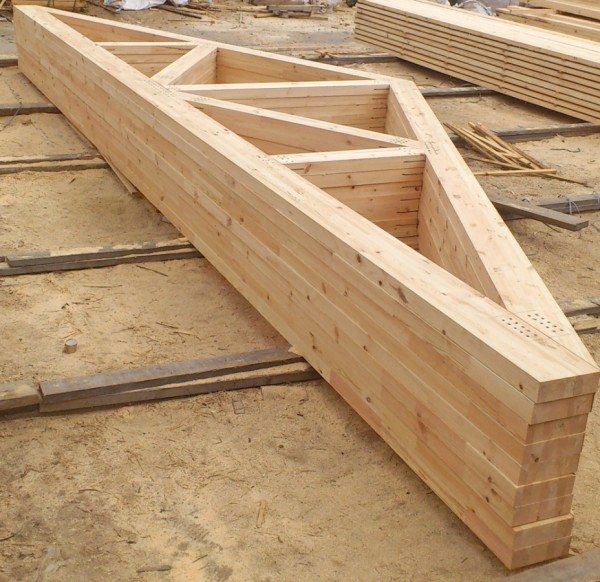
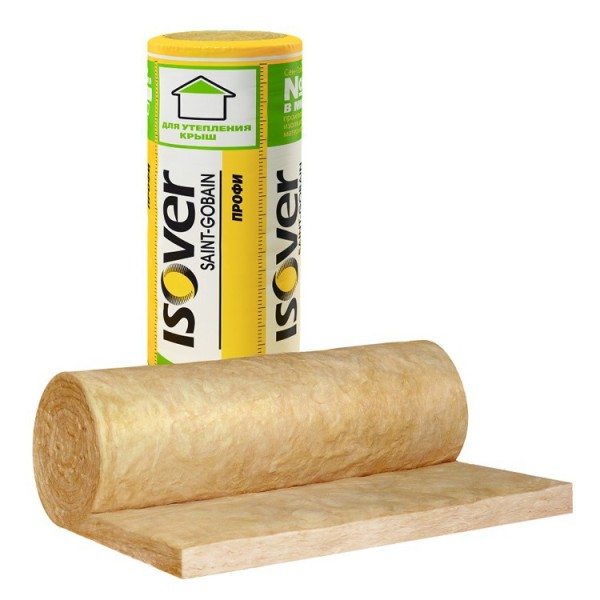
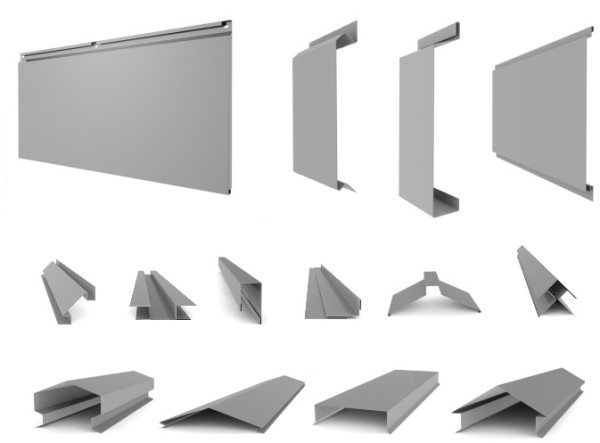
Mauerlat is fixed approximately like this:
This is how the rafters are attached with pre-drilling:
This is how the crate is attached:
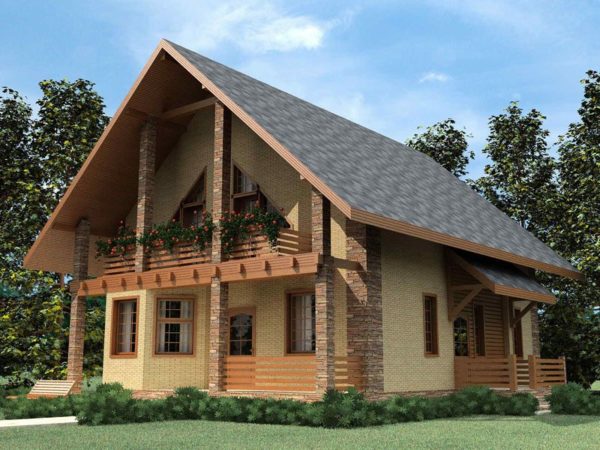

