 The construction of the roof of the house occupies a special place in the process of the whole complex of works on the construction of the house, because. It is on the shape and reliability of floors and roofs that both the appearance and the service life of the building depend. In the framework of this article, we will analyze the private construction of the roof, its design features.
The construction of the roof of the house occupies a special place in the process of the whole complex of works on the construction of the house, because. It is on the shape and reliability of floors and roofs that both the appearance and the service life of the building depend. In the framework of this article, we will analyze the private construction of the roof, its design features.
Basically, roofs can be divided into two main types:
- Flat (slope angle less than 10 degrees, flat solid surface).
- Pitched (slope of 10 or more degrees, one or more slopes in various combinations).
Flat roof

This type of roof is found in private construction much less often than pitched options, since the plane implies a high resistance to vertical loads, which are precipitation (snow) and the placement of additional objects on the roof.
This flat roof is convenient, which allows you to master its surface area for various purposes.
The floors are usually concrete slabs. This is the most reliable option. If the roof configuration is intricate, then either pre-prepared forms with reinforcement are poured with concrete, or a wooden frame is built.
Concrete slabs must be laid very precisely on the edges of the walls, joining each other as tightly as possible. All gaps and cracks are sealed with bituminous mastic.
Then a heater is laid, several layers of waterproofing and a reconciliation of the front layer, protected from adverse external influences.
Advice: any roof has an angle of inclination, even a minimal one, which ensures the precipitation.
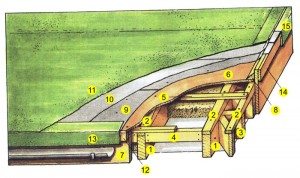
A wooden frame for a flat roof is a rather complicated construction, and should only be carried out by professionals (however, like any other).
The figure shows how difficult it is to properly arrange such a structure. 1-transverse beams, 2-battens, 3-bar, 4-spacers, 5-battens, 6-leveling layer, 7-drain board, 8-glazing bead, 9-first roof layer, 10-second roof layer, 11- final layer, 12-curb rail, 13-soft cornice overhang, 14-pediment overhang, 15-gable overhang drain.
Again, such a roof requires design taking into account critical loads, material selection, its dimensions, etc. Invite a professional.
pitched roof
The construction of pitched roofs is also divided into:
- Attic roof.In this option, there is a technical room, an attic, between the roof and the living space.
- Bare roof. Here, the roof slabs serve simultaneously as the ceiling of the upper living space.
Before planning the shape of the roof and the angles of inclination, the construction of the roof must take into account the following factors:
- The maximum thickness of the snow cover. The greater the angle of inclination of the roof, the less snow accumulates on it. For example, in the southern latitudes (Ukraine, the Caucasus), snow weighs 80-120 kg per square meter, and in the northern latitudes - up to 250 kg per meter. The difference is obvious, so the architecture is different.
- Roof material. Directly depends on the angle of the roof. Plus, different materials have different weights, which also needs to be taken into account.
Roof forms
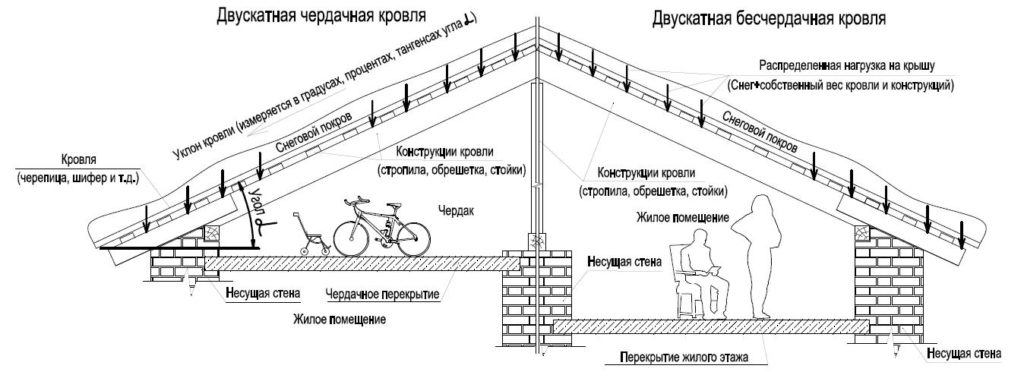
Let's take a closer look:
- Shed roof is the simplest roof construction. Precipitation flows in one direction, everything is simple and reliable, although the view of such a roof is not presentable, therefore, a shed roof is more common in sheds and other non-residential buildings.
- The gable roof is the most common form. Simple, reliable, beautiful, tasteful.
- A four-pitched (hip, half-hip) roof is also a very popular view, especially in villages and summer cottages.
- The attic form allows you to arrange an almost full-fledged residential floor, while maintaining the main residential volume.
