 It will not be a secret to anyone that the construction of a roof cannot be carried out without first drawing up a roof scheme. The scheme of the roof of the house is needed in order to be sure that you did not make a mistake with the choice.
It will not be a secret to anyone that the construction of a roof cannot be carried out without first drawing up a roof scheme. The scheme of the roof of the house is needed in order to be sure that you did not make a mistake with the choice.
Let's first figure out which roof is better: pitched or mansard.
Pitched roofs have many different technical advantages, such as prevention of rotting and structural failure, accelerated water runoff, and less snow load.
In addition, roofs that have a slope exceeding 1/6 of a flat roof have another undoubted advantage. All the space that is under the roof can be easily turned into a living space.
Also, pitched roof schemes allow the installation of skylights.If we proceed from the ideal, then the size of the windows should be such as to match the distance between the rafters, which will save material and allow you not to do extra work.
In other matters, pitched roofs serve to retain heat, remove precipitation and protect the house "from above".
Currently, there are the following types of pitched roofs:
- simple roofs;
- Multi-slope;
- single slope;
- Gable roof.
This type of roof is one of the varieties for covering buildings. They are called so because such a roof is formed in a system of intersecting slopes that help drain rain and melt water.
Typically, such roofs have a slope of more than 10 degrees and provide not only protection, but also the aesthetics of the building. Such roofs are built mainly where houses do not have attics.
As for the pitched roofs, then, perhaps, enough about them, and now let's talk about such an option as mansard roofs, because it is he who begins to prevail in recent times.
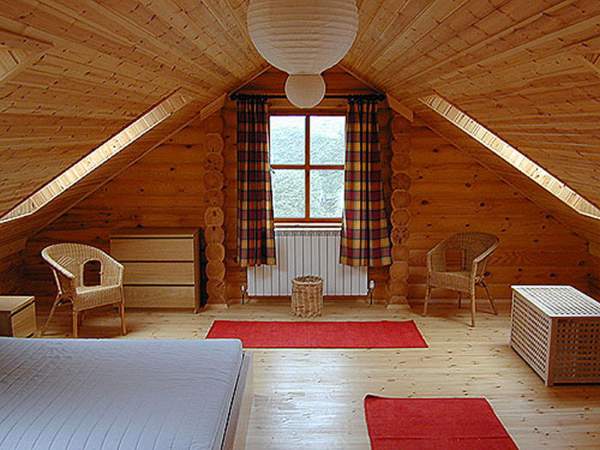

The attic is a floor that is located in the attic space, while the facade of the building is completely or partially broken or has a slope. In principle, this is precisely the advantage of attics.
If the roof design scheme is chosen correctly, then extra meters appear that allow you to make an office space or a cozy apartment.
To your attention! The attics have one unique property: they create comfort and have a lot of space. In this regard, there is an opportunity for a flight of fancy, which will help you choose a room that will be located in the attic.
For example, you can create a cozy office, a wonderful library, a winter garden or your own bowling alley.In this case, everything depends only on your imagination and, of course, on material possibilities.
In addition, the construction of an attic is not very expensive, and is much cheaper than building a new apartment in a new building.
It follows that a square meter will cost about 30% cheaper. In addition, during the design of the attic, no one needs to be evicted from the house.
In addition, you need to remember that the roof is designed not only to protect the building from precipitation, but also to give beauty and sophistication to the house.
Regardless of the configuration of the roof, it is possible to distinguish a supporting structure in it, which is represented by a crate and roof trusses, and a roof.
Whether certain elements are present in the roof depends on its shape and design features.
The shape of the roof depends on the size and purpose of the building.
The shed type roof scheme is designed for garages, outbuildings and sheds. For residential premises, mansard or gable roofs are most often used.
They are made without much difficulty, and any roofing material is suitable for them. However, for the southern regions, it is preferable to arrange a hip roof, as it resists the wind better.
Roofing materials

