 A homeowner who is just building his own estate, or who decides to renovate a worn-out roof, sometimes finds it difficult to choose a cover for it. After all, roofing materials are now on the market in such abundance that it is difficult to simply keep track of even the names of new products, not to mention their properties. The following article will help you figure out what is behind this or that name.
A homeowner who is just building his own estate, or who decides to renovate a worn-out roof, sometimes finds it difficult to choose a cover for it. After all, roofing materials are now on the market in such abundance that it is difficult to simply keep track of even the names of new products, not to mention their properties. The following article will help you figure out what is behind this or that name.
Important information! The erection of the roof is the last, but very important stage of the general construction cycle. And the roof is designed in advance, simultaneously with the choice of an architectural solution for the house as a whole. During construction, when the foundation and walls are built, and even more so when the truss system is erected, it may be too late to change the type of coating.After all, all of the listed structures perceive loads from the roof, and if they are more than design, such material cannot be used.
In order not to make a mistake in choosing a coating, it is worthwhile to imagine what types of roofing materials have, how they are classified, and what to expect from a particular product. The most common characteristic is the form of release of the material.
It can be identified:
- Roll materials - "champions" for coatings for flat roofs
- Sheet roofing material – allow you to quickly cover large roofs
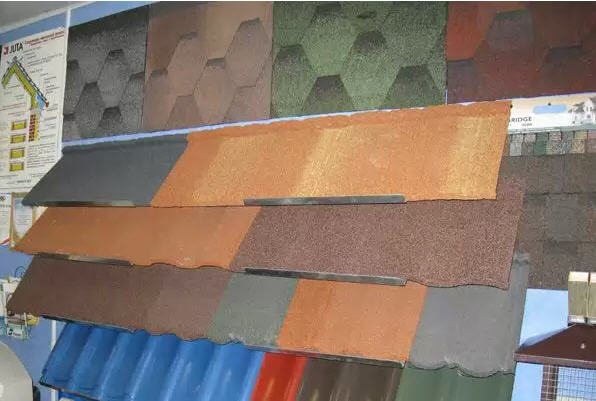
- Small-piece materials - as a rule, the most durable and prestigious, convenient on roofs of complex configuration and easy to repair
- Bulk materials - quickly applied, easy to install. Provides seamless coverage, long service life and easy repair
There is no single answer to the question of which material is best for roofing - there is a solution for each case. Now - in more detail about each of the classes:
Roll materials
Roll materials are distinguished by:
- Mind basics
- Mind astringent
- Type of protective outer layer
- Application method

This class of materials is obtained by applying bitumen or bitumen-polymer mastics for the roof on any basis: glass-canvas or fabric, cardboard, foil or asbestos paper.
The second method is rolling a mixture of mastic with a filler (mineral or rubber) and additives (antiseptics, plasticizers, etc.)
Bitumen is primarily used as a binder, as well as: bitumen polymers, polymers or tar.Protect these types of roofing materials with a sprinkle of mineral chips, foil or polymer film.
The most popular of this class is the classic roofing material. This is an elastic roofing material, cardboard impregnated with bitumen. There are many types and brands of it, they differ somewhat in physical and mechanical properties.
The main advantage of this material is its apparent cheapness. However, it is morally obsolete for a long time, and in most cases it is already used as an auxiliary material - as a base for other types of coatings, for waterproofing structures, etc.
Another thing that helps him stay afloat is the repair of multi-storey buildings by some housing offices. Since the service life of this material is no more than 10 years, they constantly have work, and therefore money.
New roofing materials, even from the same group, are far superior to it in terms of practicality - both during installation and in operation. They are produced on the basis of fiberglass, non-woven polymer fabric or polyester.
Often, almost the same materials are sold under different names, so when buying, you should first of all study their composition.
There are two main compositions in impregnation: SBS and APP. The first retains high elasticity even at a temperature of -30 ° C, which allows it not to harden or break even in severe frosts - and this is a guarantee that the roof will last a long time.
