This article is about roof heating. We will find out why the corresponding systems are needed and how they are arranged.
In addition, we have to find out exactly where the elements of heating systems are mounted and what values of thermal power can be based on when designing them.

Why is it needed
One of the usual attributes of the winter and spring urban landscape is massive icicles hanging from the edge of the roof and from gutters. Where do they come from?
There are two reasons for their appearance:
- Thaws and off-seasons are characterized by diurnal fluctuations in air temperature near zero.During the day in the sun, the snow melts intensively, at night it freezes.
- For the so-called "warm" roofs are characterized by melting snow even at low (down to -10C) temperatures. The reason for excessive heating of the roof is heat leakage from the attic or attic under it.
Actually, it is with the icing of the roof that all heating systems are designed to fight: they melt the ice and provide an unhindered outflow of melt water.
What's wrong with ice on the roof?
- The most obvious consequence of icing is the danger of falling icicles and ice growths. The fall of a piece of ice with sharp edges from a height of fifteen to twenty meters can, you know, do a lot of trouble.
- Frozen drains often break under the weight of the ice. This is not only dangerous for passers-by: the restoration of gutters costs quite a lot of money.

Please note: the removal of a large mass of snow from the roof can also damage the horizontal section of the drain.
To solve this problem, snow retainers are mounted on roof slopes - artificial obstacles installed across the slope.
- Ice plugs in drains prevent water from draining, which as a result flows under the roof elements laid with a slope.
- Finally, as you know, water expands when it solidifies.. When this happens in the pores and cracks of a soft roof, between elements of a tile, slate or metal coating, the result is predictable: sooner or later we will get a leak.
The obvious solution is to periodically clean the roofs. The solution, however, is not perfect: working at height when the roof is iced is extremely dangerous, and the roof itself is quite easy to damage.
The device of heating systems
Despite the initiative once put forward by the mayor of St. Petersburg to cut off the ice growths with a laser, this idea did not take root. It has confirmed its right to exist by many years of practice using a much simpler scheme to implement - laying a hermetically insulated heating cable in all problem areas.
The electric current flowing through a conductor with high resistance provides heating of the shell - weak, absolutely safe for any roofs, including roofing felt, but sufficient for melting ice and snow.
Stacking zones
Where are roof heating systems installed?
- Along the edge of the roof. The heating cable prevents ice growths from forming on it: they turn into water and are harmlessly removed through gutters. The heating element can be laid in one line along the edge or in a snake.
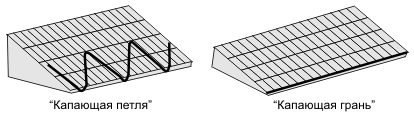
Useful: the cable laid at the edge of the slope is often protected from accidental damage and debris with galvanized steel sheet and other roofing materials with a sufficiently high thermal conductivity. The solution is quite rational, but part of the power is wasted.
- 22222222 The drains themselves, of course, also need heating - both horizontal and vertical sections. Otherwise, gradually freezing water will quickly narrow their clearance to zero.
- Another problematic place is the valleys (inner corners between adjacent slopes). And there, ice growths that are dangerous for the condition of the roof are often formed.

Cable types
If the principle of operation is the same for all heating cables, then in details their device can differ quite noticeably.
Resistive
This implementation is the simplest: one or two conductive cores are protected by insulation - that's the whole device.
Resistive heating cable is quite cheap; however, when buying it, it is worth considering a few nuances.
- The two-core cable has a fixed length and is selected according to the required electrical power. You can’t cut it: you will deprive the heating element of the jumper between the two cores, and it will not be easy to restore it while maintaining tightness.
- When the length of a single-core cable changes, its electrical resistance will also change, and after it, the current at a constant voltage and the degree of heating.
- The resistive cable heats with a constant power along the entire length. If it overlaps (for example, when a large amount of snow falls and the fastening is damaged), it may burn out.
Self-adjusting
This type of heater is noticeably more expensive; however, their qualities more than make up for the difference in cost. How is a self-regulating cable made?
Inside the hermetic braid, two current-carrying wires are separated along their entire length by an insert made of a mixture of a polymer with a high thermal expansion coefficient and coal dust.
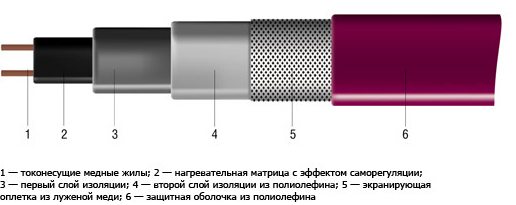
When heated, the insert expands; at the same time, due to an increase in the distance between the particles of conductive coal, its resistance increases, and the current flowing through it decreases. Following it, the thermal power of this section also decreases. On cooling, the process is inverted.
What do we get thanks to such a device?
- Profitability. The cable heats up more where it's cold. Warm areas significantly reduce power consumption.
- Fault tolerance.With an overlap or just good thermal insulation, the cable section will simply stop heating up.
Specific power
What values of electrical power should be guided by?
- For a roof surface with good thermal insulation, a power of 250-350 W / m2 is sufficient.
- For a “warm” roof, the specific power rises to 400 W / m2: much more ice is formed on it.
- For roof gutters with good thermal insulation, the need for thermal power is 30-40 watts per linear meter.
- “Warm” roofs have more values: 40-50 watts for plastic gutters and 50-70 for metal ones.

Please note: do not be afraid of excessive power consumption. Roof heating works on average no more than three weeks per year. When using self-regulating cable and thermal control systems, the average power consumption is much lower than the nominal one.
Conclusion
We will assume that our acquaintance with an unusual heating system took place. The video in this article will offer you additional information on this topic. Good luck!
Did the article help you?
