 The way in which soft roofing is installed depends on the structure of the roofing material, the angle of inclination of the roof and the material of its base. This article will talk about how a soft roof is covered - installation of tiles, roll and mastic coatings.
The way in which soft roofing is installed depends on the structure of the roofing material, the angle of inclination of the roof and the material of its base. This article will talk about how a soft roof is covered - installation of tiles, roll and mastic coatings.
The base on which installation is carried out in the case of a soft roof should be made strong, immovable, smooth, dry and well ventilated.
The installation technology requires that the moisture content of the material used to make the base (plywood, boards, etc.) does not exceed 20% of its dry weight.
It is recommended to choose a solid crate, which is not only safe to walk on, but also a good sound and heat insulator.
A solid crate is made by attaching one of the materials close to the rafters:
- moisture-resistant plywood, the thickness of which is at least 9 mm;
- dry straight edged or sawn boards;
- wood fiber boards with longitudinally oriented fibers.
It is worth noting that a wooden solid crate is not more expensive, sometimes even cheaper than a well-made cellular base for other roofing materials.
The cost of work also increases due to the exact observance of the lathing step: the total cost of the base is calculated by adding the cost of the lathing and the anti-condensation film used with other materials, which is not required when installing a soft roof - the roof is installed on a continuous lathing.
Important: if the installation of a soft roof is carried out in hot weather, the material should be stored in the shade, which will facilitate its installation and make it easy to remove the polyethylene film. During rain, the soft roof should not be laid; it is necessary to wait for the roof to dry completely.
The material with which the installation is most simply carried out is a soft roof, equipped with a self-adhesive layer and a protective film made of polyethylene.
The installation of such materials is carried out as follows: the protective film is removed, after which the tiles are attached to the base with nails, and some types of materials can be attached without their help.
The adhesion of the tiles to the adjacent tiles and the base occurs under the action of sunlight, resulting in a coating with good tightness.
Since the laying of the material is overlapped, the reliability of the laying can be increased by fixing the tiles to the previous one with four nails.In this case, special galvanized nails for soft roofing should be used, the size of which is 30x10x3 mm.
The device of a soft roof from rolled materials
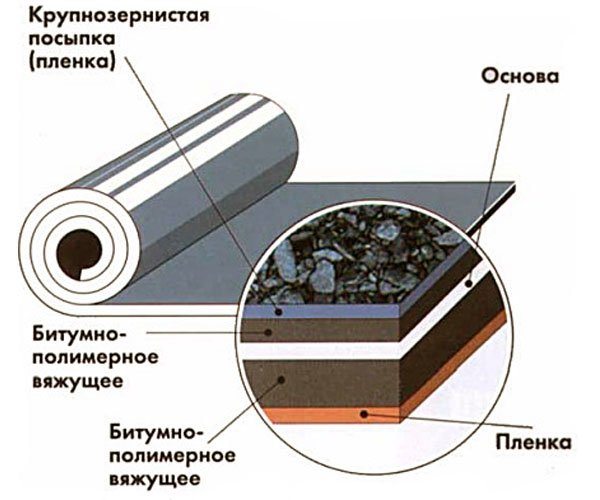
Installation of a rolled roof ensures high water tightness of the roof even at a slope of 0 to 50 degrees. Any base is suitable for laying this material.
The figure shows an approximate scheme for laying a soft roof made of rolled material, which differ into several groups according to the method of installation:
- Bonded materials:
- on bituminous hot mastics;
- for cold polymer, bitumen-polymer and rubber-bitumen adhesives and mastics.
- Surfacing roll materials:
- on modified and oxidized bitumen
- using gas burners by the fire hot method;
- fireless hot method using equipment using infrared radiation;
- fireless cold method, dissolving the thickened bituminous layer.
- Materials with an adhesive layer, having a protective coating in the form of a film of silicone or paper, removing which, the roll rolls out on a pre-primed surface.
The easiest way to lay the roofing carpet is by continuous gluing rolled roofing materials to the base.
Sometimes partial gluing is also used, which excludes the occurrence of excess pressure due to the appearance of a gap between the base and the roof, which communicates along the roof contour with atmospheric air from the outside. . Roofs made by this method are called "breathing".
Such roofs not only prevent swelling of the material, but also provide a more efficient removal of moisture from it, which can be further improved by fixing the cross section of the air layer, for which the sprinkles applied to the rolled material are used.
In addition, a "breathing" roof eliminates the possibility of material breaks above base cracks and joints, since their deformations are not reflected on the roofing carpet.
The disadvantage of this type of roofing can be attributed to the difficulty in finding a specific place of leakage.
In the event of a rupture of the roofing carpet and water getting into it, it spreads into all air sinuses, after which it penetrates into the interior of the building through a loose joint of the base.
Therefore, a leak spot on the ceiling will not be evidence that the carpet was damaged at this particular point, and it will be rather difficult to find the real place of the leak.
In order to perform partial gluing of the roofing material to the base, the following can be used for the bottom layer:
- material with perforation;
- standard material, on which the adhesive mastic is applied either in the form of spots distributed evenly over the surface, or in the form of intermittent or continuous stripes;
- welded roofing material, the welded bottom layer of which is applied to the canvas in the form of intermittent stripes.
Quite high quality is the use of various materials equipped with an adhesive layer when arranging the roofing carpet. Such materials can also be used in the repair of roofs, which requires particularly careful preparation of the base.
Roofing from mastic
An example of a mastic roof
Polymer and bitumen-polymer mastics can be used to cover surfaces made of various materials, such as roofing material, steel, concrete, etc., regardless of the complexity of the roof structure and slope angles.
The only condition is an ideal smooth surface, which is required for applying the mastic with a layer of the same thickness, which is the main disadvantage of this coating.
Mastics, when applied to the substrate, must be in liquid form, after application they harden as the solvent evaporates, forming a continuous sealed seamless film.
The amount of dry residue in the mastic will determine the thickness of the resulting film, and for mastics without a solvent in the composition, hardening is not accompanied by a decrease in the thickness of the coating layer.
Important: if the roof slope exceeds 12º and the ambient air temperature is above 25 degrees, special fillers, such as cement or various thickeners, should be added to the used mastic to increase its viscosity.
Mastics currently produced are not equipped with a protective layer, since their color gives them all the decorative properties, and the material used is sufficiently resistant to negative external influences.
For additional protection of the roof covering from various influences, a protection layer of coarse (2-5 mm) sand, fine (10-20 mm) gravel, bituminous or asbestos-cement sheets of small size, etc. is applied.
Useful: river pebbles are considered the best material for creating a protective layer of mastic.
It is important to remember that soft roofing equipment must be produced by competent specialists.Trying to save on such important points as creating a project, choosing a coating material and hiring workers, you can later face triple the cost of premature repairs.
Did the article help you?