One of the simplest roof structures is a gable roof: even a non-specialist can build it with his own hands. How to calculate the structure and build a roof frame? At one time, I had to master the technique of building such roofs. I will share my experience with you.
- Gable roof construction
- Types of truss systems
- Calculation of rafters for a gable structure
- Equipment for work
- Materials used
- Set of tools
- Roof installation
- Stage 1. Installing the Mauerlat
- Stage 2. Installation of racks, run and rafters
- Stage 3. Installation of the crate, waterproofing and roofing
- Conclusion
Gable roof construction
Types of truss systems
The gable roof is one of the oldest. It is represented by two flat slopes, which are closed in the upper part along one line. The lower edges of the slopes rest on the walls of the house, which are usually on the same level.
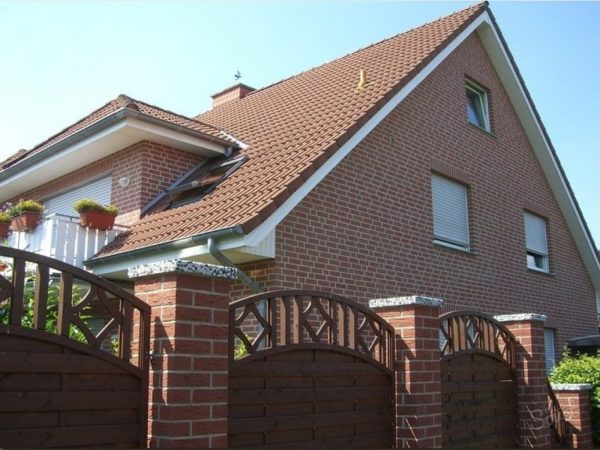

The end parts of the roof of gable structures are two vertical triangle-pediments. The pediment can be made of the same material as the walls, or made separately. In the second case, it is made thinner, or materials with less mass are used - this way you can reduce the load on the base.

Roof slopes can be located at different angles. If the angle is large enough, then under the roof you can equip the attic room. With a slight slope, the under-roof space turns out to be low, and it is used at best as an attic.
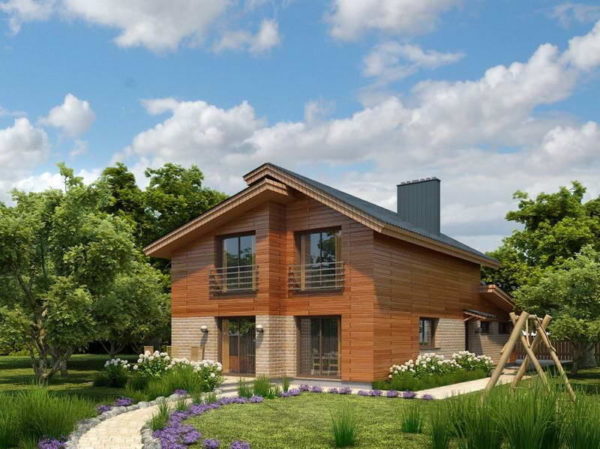

A gable roof with different slopes is also possible. As a rule, it is built when it is necessary to connect two walls of different heights or when installing two slopes with a different angle of inclination.
The basis of a gable roof is a rafter system, which can be of two types:
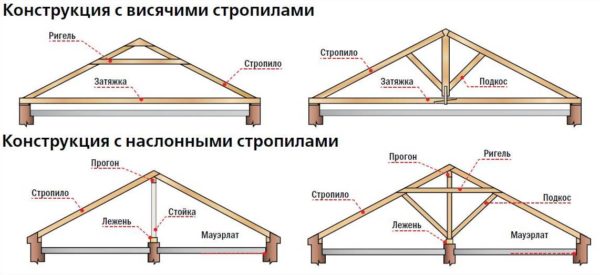
- Rafters are made when the house has a central load-bearing wall. At its end, racks are installed on which the running beam is attached. It is this run that serves as a support for the upper ends of the rafter legs, which form the slopes. Sometimes, instead of racks, a full-fledged supporting wall is erected - but this option is only suitable for houses on a massive foundation.

