
It is believed that a roofing aerator is able to give a second life to a soft roof. Let's try to figure out if this is the case.
One of the most popular in industrial and civil construction is a soft roof. Traditionally, such a roof consists of several layers that form roofing cake.
It includes a load-bearing reinforced concrete slab, on which a vapor barrier is applied, insulation, a screed made of a cement-sand mortar, and a waterproofing carpet, for which roll materials are most often used.
The service life of a soft roof depends on the quality of thermal and waterproofing, as well as on how well the roofing.
Experts have found that the most common defect observed during the operation of this roof is the accumulation of a large amount of moisture in the screed and insulation.
Let's look at the consequences that occur with increased moisture content.
- Bloating. This is one of the most common flat roof defects that can result from two factors:
- in the summer, the soft roof is heated, as a result of which bitumen-polymer materials become plastic, since their physical characteristics depend on temperature, and now the adhesion force does not depend on adhesion, but on the viscosity of the mastic;
- usually Finnish soft roof consists of a waterproofing mat located at the top and a vapor barrier layer at the bottom. The water contained in the under-roof space becomes vaporous when heated, thereby creating an increase in excess internal pressure;
- As a result, blisters appear, which are the result of the delamination of the bitumen-polymer cover mass and the resolution of the roofing carpet. In this case, the aerator can be very useful, in contrast to the continuous high-quality gluing of a waterproofing carpet to the base.
- Increase in thermal conductivity. Due to the moisture accumulated under the waterproofing, the thermal insulation properties deteriorate. It has long been known that when moistened by 1-2 percent, thermal conductivity increases by 30-40 percent. This means that heating costs a lot. Waterlogging can not only increase heat loss, but also promote mold growth.
- Destruction of the waterproofing carpet and screed.Most often, cement-sand mortars are used for leveling screed, which are capillary-porous materials. In such materials, the pores are interconnected and filled with air. As a result of moisture ingress, no matter what happens if there is an aerator for the roof, the pores are partially filled with water. With a decrease in air temperature, the water contained in the pores begins to crystallize and increase in volume. As a result, a huge crystallization pressure is created, which causes the appearance of microcracks and the destruction of the leveling screed. The same process occurs in the waterproofing layer.
Where does moisture come from?
Tip! Before choosing aerators for the roof, you need to understand where does moisture come from? In fact, the insulation can be moistened from the environment, when moisture penetration is due to defects in the roofing carpet, and from the inside of the structure through damage to the vapor barrier layer.
Also, the presence of moisture may be due to climatic conditions that cannot be influenced.
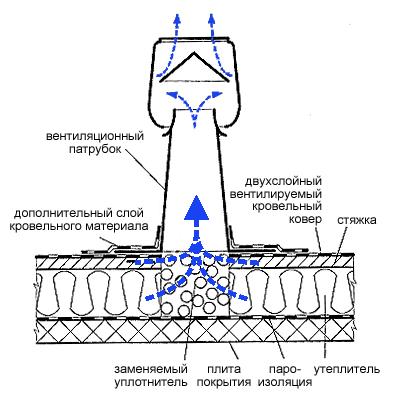
In the event that the thermal insulation layer contains moisture above the norm, then eliminating the flow of water through the roofing carpet and areas of intense moisture without drying will not lead to the desired result.
In this case, it is necessary to carry out repairs of the roof with a complete disassembly and replacement of the insulation. It is worth noting that this is a very expensive process, and not everyone can afford it.
True, excess moisture contained in the roof, as well as the resulting condensate, can be removed by evaporation and costly work to replace the waterproofing carpet and insulation can be avoided.
In addition, drainage will help to avoid leaks that will inevitably appear as a result of repair work.
To your attention! Drainage of a heater happens at the expense of the device of ventilating aerators. Roof aerators operate on the principle of using the difference between internal and external pressure, as well as by creating draft in the aerator pipe, which occurs as a result of low pressure generated by external wind currents.
Aerators are designed for:
-
- The conclusion of the water vapor rising to the roof of the interior before it has time to harm the structure.
- Reducing the pressure that appears in the roof structure and causes the formation of bubbles on the roof.
- Prevention of condensation on the lower layer of waterproofing, which flows into the thermal insulation layer.
The roof aerator is represented by a pipe with a diameter of 6.3-11.1 cm, which is covered with umbrellas on top so that atmospheric precipitation does not get into it. Most often, aerators are made of low-density polyethylene.
How to install a roof aerator?
- In the place where the ventilation pipe will be installed, a window is cut out in the screed and roofing carpet. The window should reach the heater.
- If there is a wet insulation in this place, then it must be replaced with a dry one, which will have the required thermal conductivity.
- Next, on the lower base of the pipe, you need to apply mastic, which is designed to attach the aerator to the roof. Self-tapping screws are also used for fastening to the screed. Six self-tapping screws should be evenly distributed around the circumference of the aerator skirt.
- From above it is necessary to make an additional waterproofing layer on the basis of the ventilation pipe.
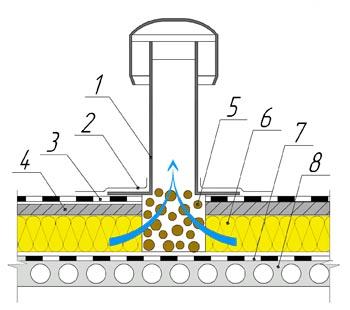
2. additional layer of roofing material;
3. main roofing carpet;
4. coupler;
5. replaceable insulation;
6. insulation;
7. vapor barrier;
8. coating plate;
The need for ventilation depends on the size and shape of the roof, the condition of the vapor barrier and the humidity of the indoor air.
If the structure has a flat roof with a simple configuration and other normal conditions, then it is advisable to install aerators at the rate of: one aerator for every 100 sq.m.
At the same time, it must be remembered that the distance between the aerators should be no more than 12 meters. In the event that there is a pronounced valley and ridge on the roof, then aerators should be installed on the watershed in the valley and along the ridge.
For buildings where high humidity is observed (for example, laundries, baths, saunas and swimming pools), design organizations must calculate ventilation.
You can install a roof aerator on your own, without resorting to outside help, of course, only if you have previously encountered construction work. In the event that this craft is new to you, then it is better not to experiment.
Did the article help you?