As for roofing materials, slate will be the most durable, however, recently, due to its unaesthetic appearance, it is used less and less.
Tiles are suitable for low-rise buildings, however, they require reinforced rafters, since tiles are not light in weight.
Tip! If the roof has a complex configuration, then roofing steel is used.Roll roofs can be used for outbuildings or for temporary roofing.
As for one-story houses, as a rule, roofs with inclined rafters are arranged in them, which at one end rest on the outer wall, and at the other - on a rack or on a run, which is installed above the middle wall. The elements in the rafters will be connected using rafter staples or nails.
In the event that the wall is chopped, then only brackets are used to fasten the rafters, and for stone walls there is a method of fastening:
- A metal ruff is hammered into the wall, it must be driven in no lower than the fourth masonry seam.
- To the ruff with the help of twists, the rafters will be attached with wire in two loops.
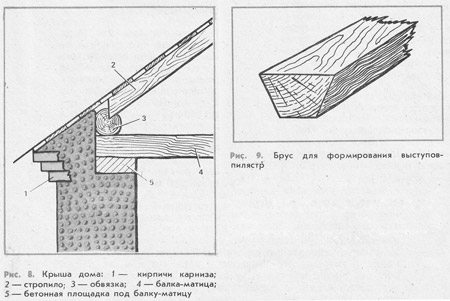
- The ends at the rafters in a stone house use a beam as a support, which lies along the length of the wall. It is he who distributes the load that comes from the rafters. In places where the house pipe exits, between the crate and the rafters, it is necessary to leave a 13 cm gap.
It is worth noting that almost all construction farms have their own characteristics.
The basis of the truss truss is a triangle, which is the most rigid and economical design. It is formed from a puff and two rafter legs.
The legs are attached to the ridge run. The lower ends of the legs are attached to the outer walls of the house. Such a design can only withstand a roof that has a small weight.
In order to ensure reliability, the trusses have internal props.
These farms are needed in order to create the desired roof slope - a diagram of which must be drawn up in advance.
In turn, the slope depends on:
- Climatic conditions: if there is a large amount of precipitation, then the slope should be about 45 degrees. If the winds prevail, then the slope should be made much lower.
- Type of roofing material: if piece roofing material is used, then the slope should be at least 22 degrees, 5-25 degrees for rolled materials, and 25-35 degrees and higher for tiles and slates.
The only thing to remember is that with an increase in the slope of the roof, the consumption of roofing materials will increase, which means that the cost will also increase.
Depending on how the trusses are attached, there are inclined and hanging rafters.
hanging do-it-yourself roof rafters located in the same plane, based on the outer walls and rigidly connected to each other.
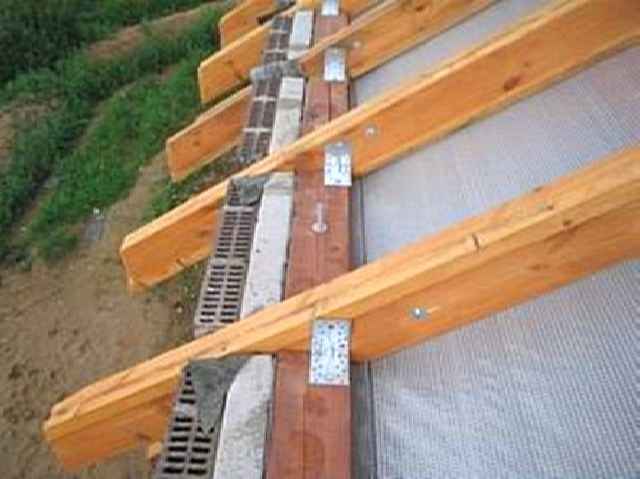

The support for the ends of the rafters located below are Mauerlats, which are hewn into two edges. If the hanging truss truss is simple, then it consists of a puff and rafter legs.
In order to avoid deflection of the rafter legs, if they have an insufficient cross section, a lattice made of a rack, a crossbar and struts is introduced.
This allows you to increase the rigidity of the structure. The rafter legs are strengthened with staples and tied to the ruffs with a wire with a thickness of 4-6 mm. This will help protect the roof from blowing off in strong winds.
After the rafter structure is completed, a run is made, which serves as the basis for the ridge. For the manufacture of a ridge run, either logs with a wide section are used, or two boards, the thickness of which is about 5 cm.
Mansard-type roofs require trusses with a special design. They can also be mounted on the inner wall, or without it.
A feature for roofs of this type is that they do not have a tightening, but instead there is an interfloor overlap. The reason for this is that the lower belt is the basis for the future floor.
As for the crate, it serves as the basis for the roofing and, depending on what, it can be made of bars, boards or tesa.
She perceives the load coming from the roofing material, and puts pressure on the rafters, which in turn transfer the weight to the load-bearing walls.
The crate is made both solid and sparse. In a continuous crate, the gap is not more than one mm and it is made of two layers: the first layer is discharged, and the second is solid, made of boards that are laid at an angle of 45 degrees relative to the boards of the lower layer.
Solid lathing is most often used for soft roofing, slate, soft tiles and metal tiles. Sparse is most often done under a steel roof, cement-sand and clay tiles and for corrugated asbestos-cement sheets.
The batten bars are attached to the rafters with nails, which should be as long as two bars in thickness. At the junctions and intersections of slopes and overhangs of cornices, a continuous crate is always made.
Usually coniferous wood is used for the crate. True, if the house is brick or block, then it can be metal or reinforced concrete.
The optimal dimensions for the crate are bars having a size of 50 by 50 or 60 by
60 mm. The average distance is about one meter.
For roofs with a slope of more than 45 degrees, the distance increases to 120-140 mm, and if the house is located in a snowy area, then it decreases to 80-60 mm.
There are ready-made roof structures that reflect almost all existing roof configurations.
Sheathing bars are usually attached to the rafters as provided by the design in advance. If the rafters are wooden, then the crate on them is simply nailed.
Regarding reinforced concrete rafters, they either have holes for nails, or outlets with a diameter of up to 6 mm, which firmly fix the crate bars. There may also be special spikes on which you need to prick the purlins.
In any case, this is not difficult, since you just need to find roof diagrams that will reflect how the fastening should be carried out.
Did the article help you?