If the central load-bearing wall is not in the middle of the building, then you will have to make a roof with an offset ridge and slopes of different sizes, located at different angles.
- hanging rafters mounted in the absence of a central supporting structure. The rafter legs are connected to each other without an upper run, relying on each other (and on the ridge beam). To increase rigidity, intermediate elements are added to the structure - puffs and linings that prevent the rafter legs from moving apart.
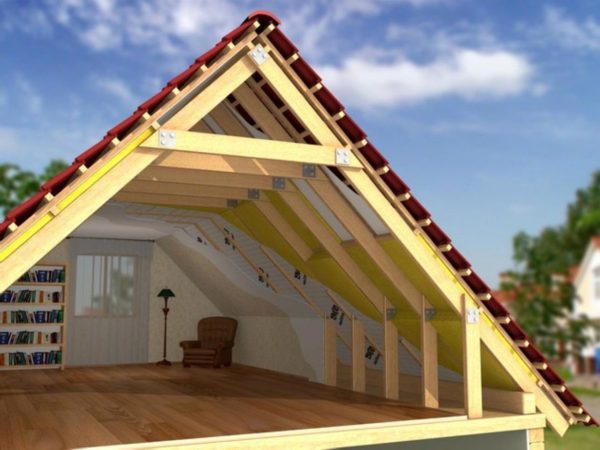

The choice of truss system is determined precisely by the design of the building itself.:
- there is a middle wall - we make a layered structure;
- no wall - We install hanging rafters.
Calculation of rafters for a gable structure
The most important stage of work is the calculation of the main parameters of the frame of the future roof. There are three ways to go here:
- Take advantage of a ready-made solution, making the truss system an exact copy of the frame of an already built roof. Ideal for typical houses, but it is not always possible to find a suitable copy for copying.
- Use an online calculator for the calculation of the truss structure. Option suitable for preliminary calculation and evaluation of various options. The calculators that I have worked with are quite accurate, but there is a risk of not taking into account something.

- Do your own calculations. To do this, use the formulas based on SNiP 2.01.07-85 "Loads and Impacts" and other regulatory documents. This option is the most difficult, but also the most reliable.
Full self-calculation of loads is very time-consuming. I will describe the main steps.
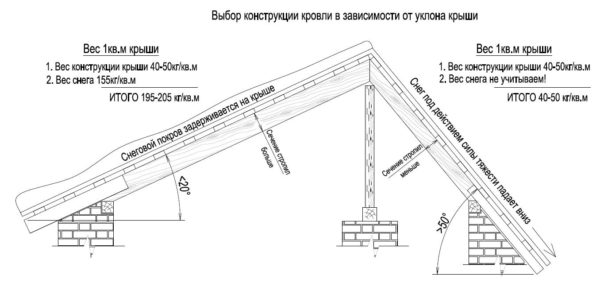
First, we need to determine the load on the roof:
- Weight load calculation - the area of \u200b\u200bthe slopes is multiplied by the specific gravity of the roofing pirogue. This value consists of the mass of the crate, waterproofing, insulation and roofing material, and averages from 40 to 50 kg / m2.

- Snow load calculation - We multiply the normative snow load for your region by a coefficient that depends on the angle of the slope. If the slopes are located at an angle of 60 °, then this coefficient is taken equal to zero, if 30 ° - to one. Intermediate values are calculated by the formula µ = 0.033 (60 - α), where α is the slope angle.
The normative value of the snow load is expressed in kg / m3 and depends on the region. On the territory of the Russian Federation, the minimum value is 80 kg / m3, maximum - 560 kg/m3.
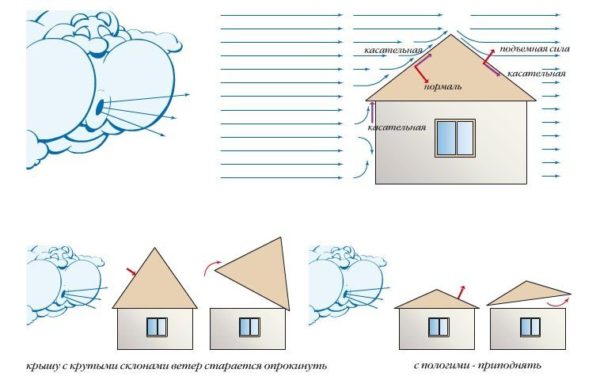
- Wind Load Calculation - the normative wind pressure in the region is multiplied by the correction factor for the height of the building and by the aerodynamic coefficient (for strength, it is desirable to take the minimum value - 0.8). Wind pressure standard is from 17 to 85 kg/m2, and the height coefficient is determined from the table below.
| Height, m | open area | Area with obstacles up to 10 m | Section with obstacles up to 20 m (urban development |
| Up to 5 | 0,75 | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| 5—10 | 1 | 0,65 | 0,4 |
| 10—20 | 1,25 | 0,85 | 0,53 |

The obtained values are summarized, obtaining the final value of the load on the roof.

