Thermal insulation boards made of expanded polystyrene are one of the most popular products on the market for insulating building structures. I want to talk about the purpose, properties and characteristics of this material, as well as dispel some of the myths that have become widespread in recent times.
Expanded polystyrene in the form of plates
Purpose, composition, production

Expanded polystyrene (EPS) boards have been produced for several decades. This the material is used for thermal insulation of building structures, including walls, foundations, roofs, floors, partitions etc. High popularity is due to ease of installation, good technical characteristics and relatively low cost.

In construction, two main types of expanded polystyrene are used: ordinary foam (PSB) and extruded polystyrene foam (EPS, XPS). The second type is superior to polystyrene in all main indicators. The only disadvantage of EPS is its reduced vapor permeability and air permeability, therefore, when using it, it is recommended to pay attention to high-quality housing ventilation.
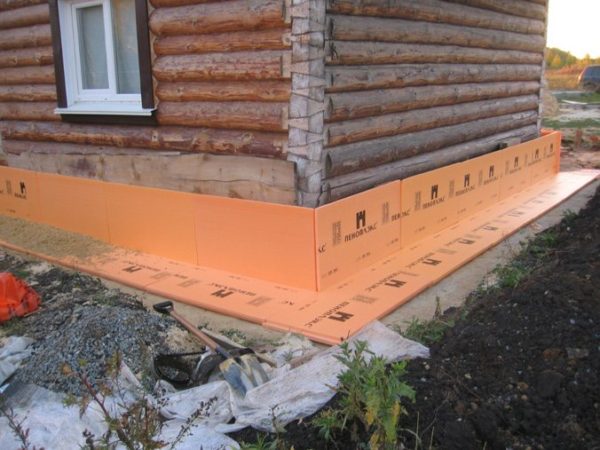

The purpose of expanded polystyrene covers a wider area, but here we are talking about plates that are used as a building heat-insulating material.


I just want to dispel the myth. A number of sources claim that extruded polystyrene foam is something new and unexplored, which means that we cannot say anything about its effectiveness. In fact, the material was obtained in the USA back in 1941, and today it is one of the most studied and proven thermal insulators (by the way, in the USA they completely abandoned the use of foam in favor of extrusion PPS).
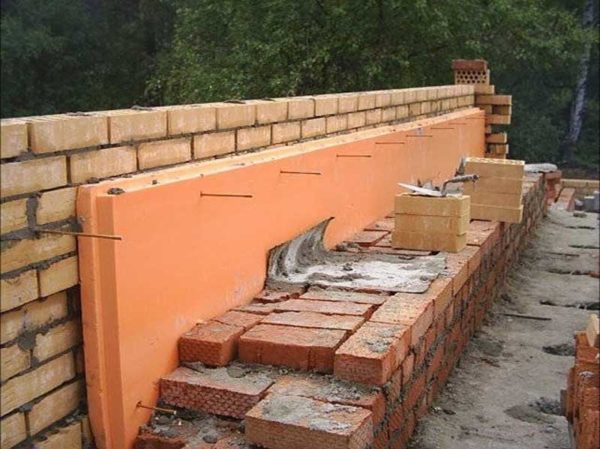


After the entry into force of GOST 15588-2014 “Polystyrene heat-insulating plates.Specifications”, we can conclude that in Russia there is also a trend towards abandoning conventional foam in favor of using extruded PPS. This material is more in line with fire and toxicological safety standards.


PPS is obtained from polystyrene, sometimes polydichlorostyrene, polymonochlorostyrene and styrene copolymers are used. The composition also includes foaming agents, including low-boiling hydrocarbons, blowing agents, freons and carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide has been more often used recently because of its fire safety). Finally, additives are found in the composition of PPS boards: dyes, modifiers and fire retardants.
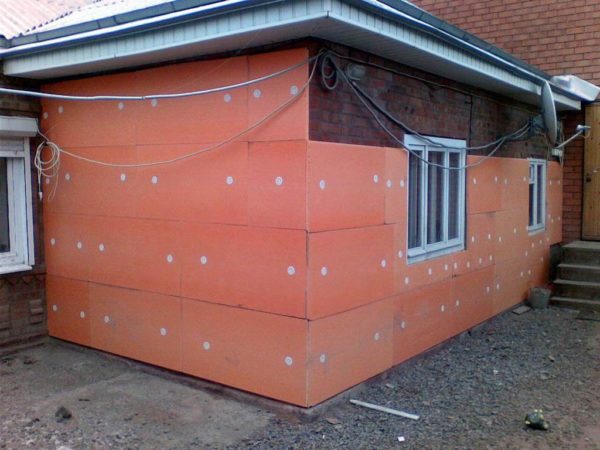


There are several ways to produce PPP, but we will focus on two that are used most often:
- Bespressovy suspension method. Suspension polymerization in the presence of isopentane, pentane or CO2 results in pellets dispersed in polystyrene with a light boiling liquid. Then the mixture is heated with steam or air, the granules increase tenfold with the formation of cells. This is how foam plastic (PSB) is obtained;
- extrusion method. Polystyrene granules are mixed with a blowing agent at high pressure and temperature and then extruded from an extruder. As a result, a closed porous uniform structure with cells of 100–200 µm is obtained. This is how EPS is made.


