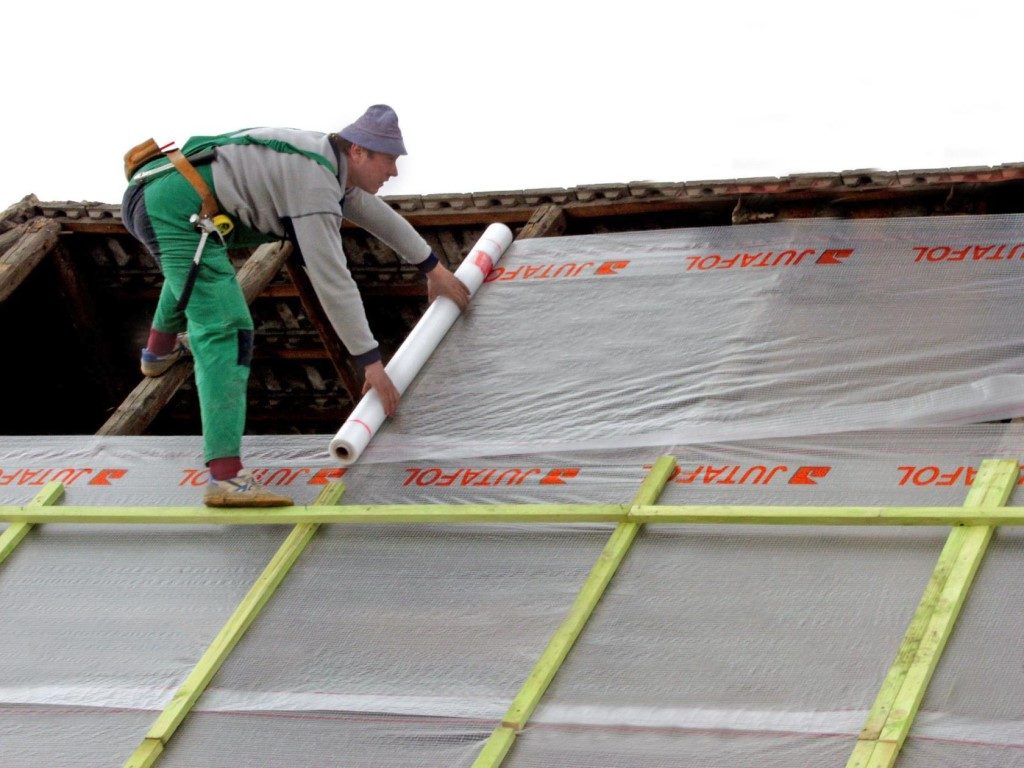
How is the gable roof truss system arranged? What types does it happen and how to make it yourself so as not to involve specialists? I've thought about this before. Now, having gained experience in this matter, I will accurately convey the technical aspects of its construction.

Features of the truss system
Device
A gable (gable) roof is formed by two inclined surfaces (slopes) that have a rectangular shape. The basis of the roof is the frame, which is called the truss system.
First of all, let's figure out what parts the gable roof truss system consists of, and how it works.
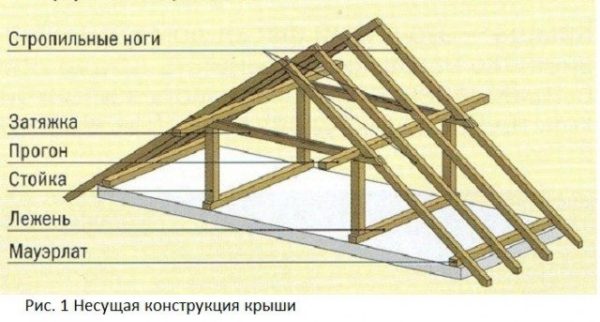
The design includes the following elements:
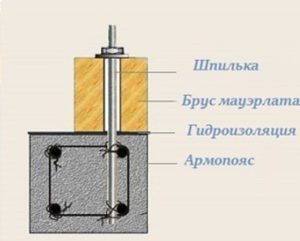
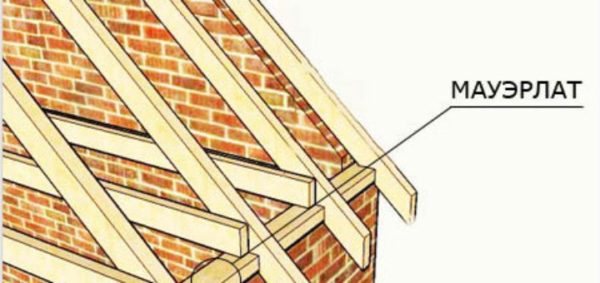
- Mauerlat. Serves as the basis for the structure. The task of the Mauerlat is to evenly transfer the load from the roof to the walls of the house.