To determine the parameters of the rafters used, we use two formulas.First, we calculate the distributed load.
Qr=A Q, Where:
- QR - load on the rafter leg, kg / m.;
- A - step of rafters, m;
- Q - total load per square meter of roof, kg / m².
Then we determine the height of the section of the rafter beam. To do this, we select the optimal (as it seems to us) section width and substitute this value into the formula.
H =K Lmax sqrt(Qr/(B Rbend)), Where:
- H - the height of the rafter section, cm;
- TO - slope coefficient. If the slope angle is less than 30 °, we take equal to 8.6, if more - 9.5;
- Lmax - the maximum length of the working section of the rafter, m;
- QR - load on the rafter leg, kg / m.;
- B - section width of the rafter leg, cm;
- Rizg - resistance of wood to bending, kg / cm² (for pine of the first grade we take equal to 140, second grade - 130);
- sqrt - Square root.
Calculation example:
We determine the parameters of the rafters for a roof with slopes of 36 degrees, with a rafter pitch of 0.28 and a length of the working part of 2.8 m, the frame is made of pine boards of the first grade 5 cm wide, the total load on the roof (weight + snow + wind) is 300 kg / m2.
- QR \u003d 0.8 300 \u003d 240 kg / m.
- H \u003d 9.5 2.8 sqrt (240/5 140) \u003d 15.4 cm.
Since, according to our calculations, we got a board more than 150 mm, it is advisable to take thicker products. I would take parts with a section of 50x175 mm with guaranteed strength.

Yes, the calculation is quite complicated (and I gave this abbreviated version!). But on the other hand, using it, you can check the dimensions of the supporting structures offered to you and make sure (or not) of their reliability.
Equipment for work
Materials used
Based on the calculation, it is possible to purchase parts for the frame, battens, insulation, waterproofing and roofing material. The indicative list of materials includes the following items:
In addition to the listed basic elements, we will need:
- Rolled waterproofing materials (roofing material) for laying at the point of contact of the truss system with the walls of the building.
- Fasteners (nails, self-tapping screws, anchors, studs with fixing nuts, etc.).
- Metal plates and brackets to reinforce the attachment points of wooden elements.
- Adhesive tapes for joining rolled materials.
- Impregnation for wood - antiseptic and reducing flammability.
Set of tools
For the construction of the rafter system, the installation of the crate and the laying of the roofing, the following tools will be needed:

- A saw on a tree (preferably several, and different ones - a miter saw for the main trimming, a circular saw for smaller jobs, a reciprocating saw or a hacksaw for fitting).
- Carpenter's axes (yes, cutting grooves is still more convenient to do with a good ax).
- Perforator with drills according to the material from which the load-bearing walls are composed.
- Drill with a set of drills.
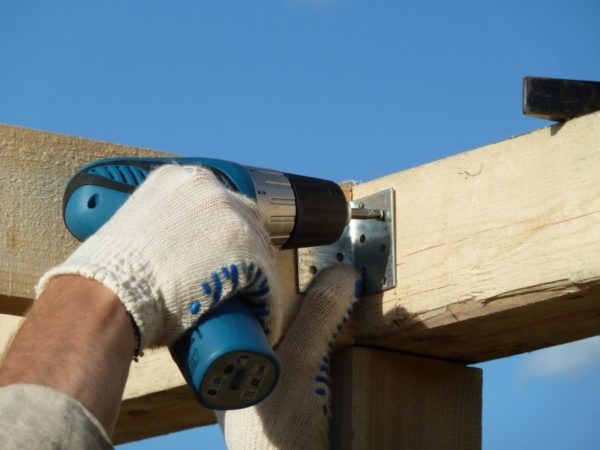

- Screwdrivers (one per master).
- Levels (laser for setting up the frame, several water levels for leveling additional elements).
- Roulettes.
- Plumb lines.
- Hand tools - hammers, pliers, chisels, etc.
- Brushes for applying moisture-proof impregnations, coating waterproofing, etc.
Since you will have to work at a height, you can not do without several ladders, scaffolds and scaffolding for building material.

