For any building, with rare exceptions, the roof is a must, and one of the most important elements. It can be arranged from different materials and have different designs. About what are the elements of the roof, and what they are intended for in each case - later in this article.
For any building, with rare exceptions, the roof is a must, and one of the most important elements. It can be arranged from different materials and have different designs. About what are the elements of the roof, and what they are intended for in each case - later in this article.
In the common people, it is customary to call the roof its uppermost layer - the roof. Accordingly, the roofs are “galvanized”, “tiled”, “slate”.
But this is only partially correct, since the chosen type of coating affects the entire structure. However, the roof as a whole is a fairly complex "layer cake", containing a large number of different details and levels.
By function, the roof structure consists of:
- Coverings - this is the ceiling of the upper residential or technical floor, which is the basis for the roof itself, and on the lower side, as a rule, for the ceiling of the premises of the lower level
- Bearing structures are elements that can take significant loads from roofing materials, and neutralize them, or transfer them to load-bearing walls or the building frame.
- Roofs are a certain set of materials, the top of which perceives the impact of various atmospheric factors, such as precipitation, temperature, humidity, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, and the rest provide the functions of maximum protection of the house from certain environmental influences
- Auxiliary equipment - these are various devices located above the roof level, or made in conjunction with it, allowing you to perform specific tasks: snow protection, lightning protection, stormwater discharge, communications, windows, etc.
Naturally, each of these levels of structure has its own components (however, depending on the specific structure of the roof, some of them may not exist), which we often do not know when we make the roof ourselves.
Let's define terms
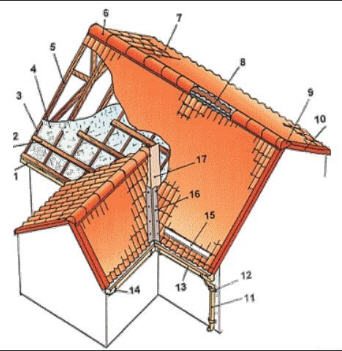
Before deciding how to close the roof of a house, you need to learn the concepts used in construction - what is what on the roof:
- Cornice strip - covers the space under the roofing material from precipitation and wind
- Timber or batten board - serves as the basis on which the coating material is attached
- Bar of counter-lattice. It is not always used, it can carry roofing material, waterproofing is attached under it. Sometimes thermal insulation
- waterproofing film
- Rafter - the main load-bearing element of the roof
- Skate - the junction of the roof slopes
- Roof material layer
- Ridge seal (allows air to pass through for ventilation but keeps rain and debris out)
- Ridge plug - an element that closes the end of the ridge
- Wind board - located at the end of some types of roofs with gables, prevents lateral wind effects on roof sheets
- Drainpipe - diverts rainfall into storm sewers or to the adjacent territory
- pipe bracket
- Gutter - used to collect precipitation from the surface of the roof and dump it into the drain
- gutter bracket
- Snow guard
- Endova (the place of the concave junction of the roof slopes) internal (located under the roofing material)
- External valley (located on top of the roofing material)
Some structures have their own, specific elements, on simple roofs (for example, flat ones) - most of the listed nodes are missing. Nevertheless, the listed set is quite typical for most pitched roofs.
What is the roof on?

First of all, it should be understood that the specific roof structure depends on the location of the load-bearing elements of the building, although it does not always exactly repeat their relief.
Just as load-bearing structures can be "in the open air", so the roof can go far beyond them. However, "on average" - they are the same. Accordingly, the shapes of the roof follow the arrangement of those load-bearing elements on which they rest.
Important information! Very often, especially in connection with a large number of undereducated specialists, confusion arises in the application of classical construction terminology.Example: A straight roof means a flat one. In fact, a straight roof is one that has the correct geometry, without changing the slope. The opposite concept is a sloping roof, the roof of which has a changing slope, for example, a mansard.
As a pitched roof (having a slope of more than 3%), no matter how many slopes it has, can be straight, and a flat roof (with a slope of up to 3%) can be broken. Due to the ease of installation and maintenance, straight roof houses are the most common design.
We form the roof
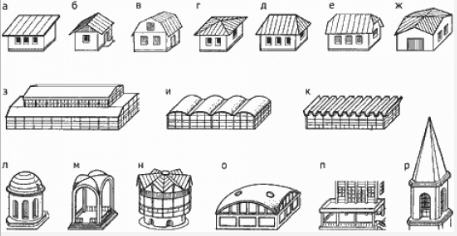
Although there are quite a few different forms of roofs, they all lend themselves to a certain classification. The main dividing line runs on the basis of "flat - pitched". And if everything is clear enough with a flat one (having a slope of no more than 3%), then pitched ones have many varieties.
There are the following forms of roofs of houses:
- Shed roof (may have different slopes)
- gable roof - the triangular planes located at its ends are called gables, or tongs. Can be made both together with the walls, and sewn up separately, with other material
- Mansard - a sloping roof that has a change in slope on the roof surface. not necessarily under mansard roof it is the attic that is located, but most often it is so.
- Hipped roof - a kind of hip, (see below), where all the slopes are the same triangles
- Hip hipped roof - where the end slopes are covered with a triangular-shaped roof, and the other two are trapezoid-shaped
- Half-hip roof - her gables are not brought to the level of the side overhangs of the roof. Also under the end overhangs can be located (in the walls or roof) skylights
- The roof of oblique surfaces - is arranged on buildings where the top of the walls is at different levels
- Roof with skylights - in fact, it is a two-level roof, while each of the levels can have its own shape, the walls of the upper level rely on the supporting structures of the lower one, as a rule, they are made of light-transmitting material
- Vaulted roof - made of one or more arcuate surfaces in terms of
- Folded roof - a set of several combined sections of a gable roof
- Dome - a hemisphere based on load-bearing walls or columns
- Cross vault - a combination of four, sometimes more, arched vaults
- Multi-gable roof - comes in many forms, for example, one of the options for how to make a roof on a hexagonal house. It is a connection of several slopes at different angles
- Spherical - a round arch, at several points resting on the base
- Flat roof - has a slope of no more than 3%, based on load-bearing walls or columns of equal height on 2 or more sides
- Spire - a joint of 3 or more triangular slopes with a very large (from 60 °) slope
Naturally, the structural scheme of the roof also determines the presence or absence of certain elements. For example, on a flat roof it makes no sense to arrange rafters, and on a pitched one they do not always do hydro - and thermal insulation of the floor.
The main thing is that the existing building technologies, architectural science, allow you to choose a roof for any building under construction or reconstructed, no matter how complex its design.
So that space is not wasted

The problem of free land for countries with a small territory is always relevant. And in any large city, usable space is a popular and expensive commodity.
You do not need to be an expert in geometry to understand that the area of the roof cannot be less than the area of the ground on which the building stands. And architects are trying to combine several functions: if a building needs a roof anyway, why not get additional benefit from it?
This is how very interesting roofs appear, which not only protect the owners from precipitation, but also provide them with additional amenities.
Somewhere a park or farmland is laid out on the roof. In Asian countries, where population density causes a terrible shortage of free land, sports grounds are being equipped on the roofs of skyscrapers.
But even in our area, no one bothers the owner of his own household to arrange a gazebo, a winter garden on an open roof, and an office, a workshop or a gym in the attic. It is enough to show imagination and make efforts, and, most importantly, to have sufficient funds.
Did the article help you?