In addition, it performs another important function - it provides fastening of the entire roof to the walls. As a rule, a mauerlat for a gable roof is made from a bar with a section of at least 100x100, which is attached to the walls along the perimeter of the building;
The Mauerlat is fastened to the walls using anchors or rods (studs);
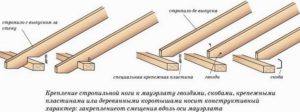
- Rafter leg or just a rafter. This, one might say, is the main element that forms the roof frame.
Rafter legs are installed in pairs opposite each other and form a triangle. As a rule, they are made from a bar with a section of 50x150 or 100x150 mm.
A pair of rafters is called a truss truss. This roof element ensures uniform transfer of loads arising from the weight of the roof, wind and precipitation to the Mauerlat;
- Skate ride. This detail serves as the top of a gable roof, however, in some cases, the tops form rafters, and the ridge run is installed under them.
In any case, this part is a beam that connects the individual roof trusses into a single structure.
I must say that in addition to the ridge run, sometimes farms are connected with ordinary runs, i.e.beams that are located on the plane of the slopes, as shown in the diagram above.
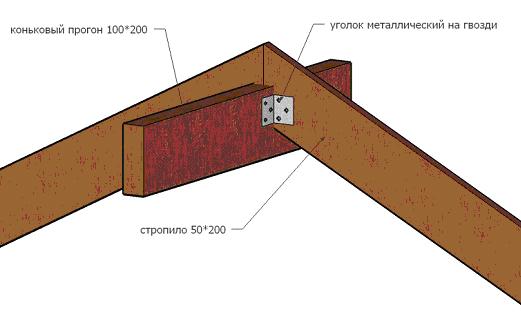
- Racks. Vertical structural elements that transfer the load from the rafters to the internal walls;
- Sill. It is a beam that evenly distributes the load from the racks to the internal walls;
- Puff. A detail that connects the rafters in their lower part, forming a triangle;
- Upper tightening (bolt). Connects the rafters at the top;
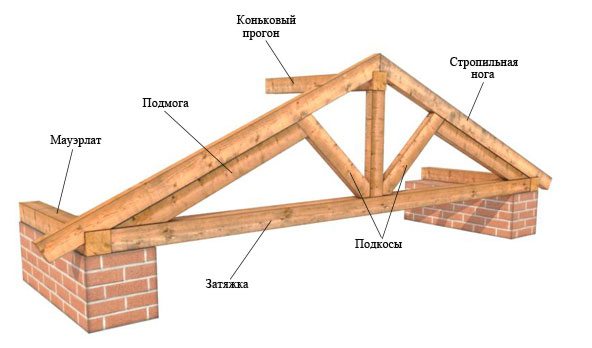
- Strut. Truss element that gives it rigidity. The struts transfer the load from the rafter legs to the puff or lying down;
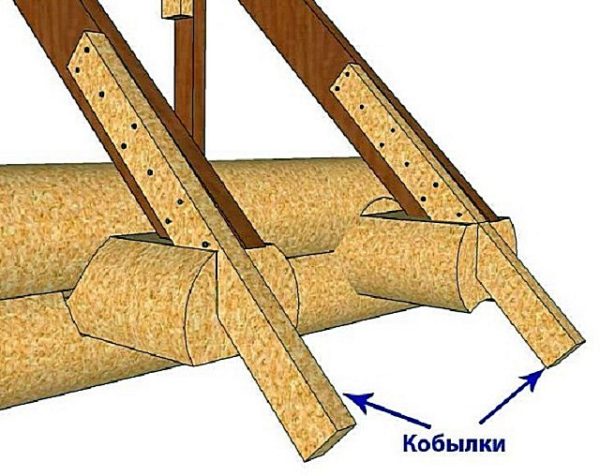
- Filly. They serve as a continuation of the rafter legs outside the walls, forming a roof overhang;
- Crate. Boards that are mounted parallel to the ridge run and connect the roof trusses. The crate serves as the basis for the installation of roofing material.
The step of the lathing depends on the type of roofing.
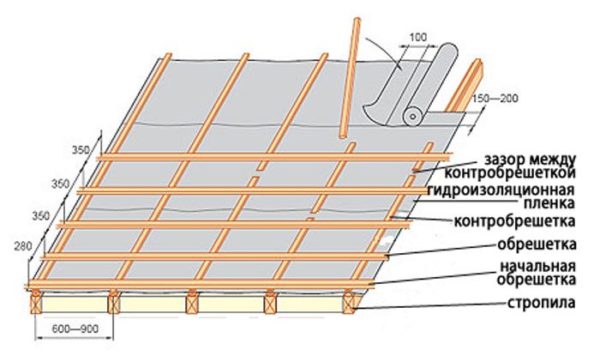
Some materials, such as bituminous shingles, require continuous battens. In this case, the boards are mounted close to each other, or the sheathing is carried out with sheet materials such as plywood or OSB.