You also need to take care of personal protective equipment, including overalls, helmets and safety systems.
Roof installation
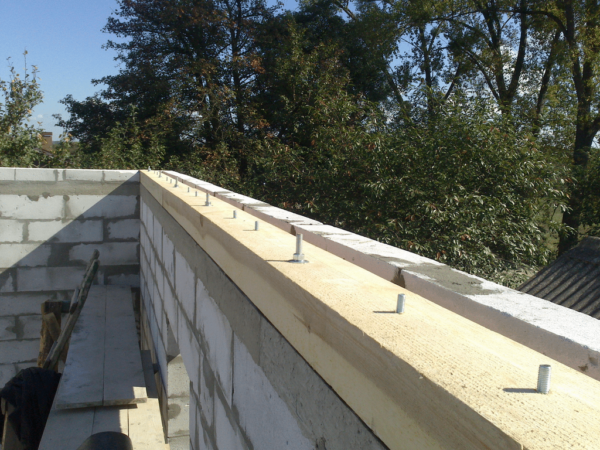
Stage 1. Installing the Mauerlat
We begin to mount the gable roof frame with the installation of a support beam - Mauerlat. For its manufacture, we take a bar 100x100 or 150x150 mm from dry pine wood.
We mount the Mauerlat according to the following scheme:
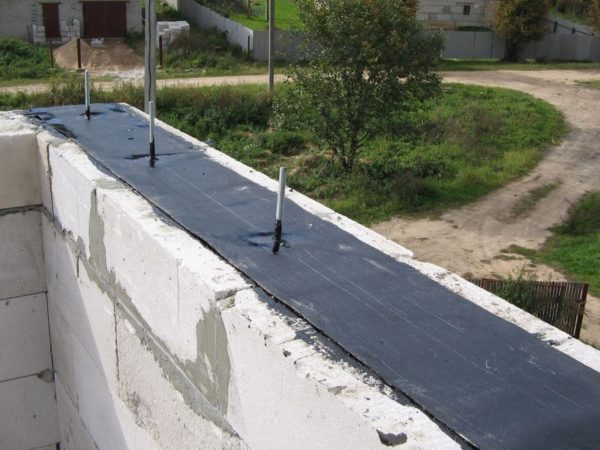

This is not the only way to fix the Mauerlat on the wall railing. Sometimes steel studs with a thickness of 12 mm or more are embedded in brick or blockwork, and a beam with drilled holes is put on them and fixed with nuts with wide washers. This method is more reliable, but also more time-consuming - you need to lay the studs in advance, even at the stage of building the supporting structure.

Stage 2. Installation of racks, run and rafters
Instructions for installing the roof frame - rafters and additional elements - depends on the design of the truss itself systems. Here I will give a description of the installation of a layered roof type:
As I noted above, this is not the only design scheme. Other options for truss systems are also possible, but if you do not have experience, you should start mastering the technique with simple and proven algorithms.
Stage 3. Installation of the crate, waterproofing and roofing
So, the supporting structure of the gable roof is ready. Now we need to turn the frame into a full-fledged roof. This work is not so large-scale, but still time-consuming.
Main stages:
- Installation of waterproofing. On the rafters we horizontally roll out the rolls of the waterproofing membrane, fixing it directly to the rafter legs with the help of galvanized brackets. We lay the waterproofing with an overlap (from 100 to 300 mm, the greater the slope angle, the less overlap). The joints of the panels must be glued.

In places where ventilation and chimney pipes pass through the roof, as well as along the ridge, we lay additional waterproofing.
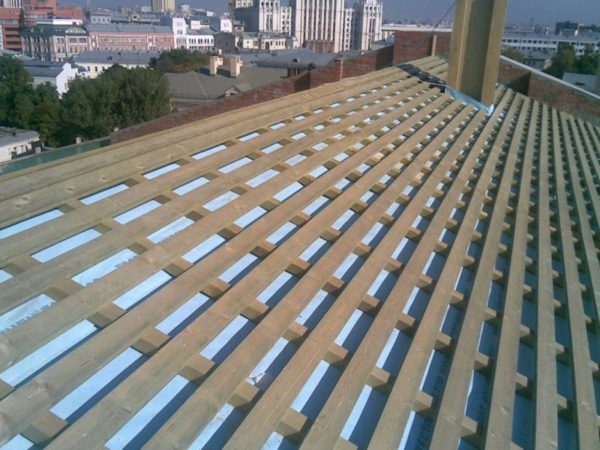
- Installation of the crate / counter-crate. Additionally, we fix the waterproofing material by stuffing wooden bars along the rafter legs with a section of at least 30x30 mm.On top of these bars, we mount the crate under the roofing material - slats, boards or plywood sheets. For fixing the crate, we use wood screws.