- Tent form. All four slopes converge at one point. Applicable to square structures.
- The spire-shaped form is found on the roofs in the form of "bells and whistles". Weathercocks, cockerels and other decorative elements are placed on such spiers.
Roof structure
The design is influenced by such factors as:
- The span to be covered.The larger it is, the more powerful the rafters are needed, and the smaller the step between the rafter legs.
- Roof slope. The greater the degree of slope, the lighter the roof can be. If the angle is more than 50 degrees, then the snow will not be able to accumulate on the roof surface, but will go down. If the angle is 20-30 degrees, then snow can accumulate, putting additional pressure on the floors, which means that the dimensions of the rafter beams must be chosen large.
- Lifetime. The material can be selected depending on the expected service life of the entire building. Without a major overhaul, a wooden roof will last 30 years, metal or reinforced concrete - 50 years. Although in favorable conditions, many roofs serve more than one hundred years.
- fire resistance requirements. The wider the beams, the longer they are able to withstand the action of fire. But they are also more expensive.
- Thermal characteristics. The warmer the roof needs to be, the thicker the insulation layer will be laid, the more weight the structure will acquire, the more expensive it will cost.
Building a roof
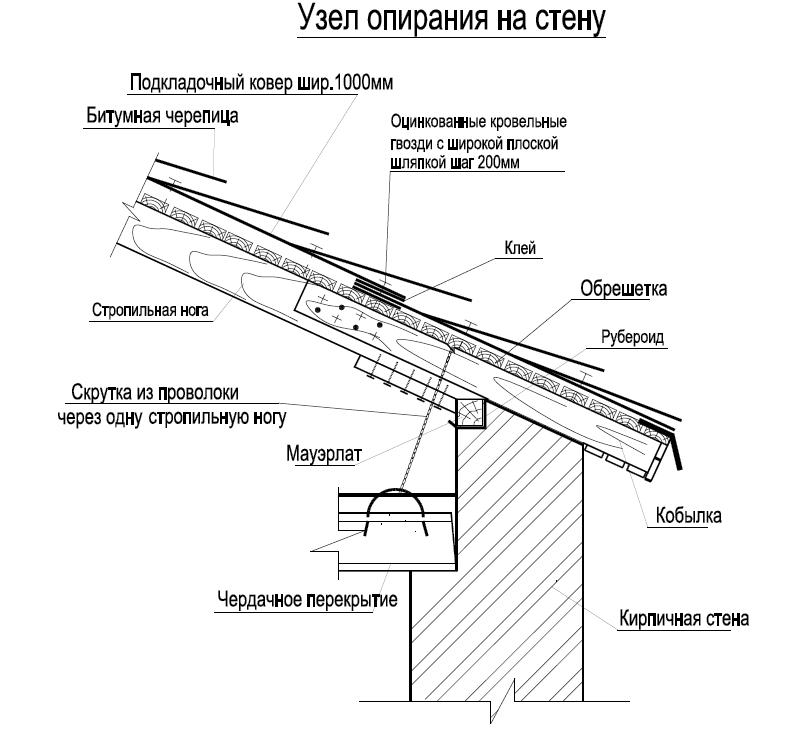
The construction of houses and sketches of roofs include the following elements:
- Rafters (layered, hanging, trusses). It is the rafter legs that take on the main load.
- Mauerlat. A beam lying along the perimeter of the roof, on which the rafter legs rest.
- Racks. Wooden auxiliary support beams.
- Stretch marks. Horizontal beams that prevent the roof from "parting".
- Crate. The basis for laying the roof on it.
Laminated rafters are the most common, because. easily realizable. The rafters rest at one end on the wall, the other on the rack.

Do-it-yourself roof rafters set depending on the load in increments of 0.6 m to 2 m. For them, they take a beam of 150x200 mm, or they are made up of thick boards from 50 mm thick. Be sure to fasten the roof frame with wire ties to the walls of the house so that a strong gust of wind does not dislodge it.
Hanging rafters are used where there are no intermediate supports, only external walls. This design is effective if the width of the house is not more than 8 meters. Otherwise, it is recommended to install supports.
Tip: the lower the ties are placed, the more effective they are. The higher, the more powerful slats will be needed for this.
Farms are used in cases where it is necessary to block large rooms that do not have supports inside. This regular roof rafter used in such premises as storages, hangars, halls, etc.
It is popular to use farms in cases of major repairs or complete reconstruction of roofs that have served their time completely. Trusses simply replace the old roof, taking on the bearing load.
You can also often find metal roof frame structures. They are used for large and wide spans, as well as in non-residential construction.
At the end of the article, we suggest watching a video clip demonstrating the construction of a wooden frame roof of a house.
Did the article help you?
