Every day our eyes are faced with various buildings, and any of them is crowned with a roof. It can be a typical flat roof of a high-rise building, or a classic gable "house". There are also unusual options that are rare, and attract the attention of passers-by. About what roofs of houses are, and which one is better to choose for your home - later in the article.
The most important parameter by which the shape of the roof is distinguished is the slope. According to it, roofs can be flat or pitched. Flat ones include those that have a height difference between opposite edges of the roof within 3%.
This means that there will be a difference of 3 cm per linear meter of the roof. With extremely rare exceptions, all flat roofs are made shed - those where the roof surface is located in the same plane.
They organize several slopes on the roof only with a very large area, but this is a rather caustic architectural solution. Flat roofs were arranged on an industrial scale during the construction of multi-apartment "Khrushchev" and "Brezhnevka", and they prevail in high-rise buildings of a later period.
However, after 20-30 years of operation, it turned out that the cost of equipping an attic roof with slopes pays off the costs of subsequent maintenance.
Therefore, in recent years before the collapse of the USSR, an active installation of new pitched (usually slate) coatings on high-rise buildings began, but due to historical circumstances, the process was not completed.
The end is the crown
The device of the roof and roof (protective coating that protects the building from wind, precipitation, and other natural and man-made harmful effects) is the last stage of installation work in the construction cycle.
However, the final result of the whole process also depends on how successfully it will be completed - without a reliable roof, the house is useless.

Therefore, there are many different types of roofs - each "in its own case." However, all roofs have common elements. And what does any roof consist of, how is it arranged?
There are three main components of any roof:
- Covering is a reinforced concrete slab or flooring made of other material, based on the load-bearing structures of the building and covering the upper floor of the house. As a rule, it serves as the basis for the ceiling of the upper level of the building
- The load-bearing structures of the roof are load-bearing elements, most often made in the form of beams (rafters) and perceiving physical loads from the roof
- Roof - a layer of special protective material that protects the building from wind, precipitation, and other environmental influences
The main elements of the roof are (from inside to outside):
- vapor barrier
- thermal insulation
- Waterproofing
- Roofing
Depending on the specific design, as well as on whether the interior of the roof is provided, various elements are used, most often wooden, designed to install each of the layers.
For a pitched roof, this is necessarily a rafter and a crate; for some roofing materials, as well as in the case of organizing an attic floor, a counter-lattice is also required.
Important information! The crate is a special layer, solid - from sheet materials such as plywood, or made at intervals, as a rule, from a board or a bar. Its purpose is to strengthen the roof structure (the lathing is attached perpendicular to the rafter legs, and together with them creates a stiffening belt), and also to serve as a frame for attaching the roofing material.
The counter-lattice can be arranged on the inside and outside of the rafter legs. From the outside, it is attached along the rafters, under the crate and over the waterproofing film.
Here, the task of the counter-lattice is due to the gap created under the roofing material, and to ensure normal ventilation of the insulation and removal of moisture. Inside, it is also attached along the rafters along the vapor barrier layer, and a finishing material (drywall, etc.) is installed on it.
Roof types
What types of roofs are there, and on what grounds are they classified? First of all - according to the degree of slope of the roof:
- Flat (with a slope up to 3%)
- Pitched (where the roofing material is inclined relative to the ground, usually not less than 10%)
Also, the roof can be attic (where between the roofing material and the roof slab there is a space formed by the supporting structures), and combined - where the roof is laid directly on the roof slab of the upper floor.
In turn, the attic roof can be:
- Insulated - where the roof incorporates a layer of thermal insulation
- Cold - where only the roofing slab of the upper floor is thermally insulated, no insulation is provided in the roof structure itself, the temperature in the attic space corresponds to the ambient temperature
And the combined one is divided according to the degree of "purging":
- ventilated
- Non-ventilated
- Partially ventilated
Separately, one should dwell on the degree of useful use of the roof, since in a large city it turns out to be a good way to expand living space.
What roofs are on this basis? This:
- Non-exploited - not intended for any use, but sometimes requiring maintenance, such as snow removal in winter
- Operated - where the roof surface has, in addition to the main purpose, also additional functions