But materials based on it (Izoelast, Bikroelast, Termoflex, etc.) are sensitive to ultraviolet, and therefore require a protective coating.
APP retains plasticity down to -20 °C, but is very resistant to other atmospheric influences.Materials on any of these bases have a service life of 15-25 years.
The bases are:
- Fiberglass. On the basis of fiberglass, the cheapest roofing materials are produced, but they are also the lowest quality. Most often they are used as substrates for other materials - rolled, sheet, piece.
- Fiberglass is up to 5 times stronger than fiberglass, and three times more expensive.
- Polyester materials (for example, polyester) are equal to fiberglass in strength, have better adhesion to mastic impregnation and are much more elastic (elongation of glass materials - 2-4%, polyesters - 15-20%). The most expensive type, but also the best roofing material in its class.
When laying the deposited materials, 3-5 rolls are first laid out in parallel in a row, taking into account overlaps (7-10 cm) and unwound by 3-4 m. Up to a slope of 15%, laying goes along the slope, with a larger one (up to 25%) - across his.
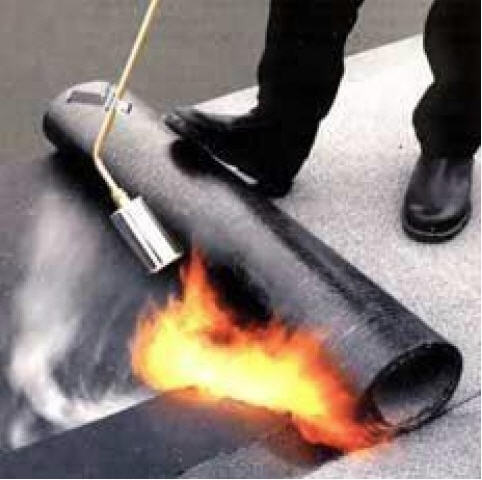

The overlap goes along the slope. Laying starts from the bottom edge. All rolls, except for the first one, are rolled up, and the first one is placed on a special roller, and, starting from the edge of the web, is heated with a special burner.
As the canvas warms up, it is laid, rolling with a special roller. The panels are also joined along the length with a gap of at least 100 mm. The second layer of coating must be applied with an offset of 100-200 mm relative to the seams of the first.
Self-leveling roofing is a bitumen-polymer mastic applied to the roof in liquid form. It cures very quickly, gives a highly elastic coating, is easy to repair, can be applied to surfaces at any angle.
Has a service life of 25 years. The main disadvantage is the high price.
The mastic can be laid using a special sprayer, brush or roller.The process of its application is absolutely similar to conventional painting.
Important information! Roll solutions are by far the most affordable and common for flat and low-slope roofs.
Sheet materials
The review of roofing materials, perhaps the most extensive class, will continue, even if you look at the substances from which its representatives are made:
- Metal
- asbestos cement
- cement fiber
- Fiber with polymer-bitumen impregnation
- Polyesters (including transparent roofing materials)
The main categories of metal sheet materials are:
- Copper - has a very long service life (more than 100 years), but also costs more than all the others
- Aluminum is the lightest of all representatives of the class. It also has a fairly long service life.
- Zinc-titanium is a relatively new material. It combines the qualities of the previous two, but is much cheaper than copper. On the roof is very similar to her color.
All these materials are folded - they are interconnected by engaging the edges of adjacent sheets and creating a mechanical (flattened) seam.
This work can be done directly on the roof, or on the ground. In the latter case, several sheets linked to each other are called a picture. Articles describing these roofing materials refer them to the elite group.
Next comes the bulk group:
- Galvanized steel - laid on the roof in the form of sheets or rolls, provides a fairly light, strong and durable coating, at the same time - quite inexpensive
- Decking is a roofing material made of the same galvanized steel, but having a cross-sectional profile, thanks to which it is able to withstand much greater loads compared to a flat sheet. It is produced both in a “pure” form, and painted, or with a polymer coating.