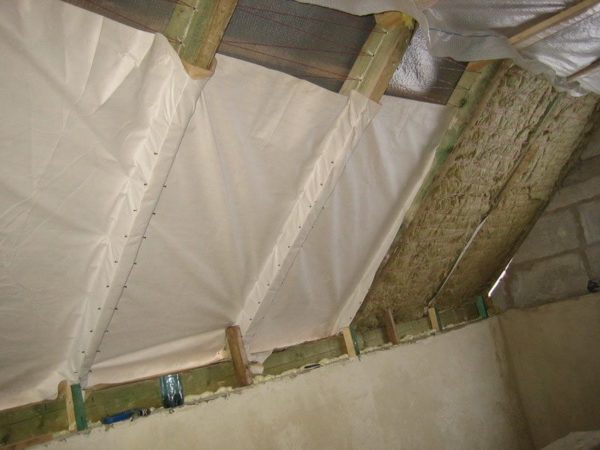
- Thermal and vapor barrier of the roof. On the inside, between the rafters, we lay heat-insulating mats that minimize energy loss through the slopes. If the price of mineral wool turns out to be unbearable, foam plastic can also be used - but in this case it is advisable to take care of additional ventilation. We cover the insulation with a vapor barrier membrane, and then fix it with transverse bars or sheathing made of plywood or chipboard.

- Installation of the selected roofing material. We start work from the perimeter, installing eaves and end strips. Then we mount the roofing material on the slopes, trying not to damage the waterproofing during installation. We fix the roofing sheets to the crate.

- Installation of additional elements. We install additional elements of the roof - a ridge strip that overlaps the junction of the slopes in the upper part, the strips adjoining the chimneys and ventilation, etc.

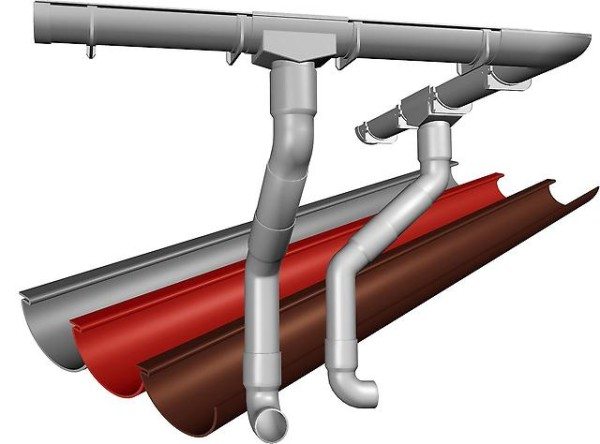
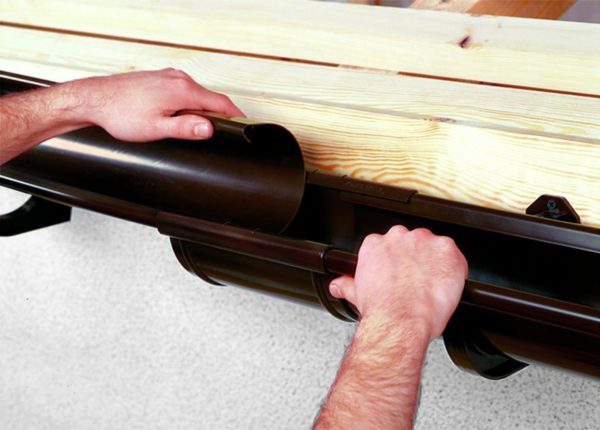
- Installation of a drainage system. We fix fasteners for gutters to the frontal board or to the end parts of the rafters. We mount gutters along the slopes with a slope towards the receiving funnels. At the edges we put funnels, from which we lower the drainpipes down.

Conclusion
A gable roof is just the option from which you can start mastering roofing skills. After studying my instructions and the video in this article, you will receive the minimum knowledge necessary for work, and then it’s a matter of practice. If you have any questions - ask them in the comments.
Did the article help you?