is determined by the product of the calculated value of the weight of snow cover per square meter of horizontal surface and the coefficient of transition from the weight of the ground snow cover to the snow load on the roof. The value of the multiplier is taken according to special tables depending on the location of the building, while the multiplier (coefficient) is taken equal to 1 with a slope of roof slopes of less than 25 degrees and 0.7 - with a slope of 25-60 degrees. If the slope is more than 60 degrees, the coefficient is not taken into account.
- The average wind load parameter is calculated by the product of the wind load value characteristic of a certain area (also taken according to the tables) and a coefficient that takes into account the change in wind pressure with height, which is taken from the table and depends on the type of terrain.
Types of truss structures pitched roof
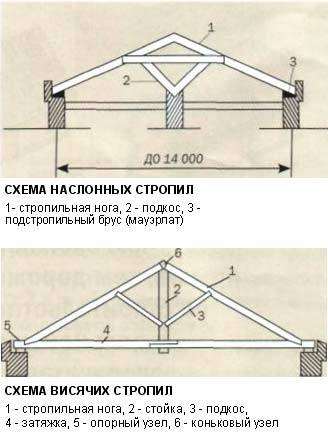
According to the type of construction, the rafters are divided into hanging and layered. The main figure in the rafter system is a triangle, as it is a figure that provides maximum rigidity.
Features of the location of the layered rafters:
- With their ends, the layered rafters rest on the walls of the house, while the middle of the elements is supported by intermediate supports.
- They are mounted in buildings with a load-bearing middle wall or intermediate supports.
- The distance between the supports when using layered rafters should not be more than 6.5 m. The presence of additional supports will increase this width to 12-15m.
- In cylindrical log houses, the rafters rest on the upper crowns, while in frame houses, the upper trim is used as a support. In brick stone and block houses, the Mauerlat acts as a support for the rafters.
- With identical dimensions of the house, a roof using a layered type of rafters will be lighter.
What are the features of hanging rafters:
- Their ends rest only on the Mauerlat or on the walls of the building, without the use of intermediate supports.
- This type of rafters is applicable in buildings with light walls.
- In a system of this type, the rafter legs function in compression and bending, and the structure as a whole creates a bursting horizontal load on the walls of the building.
- To reduce such a load, a metal or wooden puff is used to connect the rafter legs. It is located at the base of the rafter legs and above. The higher the puff is, the more securely it should be connected to the rafters.
- With a span length of more than 8 m, a rack with struts (“headstock”) is installed.
Hanging rafters have the advantage of being able to cover large spans.
Advice! When installing a single truss system over several spans, layered and hanging trusses can be alternated - hanging rafters can be mounted in places where there are no intermediate supports, layered - in places with supports.
Preparing for the installation of rafters
The elements should not rest directly on the walls, but on a support beam called a Mauerlat. The upper crown of the house (beam, log) serves as such in wooden houses.
In brick houses, this is a beam, specially mounted flush to the inner surface of the walls (outside it is protected by a protrusion of brickwork). A waterproofing layer (usually made of bituminous roll materials) must be laid between the brick and the Mauerlat.
Mauerlat is placed along the entire length of the structure or is placed only under the rafters.
A run is installed in the upper part of the pitched roof structure, connecting the truss trusses with each other. In the future, a roof ridge will be mounted on the ridge run.
The choice of the section of the elements of the truss system
The choice of a beam section for the manufacture of rafters depends on their length, installation step, calculated indicators of snow and wind loads for a given region.
For example, with a length hanging rafters at 5 m and an installation step of 1.4 m, the cross section of the elements should be approximately 75 * 200 mm. There are special tables for more accurate calculation of the section of the rafters.
As for the other components of the truss system, the recommendations for their cross section are approximately as follows:
- For Mauerlat - bars 100 * 100, 100 * 150 or 150 * 150 mm.
- For valleys and diagonal beams - timber 100 * 200 mm.
- For runs - bars 100 * 100, 100 * 150, 100 * 200 mm.
- For puffs - timber 50 * 150 mm.
- For crossbars serving as a support for racks - bars 100 * 150, 100 * 200 mm.
- For racks - bars 100 * 100, 150 * 150 mm.
- For "fillies", cornice boards and struts - timber 50 * 150 mm.
- For frontal and hemming boards 22-25*100-150 mm.
Installation of the truss system
The device of the truss system is carried out according to various technologies and depends on the roof structure. The rafters are fastened with fasteners - nails, screws, bolts, clamps, brackets.
Parts of the rafter system in contact with blocks or masonry must be protected from decay by laying bitumen-based roll materials. In addition, the elements of the wooden truss system are covered with fire and bioprotective solutions.
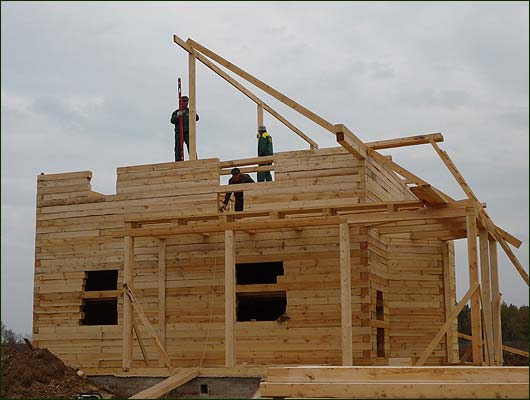

Mauerlat is attached to the walls with anchors. The rafter legs rest on the Mauerlat and are pulled by a twist of wire about 6 mm in diameter.
On device do-it-yourself roof rafters first, the extreme pairs of rafters are mounted, and then, by means of a cord, they are checked for parallelism of their faces.
Then they pull the cord along the ridge, install intermediate pairs of rafters along it, and then carefully align them.
If the rafter gets into the place of installation of the chimney outlet, roof window or ventilation, it is allowed to cut a segment from it with the installation of transverse struts from a beam of the same section.
Advice! The gap from the chimney to the wooden parts, according to building codes, must be at least 13 cm.
Rafters are one of the most important components of the pitched roof structure, so we recommend that you take their calculation and installation seriously.
Did the article help you?
