Materials from various variations of galvanized sheet are one of the leaders in the roofing materials market - it is molded, bent, various types of protective and decorative coatings are applied. And among the leaders of this market is a profiled sheet, while there are so many varieties of it that the calculation of corrugated board for strength and other performance characteristics is not an ordinary task. How to do it yourself - later in the article.

To figure out what factors can affect the decision to choose a particular brand of corrugated board, you should first understand the characteristics of the material itself - how one modification differs from another, and what they generally are.
- Technical characteristics and specifications of corrugated board
- Regulatory regulation
- Classification Options
- Real materials, raw materials, production
- Geometric dimensions
- Strength factors of corrugated board
- Correct Application
- Calculation procedure
- Determination of coating strength
- Sheet length calculation
- Calculation of the number of sheets by width
- Equipment
Technical characteristics and specifications of corrugated board
Regulatory regulation
The main indicators that the corrugated board must comply with are established by GOST 24045-2010 “Curved steel sheet profiles with trapezoidal corrugations for construction. Specifications". However, the same GOST gives manufacturers enough room for maneuver in terms of choosing raw materials, finishing materials and the geometry of the final product, allowing (within certain limits) to develop and apply their own technical specifications (TS).
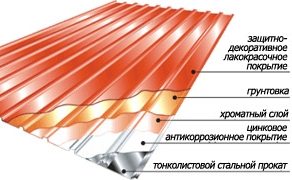
Classification Options
According to GOST, the profiled sheet is classified according to the following indicators:
- By appointment:
- For decking
- For floor decking
- For fences
- By material (grade of thin-sheet galvanized steel from which the sheet is made)
- By the presence of a protective coating and its type
According to the regulatory document, in the specifications for its specific product, the manufacturer must indicate: the shape and size of the profile section, the mass of 1 m2 its length, as well as load resistance.
When choosing a material for a protective coating, it should be remembered that it may have:
- Galvanized layer
- Paintwork
- polymer layer
In this case, the last two options can be applied both on one and on both sides of the sheet.
Real materials, raw materials, production
Geometric dimensions
First of all, the calculation of the amount of corrugated board depends on its width, since the length varies in GOST from 3 m (in increments of up to 0.25 m) - for decking, and from 2.4 m (in increments of 0.3 m) - for fences, up to 12 m for both species. But there is also a reservation that, by agreement between producers and consumers, the length can be any. The width depends solely on the shape and size of the longitudinal profile, since any corrugated board is made from the same raw material - galvanized steel strip 1250 mm wide. Since it is supplied in drums, it is clear that the length of the sheet is limited only by technological considerations.

Strength factors of corrugated board
Obviously, the greater depth of the profile "compresses" the width, but gives greater bending strength. The same indicator is affected by the thickness of the feedstock, which varies from 0.5 to 1 mm. The protective coating does not affect the calculation of the bearing capacity of the corrugated board in any way, but the accuracy of the geometry can significantly affect. All corrugated board is produced on special rolling lines, where it is given the desired configuration and sheets are cut. At the same time, the quality of the final product depends on many factors: the quality of the rolling rollers, the power of the drives, the degree of automation, the qualifications of the workers, etc.
ADVICE! From the same steel strip on different equipment it is possible to obtain a sheet of the same profile either with clear corners or with “blurred” ones.And this is not a trifle, since a sheet with a smooth relief is prone to spreading in width under the influence of loads. Ultimately, this leads to a loss of strength and roof leaks, if the “planned” characteristics of the material were initially taken into account. In addition, low-quality guillotines can, when cutting, transfer the capillary grooves, which will lead to a loose vertical fit of the sheets during installation.
Correct Application
It should be noted that, on average, the sheet strength indicators depend on the height of the profile and the ratio of the crest and bottom of the wave. However, for roofing options for corrugated board, the ratio is far from linear. It should be noted that there are three types of corrugated board:
- Wall (facade)
- Flat (bearing, formwork)
- roofing
At the same time, roofing can be used for other needs, although this is not always advisable, but other varieties as a coating are not. And this is despite the fact that the decking sheet is used for the construction of ceilings and even - as a fixed formwork, including - for horizontal structures. The height of the profile in this class, as a rule, is more than 44 mm, in addition, its edges are corrugated for better adhesion to concrete during pouring. It will also hold snow and ice well in winter. The facade type has little strength, and therefore is not applicable in roofing. In addition, the roofing corrugated board has a capillary groove of a special section, which allows you to efficiently drain water and dump snow and ice.
Calculation procedure
Determination of coating strength
The strength of the roof depends on:
- Metal thickness
- Profile heights (35-44 mm)
- Lathing step
At the same time, it is not difficult to calculate the corrugated board, since the manufacturer indicates the strength characteristics in the technical documentation for the products, and the allowable load for various crate pitches is calculated according to special tables. The distance between the support bars allows you to choose a more or less durable profiled sheet.