- A metal tile is the same coated sheet, but its profile imitates ceramic tiles. It has strength and durability higher than galvanized. But its coating is quite delicate, it is easily damaged, moreover, it is considered a “boomy” material that creates noise under the roof during rain.

In general, the types representing metal roofing material in the construction of roofs have been used for a long time, and have proven themselves well. They have a long service life, are durable, relatively light and easy to install.
Advice! When calculating the bearing capacity of rafters and walls, even when using the lightest roofing materials, one should keep in mind the snow load. After all, regardless of the roof, it is (standard) for the northern regions of 200 kgf / m2.
Asbestos cement and cement fiber are mineral sheet materials that are commonly called slate (in fact, slate is the German name for slate). The difference between them is the presence of asbestos in the composition.
These products have been produced for a long time and their properties are well studied. They are chemically inert, durable and last about 50 years. The disadvantages include relatively large weight and fragility.
Euroslate is a group of fibrous materials with various organic impregnations - bitumen, polymers, or mixtures thereof. They are very light. At the same time, they provide sufficiently high strength (up to 650 kgf/m2) and durable.
Depending on the specific type, they have greater or lesser resistance to chemical attack and ultraviolet radiation. In general, a very promising material.
Sometimes polyesters are included in the same group. These are homogeneous polymer sheets, among which there are also transparent roofing materials - the same polycarbonate.
It is gaining more and more popularity in all areas of construction. Both the roofs of huge public buildings and lanterns in the roofs of residential buildings, winter gardens, not to mention greenhouses are erected from it.
It is very durable roof material, having a cellular structure, due to which it has low thermal conductivity. At the same time, it is light and flexible, which allows architects to play with the geometry of the roof elements.
Of course, this transparent roofing material has a great future.
All sheet materials are laid on a crate made of wooden beams with a step of 30-50 cm. Laying starts from one of the lower corners of the roof and is carried out according to the principle - +1 sheet of the lower row - sheet of the upper one.
The fastening frequency depends on the type of material and is indicated in the manufacturer's technological map. The ridge, roof overhangs and its ends are closed with special elements that are supplied with ordinary sheets.
piece materials
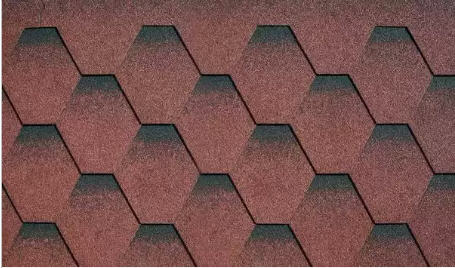
Piece materials include materials with a small size of elements, with the help of which a roofing sheet is assembled. Most of them are made from minerals, organics, or mixtures thereof.
The classic mineral roofing material is ceramic tiles. It is strong and durable, but has a lot of weight and does not tolerate a combination of rain and frost.
Almost the same can be said about cement tiles, but their durability is much lower.
Classic slate is also presented here - sawn tiles of natural stone, which has an almost unlimited service life, is relatively light, but very expensive.
Recently, a new roofing material has appeared in this group - porcelain stoneware. It is strong, durable and aesthetically pleasing, but also relatively expensive.
Various types of bitumen-mastic materials have almost the same properties as their roll counterparts, but they are laid on roofs with a fairly large slope. Easily repaired and light weight.
A separate group - wood materials - shingles, shingles, wood chips. Durable and lightweight, but expensive and need extra careful styling.
All piece materials for roofing are laid on a continuous or very frequent crate. Under them, a layer of waterproofing is necessarily laid, and if the roof is planned to be warm, then also a heater.
Installation starts from one of the lower corners. Artificial and natural stone are hooked together with the help of special curly elements, the euro-tile is fastened with nails to the upper part of the plate.
Laying is carried out in rows. Connections to roof equipment, ridge, roof edges are made with special elements from the same material, or from roofing iron.
Did the article help you?
