 Roofing work to an uninitiated master seems to be a completely impossible task. However, this is not the case, and below we will tell you what a roof is and how to equip it with your own hands.
Roofing work to an uninitiated master seems to be a completely impossible task. However, this is not the case, and below we will tell you what a roof is and how to equip it with your own hands.
Naturally, for the arrangement of the roof, you can turn to professional builders. However, not always professionals will do exactly what you need, and you should not forget about the financial side.
And by equipping the roof yourself, you get the opportunity to significantly reduce financial costs (and therefore - buy more expensive and high-quality materials for the roof), and - control the process of arranging the roof at every step, achieving the required quality.
In addition, you also master a specialty, which will also never be superfluous.
Roof functions
The roof is a multi-layer structure installed at the top of the building.
The main functions of the roof:
- Waterproofing - protects the building from precipitation and other moisture, preventing it from entering the under-roof space and further into the interior of the building.
- Heat insulating - contributes to the preservation of heat in the building, preventing it from escaping through the roof through heat exchange and / or convection
- Windproof - protects the under-roof space and the entire building as a whole from wind loads
- Aesthetic - contributes to the creation of a holistic image of the building, giving the house an attractive appearance
Based on this, modern roofing structures are created. Naturally, for different types of buildings, the roof will be different - but the general principles of its construction are the same.
Roof forms

The shape of the roof is very different. Among them, there are several main types, namely:
- Flat roof - in fact, such a roof is not perfectly flat (otherwise water would stagnate on it), but is a shed or gable roof with very little (1-5) slope angle.
- Shed roof - a roof that has only one slope, the steepness of which can vary. Shed roofing is used both for extensions to residential buildings and for outbuildings.
- gable roof - a roof that has two slopes at the same or at different angles. From the sides, such a roof is limited by vertical gable parts.
- Sloped roof - a gable roof with slopes, the angle of which varies.Most often used for arranging attics, as it allows you to make the most efficient use of the under-roof space.
- Hipped roof - a roof in the form of an equilateral pyramid.
- Hip roof - a roof that combines the features of a hipped roof and a gable roof, a roof with sloping gables.
In addition to the listed forms, there are a variety of their combinations, for example, a T-shaped or other, no less complex designs. As a result, we can say that the shape of the roof is largely determined by the geometric shape of the building and its purpose.
Roof structure