I must say that the arrangement of the gable roof truss system may vary. We will discuss the main options below.
Varieties of a gable truss system
Gable roofs are of two types:
- With hanging rafters. They are used in cases where the distance between the outer walls does not exceed 10 m, and there are no inner walls between them. The hanging rafters rest on the Mauerlat from below, and on top of each other.
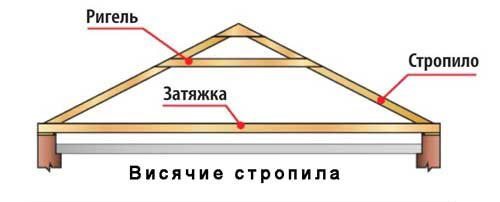
Thus, a truss with hanging rafters creates a bursting load, and transfers it to the walls. To reduce this load, puffs are used that tighten the rafter legs;
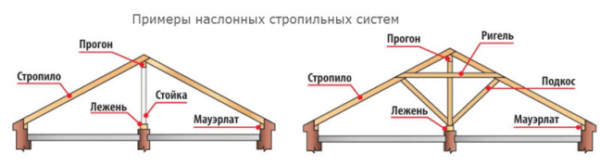
- With layered rafters. This design involves the use of racks and a bed (sometimes several beds), which transfer the load from the rafter legs to the internal walls of the house.
Such a design is justified if the outer walls are located at a distance of more than 10 meters and have inner walls.
If instead of internal walls the structure has columns, alternation of layered and hanging roof trusses is allowed. In addition, there is a combined option when the truss has racks, and the rafters are additionally reinforced with tightening.
The main nuances of the installation of the truss system
Installation of the truss system can be divided into four main stages:
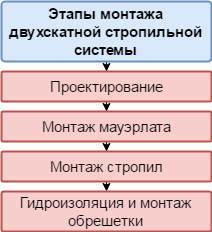
A few words about design
Roof design is to determine the most suitable design, and its further calculation. As for the design, it is selected individually in each case. I talked about the main nuances of the structures above, so we will further consider how to perform the calculation.
slope angle. The calculation begins with determining the angle of the roof slope. To choose the right angle, you need to consider the following requirements and recommendations:
- The gable roof must have a slope of more than 5 degrees;
- In regions with heavy rainfall, the slope angle should be at least 30-40 degrees, since when the slope angle decreases, the snow load increases;
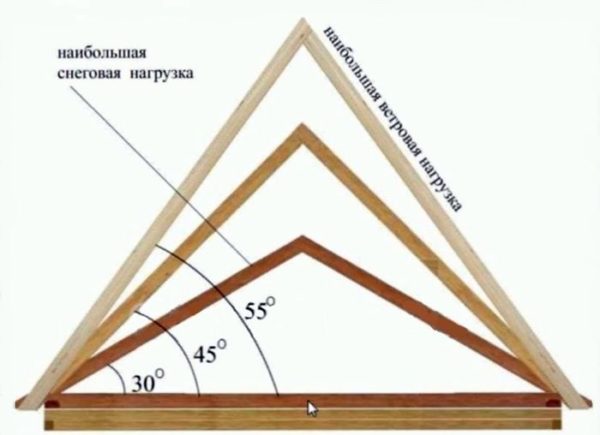
- Without special need, it is better not to make a big bias. The fact is that with an increase in the angle of inclination of the slopes, the windage also increases, i.e. wind load.
In addition, with an increase in the angle of inclination, the price of the roof increases, since the area of \u200b\u200bthe slopes increases and, accordingly, the amount of materials increases.
As for the calculation itself, this is a rather difficult task, to which a lot of construction literature is devoted. However, in our time, you can not delve into the formulas, but perform the calculation using the online calculator, which is also available on our portal.
In this case, you only need to enter the dimensions of the structure and indicate some of its features, after which the program will perform a quick calculation and give an accurate result indicating the amount of materials, their dimensions, installation steps, etc.
Mauerlat installation
The installation process of the Mauerlat is as follows:
If the house is wooden, i.e. made of timber or logs, then the gable roof truss system rests on the upper crown, which performs the function of a Mauerlat.
Assembling the truss system
The gable roof truss system can be assembled in different ways. Sometimes roof trusses are assembled on the ground, and then lifted and attached to the Mauerlat and ridge run.
If the building is large, the roof truss system is assembled "on the spot", i.e. on the walls. In my opinion, in this way it is more convenient to assemble not only large, but also small structures.
Therefore, further I will tell you how the installation of the roof is done on the spot with your own hands:
This completes the installation of a gable roof with your own hands. I must say that depending on the type of construction, the order of work may vary somewhat, but in general the principle remains the same.
Conclusion
We got acquainted with the device of a gable roof and the main points of installation.Additionally, I recommend that you watch the video in this article. If any nuances are not clear, feel free to ask questions in the comments, and I will be happy to answer.
Did the article help you?