Specifications

Consider the characteristics of foam and extruded PPS. For convenience, the data is presented in the form of a table:
| Characteristic | Extruded PPS (XPS) | Polyfoam (PSB) |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m*K | 0.028 – 0.034 | 0.036 – 0.05 |
| Density, kg/m³ | 28 — 45 | 15 — 35 |
| Vapor permeability, mg/m*h*Pa | 0.018 | 0.05 |
| Water absorption for 30 days, % by volume | 0.4 | 4 |
| Water absorption in 24 hours, % by volume | 0.2 | 2 |
| Compressive strength at linear deformation by 10%, N/mm² | 0.25 – 0.5 | 0.05 – 0.2 |
| Static bending strength, kg/cm² | 0.4 — 1 | 0.07 – 0.2 |
| Operating temperature range, °C | -50 to +75 | -50 to +70 |

As can be seen from the above data, XPS has better thermal insulation qualities, higher compressive and bending strength, it absorbs water much less and passes water vapor worse.
Fire safety teaching staff

The topic of fire safety of expanded polystyrene has been raised repeatedly due to a number of unpleasant precedents. Of course, the discussion gave rise to many myths.
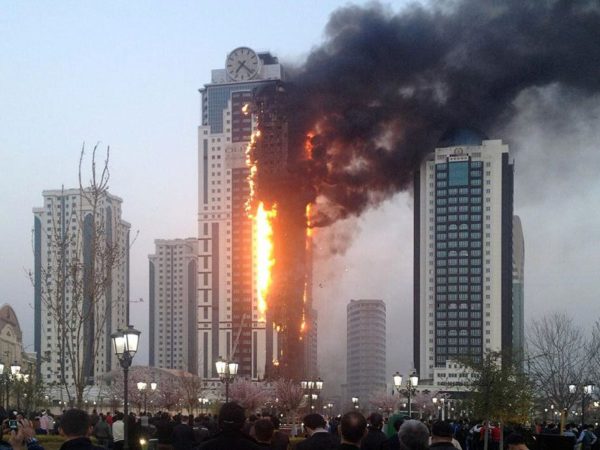
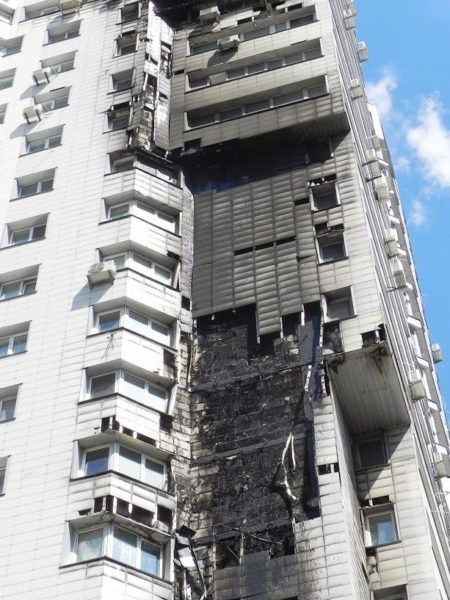


The fact is that if we consider unmodified polystyrene foam, then we will see that this insulation refers to flammable materials. That is, ordinary foam can catch fire from a match, electric welding, or another source of flame.
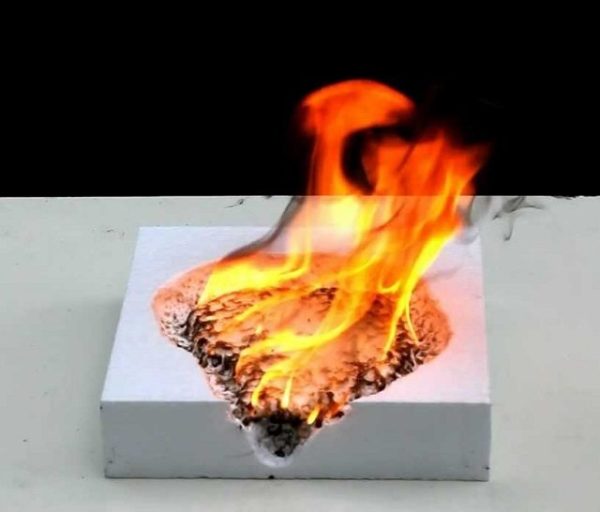