The design of the most common types of roofs has a general scheme.
It includes:
- Roof frame - truss system
- Insulation layer - special heat-insulating materials designed to reduce heat loss
- Layer of waterproofing materials
- crate
- Underlayment for roofing material
- Directly roofing material fixed on the crate
Each of these elements of the overall design of the circuit requires detailed consideration. This is what we will do in the following sections.
Construction of the roof frame
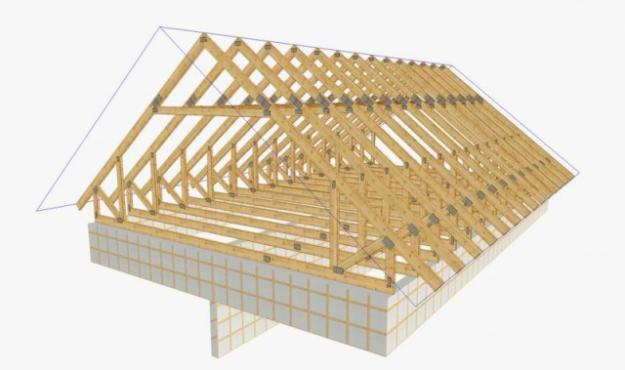
In most cases, the roof frame is a so-called truss system.
Rafters are beams that rest on the supporting structures of the building with one edge, and with the other they are connected to the same beams on the other side of the house, forming a tent structure.
Note! Most often, rafters are made of wood, and this option will be discussed below.However, when arranging the roofs of industrial buildings, or roofs that carry an increased load, metal beams (T-beams, I-beams, channel bars) or reinforced concrete structures can be used as a frame.
For the frame, it is best to choose bars and boards from coniferous trees.
Before installation, all elements of the frame structure are thoroughly dried and treated with protective compounds that not only prevent wood from rotting, but also protect wood from fire, seriously reducing its combustibility.
It is best to perform all work on preparing the rafters for installation on the ground, and directly on the roof, only cut the parts to size and connect them together.
Do-it-yourself roof rafters they can rely both on the supporting structures of the building themselves (in this case, waterproofing must be laid under each rafter leg - a sheet of roofing material), and on a special support.
Mauerlat acts as such a support - a bar securely fixed to the end of the wall with the help of long anchors or metal bars embedded in the masonry.
We fasten the lower parts of the rafters to the Mauerlat with metal brackets, and connect the upper parts to each other and fasten them together to a long ridge beam that runs through the entire roof.
If the building is very large, then the rafters need to be strengthened. To do this, we connect them in the upper part in the shape of the letter "A" with wooden beams - braces.
Additionally, we fix the structure with vertical supports, which we install on each pair of rafter legs, or through one pair.
Roof waterproofing and insulation
 After completing the roof frame, care must be taken to ensure that the under-roof space is warm and dry.
After completing the roof frame, care must be taken to ensure that the under-roof space is warm and dry.
For this:
- Between the rafters we lay plates of roofing insulation material.
- From below, we close the insulation with vapor-permeable membrane materials that release moisture from the insulation and prevent condensate from accumulating in the thickness of the insulated roof.
Note! Condensation not only contributes to the development of putrefactive processes and the growth of fungus in the roof - it also reduces the effectiveness of thermal insulation, since wet roofing insulation loses its thermal insulation properties.
- We lay a waterproofing material on top of the rafters, which we fix with galvanized wire staples directly on the rafter legs. In this case, the laying of waterproofing should be continuous, even and without sagging.
Sheathing and roofing
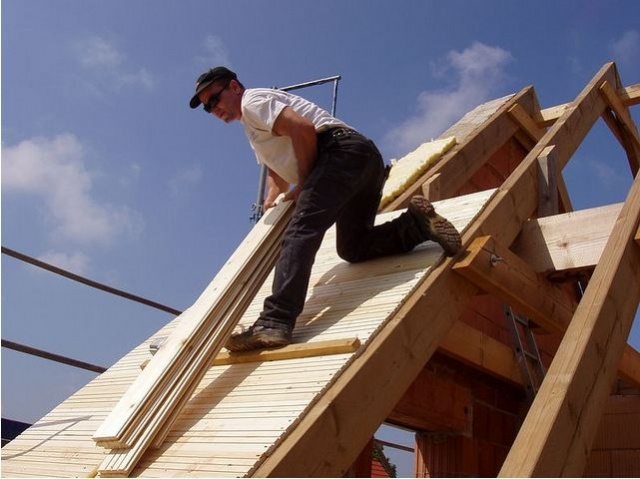

Most roofing materials are not laid directly on the rafters, but on a special structure - the crate.
roof lathing it is carried out either from wooden beams stuffed onto the rafters with a certain step - then the crate is called sparse, or from plywood or OSB-boards.
A solid crate of these materials is more often used for laying roofing materials such as shingles.
If necessary, we lay a substrate on the crate - a polymer material that provides the most efficient roofing. Most often, the substrate is purchased in the same place (and from the same manufacturer) as the main roofing material.
The final stage of roofing work is the arrangement of the roof itself. Roofing material (slate, tiles, metal tiles, roofing tiles, etc.) is attached to the crate either on an adhesive basis or using special fasteners.
We complete the work with the arrangement of difficult places - the junction of the roof to the walls, ridges, ribs, cornices, etc.
As you can see, the scheme for arranging the roof cannot be called simple - but there are no special difficulties that are inaccessible to understanding. In any case, with proper preparation and at least minimal building skills, you can handle such a thing as roofing!
Did the article help you?