Residents of small countries with a high population density, and megacities, where land is valued very highly, are especially fond of arranging original roofs.
Here are just a few of the ideas that are used in modern architecture:
- Sports grounds
- Recreational areas, solariums
- open cafes
- car parks
- "Green" roof - there is a layer of soil on the roof, and live plants and grass cover are planted in it
- Roof-garden, or roof-greenhouse - special equipment is installed here that allows you to grow greens, vegetables and fruits
What does this type of roof consist of, how does it differ from the usual one? First of all, these are more powerful load-bearing structures designed for increased loads, especially when cars move along it.
There are also higher requirements for layers of thermal and waterproofing, primarily for "green roofs", which can damage soil moisture and plant roots.
The exploited layer is also specially calculated - it must protect the insulation layers from mechanical damage, and not create additional threats for them - such as high humidity or the same "vegetative" problems.
Advice! The operated roof does not have to be located above ground level. Such a roof, organized, for example, over an underground garage, will allow "turning on" an additional territory of the site.
But still, in private housing construction, where, as a rule, problems with land plots are not so acute, various types of pitched roofs are most often arranged.
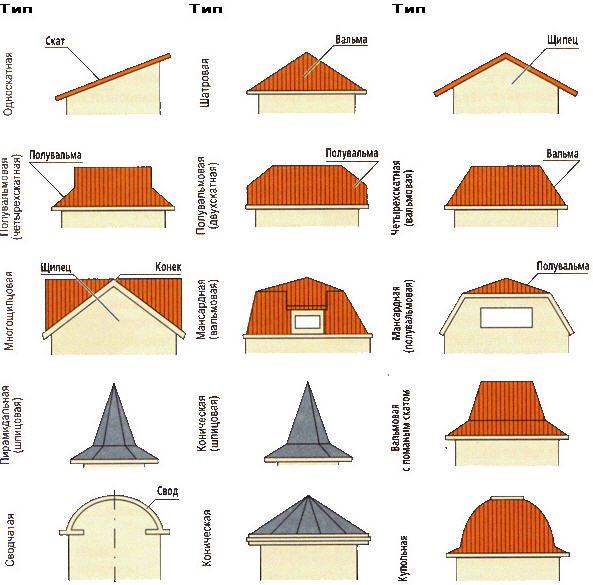
Pitched roofs, first of all, are divided by the number of their planes:
- Shed
- gable
- hip roofs
- Multi-forceps
There are more complex forms that are also included in one type or another (for example, a conical or pyramidal roof).
Most often, the choice of a particular type of pitched roof is determined by the weather conditions of the region and historical traditions.For example, in the northern regions, with abundant snow and long winters (for example, northern Russia, Finland and Switzerland), gable roofs with long overhangs traditionally predominate (in a classic alpine chalet, they practically reach the ground).
Also, the amount of precipitation also affects the slope of such a structure as do-it-yourself roof - after all, at 60 or more degrees, snow practically does not linger on the roof.
Advice! In cold climates, the problem of winter cleaning of roofs from snow is quite relevant. However, you should not be too zealous with the slope of the roof - after all, snow serves as a good heat insulator, so its moderate layer will not hurt a cold attic. In addition, the greater the slope, the higher the cost of installing a roof.
In Western Europe, various types of hipped (four-pitched) roofs historically dominated. With such a roof, the sections of the roof along the length of the house are trapezoids, and from the ends they are closed by triangles.
A special case is hipped roof - it is arranged on houses that are square in plan, respectively, all four slopes will have the same triangular shape.
Important information! The hips are precisely the triangles located at the ends of the house, the trapezoid slope is called that, it is not a hip!
But various variations are especially common, where the hips have overhangs of a shorter length than the side slopes, the so-called half-hip roofs.
They are so loved in Denmark that the second name of the half-hip is the Danish roof. As a rule, an attic floor is organized under such a roof.
Important information! Gable roofs have gables lined with wall material, and their heat transfer occurs mainly from the slopes. Hips replace the upper part of the wall, allowing you to save on masonry, and this is convenient for areas with a mild climate, where the roof is easy to insulate. However, the device of such a roof is quite laborious, since a much more complex truss structure and junctions between the slopes are required.
Almost any type of roof can be straight and broken - having a change in slope within the roof. As a rule, such designs are also used for attics.

A type of sloping roof is a half-timbered roof, which actually combines a hip or half-hip and a gable, sometimes a conical roof. These types of roofs are also characteristic of old Western European architecture.
The most difficult to perform, but also giving the most unusual roofs of houses as a result, are multi-gable roofs. It provides for the combination at different angles of several slopes. Sometimes such a combination is also performed at different vertical levels.
Sometimes such roofs are arranged for purely utilitarian purposes: for example, they attach some kind of room to the house.
At the same time, the wall of the existing house is also the wall of the new building. In terms of economy, it is usually easier to install an additional gable in addition to an existing roof than to create a separate roof for an extension.

This solution is also convenient for, for example, small motels or cafes with separate rooms located at different angles. A large roof height is not required here, so it is easier to install your own gable for each room.
Wealthy homeowners can afford to create a roof of complex shape and for purely aesthetic purposes, wanting to emphasize their individuality.
Despite the complexity and high cost of the device, the slopes of the roofs of such buildings facing the moon always attract the attention of passers-by and passers-by, amusing the pride of the owner.
But, regardless of who has what goals, one thing is certain: every home needs a roof, and their various forms and types will be encountered daily in the foreseeable future.
Did the article help you?