Simple PPS belongs to the G4 flammability class according to GOST 30244-94, moreover, this material releases a lot of toxic substances during combustion, such as hydrogen bromide and hydrogen cyanide. However combustible material does not have approval certificates for use in construction work.
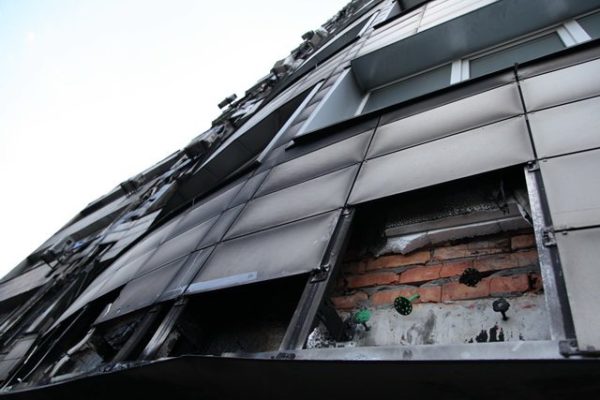

According to the new GOST 15588-2014, expanded polystyrene modified with flame retardants is allowed for work in construction, which, if installed correctly, does not pose a fire hazard. This material has a flammability class G1, that is, it does not support combustion. Russian manufacturers often add the letter "C" to the name, which means "self-extinguishing", for example, PSB-S.

From the foregoing, we can conclude that rumors about the fire hazard of polystyrene foam are justified only when it comes to the use of low-quality goods, which are flammable materials. It is also important to comply with the technology of work and safety rules. Properly mounted EPS class G1 does not pose a danger.
Resistance to biological corrosion
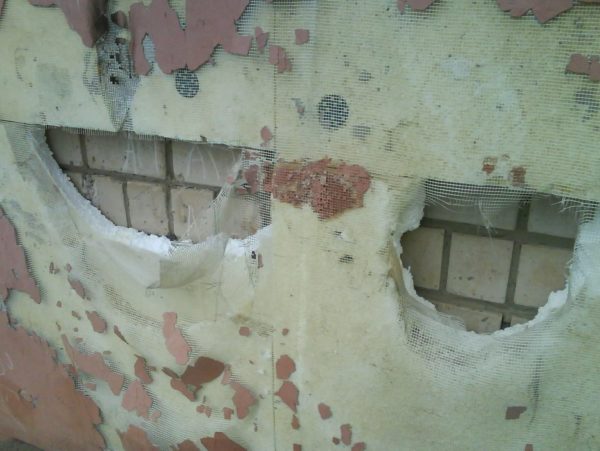

The biological stability of expanded polystyrene is also often questioned. This is due to numerous consumer complaints that mice eat insulation. More precisely, they do not eat, but use it to build nests.
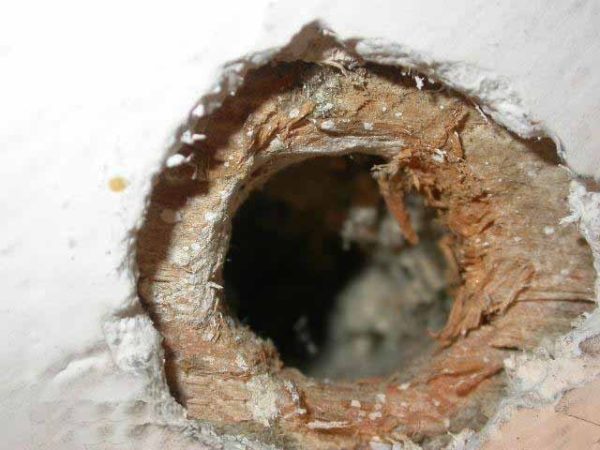

Most often, such complaints come from those who install the insulation with their own hands, not observing the technology of work.
In order not to go into endless debate, I will give the results of studies conducted, including on house mice, field mice and rats:
- Polystyrene (the main component of PPS) does not provide any nutritional value to living organisms, including bacteria, mosses, fungi, insects and rodents. At the same time, there is evidence that mold fungi and bacteria are able to settle on the surface of the plates;
- Rodents can gnaw through EPS slabs when they become an obstacle on the way to food or water, and also when they interfere with other natural needs of animals. However, under such conditions, rodents react similarly to any other material;
- Given free choice, mice and rats only affect PPS if they have nowhere else to find material for nest building, bedding, or tooth grinding;
- If other nesting material, such as paper, burlap, or cotton, is available, mice choose PPS last;
- Extruded PPS is much less likely to be spoiled by mice and rats than polystyrene.