When calculating, it is also necessary to take into account those factors that affect the performance and durability of the coating. Among them:
- Precipitation in the form of rain and snow
- wind load
- temperature fluctuations
- Harmful chemical emissions into the atmosphere
- Solar radiation
- Humidity indoors and outdoors
ADVICE! The decision in favor of more frequent lathing, and, due to this, corrugated board with lower strength characteristics, in most cases turns out to be more economically justified. This is due to the fact that the cost of consumable lumber will be lower than the difference in price between sheets of different thicknesses.
Sheet length calculation
Two factors influence how to calculate the corrugated board along the vertical slope. On the one hand, experts recommend choosing a sheet length so that it fits from the ridge to the overhang without joints. This is understandable - fewer connections - less likelihood of leaks. On the other hand, if the ramp is long enough, working with the profile becomes more difficult, since its tendency to deformation increases due to kinks during transportation, and it is more difficult to perform installation operations. On average, the length of the sheet is up to 6 m.In the event that the corrugated board covers the entire slope - the question of calculation is not worth it, but if several vertical rows are assumed - the formula is applied:
N= (A+B)/D, where:
A - the length of the slope
B - protrusion beyond the edge of the cornice 50 mm
D - sheet length
N - number of sheets
Then add to the resulting value:
N1= N + N*C/D
C - Overlap of sheets, for different manufacturers it ranges from 150-200 mm
For example, with a slope length of 8 m and a selected sheet length of 4.5 m, the calculation will look like this: N \u003d (8000 + 50) / 4500 \u003d 1.79, when rounded to the nearest integer, we get 2 sheets. Since there is one overlap per 2 sheets vertically, we add it here: N1=2+ 2*150/4500. However, due to the fact that during rounding a margin of the order of 0.2 of the sheet length was formed, which is 900 mm for a length of 4500 mm, the final figure will not change, and the required number of sheets vertically will remain equal to 2.
Calculation of the number of sheets by width
On average, this calculation is quite simple - the horizontal length of the slope is divided by the working width of the sheet (you should not forget about the amount of sheet overlap, which is included in the full width) and added 50 mm to the ledges. For roofs of complex configuration, each slope is calculated separately. At the same time, the following mistake is sometimes made: the remains of sheets that require cutting (when installing skates and valleys) are taken into account for use on other parts of the roof.But, although the profiled sheet is not horizontally oriented (it can be laid both from right to left and vice versa), the direction of all sheets on the slope can be only one, since the shelves of the lock (overlap) at different edges have different widths (with a difference of at least 2 mm ). Therefore, the rest of the sheet can only be used on a slope with the opposite laying direction. In practice, the amount of material needed is rounded up to the nearest integer.
Equipment
In addition to the sheet itself, one should also not forget about various components, which include:
- ridge bar
- Gutter plank
- End plate
- endova
- eaves plank
- Apron for chimneys
- junction bar
It is also necessary to calculate the number of fasteners (5-7 screws per sheet) and sealing tape if several vertical rows are installed.
The instruction on how to calculate the amount of corrugated board is not particularly complicated. Therefore, it will not be difficult to carry out this procedure on your own, if, nevertheless, difficulties arise, a consultant from the seller's company will help to carry it out, because this is in his interests.
Did the article help you?