Expanded polystyrene has a high biological stability. If the installation instructions for the plates are followed, then neither rodents, nor mold, nor bacteria are afraid of them. The increased love of mice for polystyrene is nothing more than a myth.
Advantages and disadvantages of teaching staff
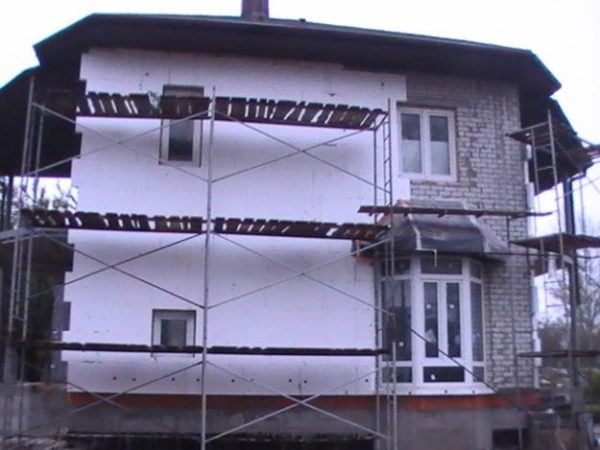

The advantages of PPS boards include their following qualities:
- Excellent indicators of heat transfer resistance;
- A light weight;
- Simple and convenient installation;
- The ability to cover the plates with plasters and putties;
- High strength EPS;
- Relatively low price;
- Durability;
- Resistance to biological corrosion;
- Moisture resistance, low absorbency;
- Environmental Safety.
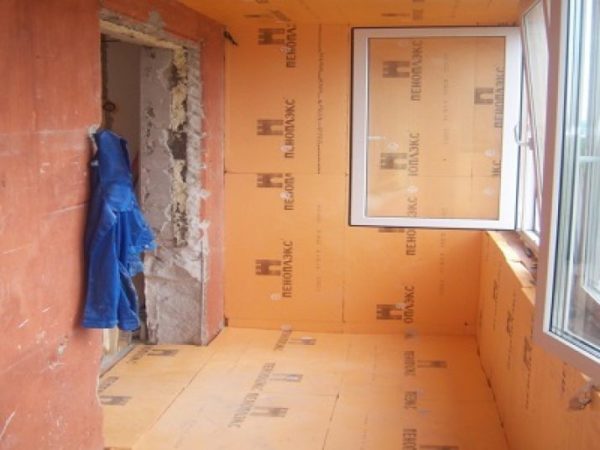
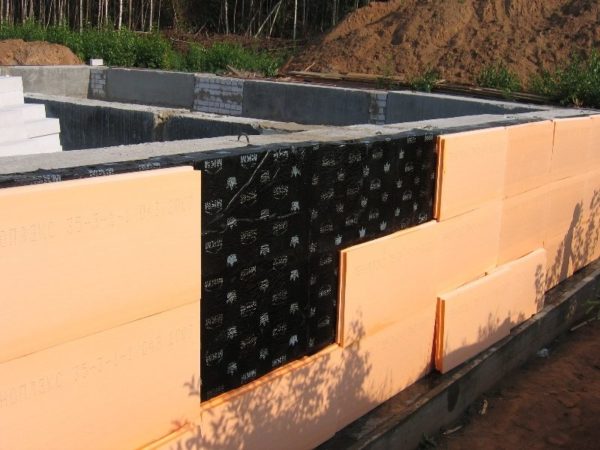


Among the disadvantages are the following features of expanded polystyrene plates:
- Fire hazard when using untreated PPS;
- Low vapor permeability, the need for increased ventilation;
- Possibility of damage by rodents;
- Low resistance to organic solvents;
- Destruction of polystyrene at temperatures above 160 ° C with the release of styrene.
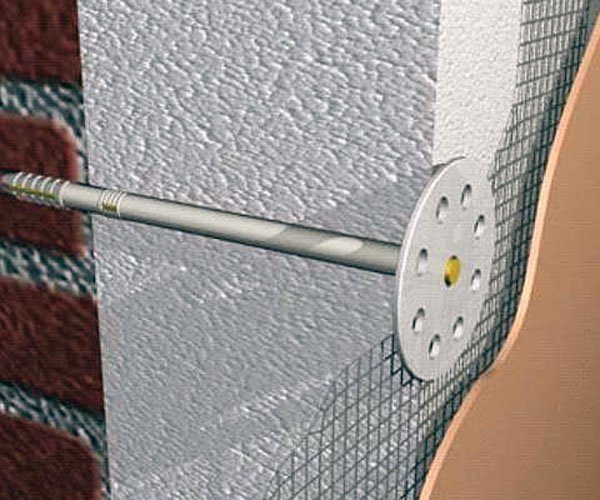


Like any other material, PPS has a number of advantages and disadvantages. It is an excellent heater that is easy and pleasant to work with, it is available in most regions of the country and is very effective as a thermal insulation of building structures.
Conclusion
Now you know about all the characteristics and features of polystyrene foam boards. Moreover, you will no longer take a word, listen to fables and myths. And do not forget to watch the video in this article, where you will find a lot of interesting thematic information.
Did the article help you?
