This article will talk about what a filly is - a roof using it has cornice overhangs closed with boxes, which are lengthened with the help of a filly, as well as how exactly the cornices are closed.
The filly is a piece of board used to lengthen the rafter leg, used in the arrangement of the roof overhang. It is used in cases where the length of the boards used to make the rafters is insufficient. The overhang of the roof is designed to divert water from the walls and prevent them from getting wet by melt and rain water that flows onto them from the roof.

If such a roof is being erected, the fillies are mounted with an indent from the wall of at least 40 centimeters. The board used for their manufacture must have a smaller width than the board from which the rafters are made.
So, in the manufacture of rafters from boards with a section of 150x50 mm, a board is taken for the manufacture of fillies, the section of which is 100x50 mm, etc.
The use of fillies in the process of installing the rafter system allows you to:
- Use wood of shorter length in its manufacture;
- Both the lifting of the rafters and their installation on the Mauerlat are facilitated by reducing the weight of the rafter structure;
- Drawing the line of the cornice overhang is much easier when using light short fillies than using rafter legs;
- In case of damage or decay of the filly, it can be painlessly replaced without dismantling the entire roof.
Filly can be made using decorative carvings, which allows you to further decorate the house and give it an original look.
Installation of cornice overhangs without the use of filly
The implementation of a box or wooden frame under the eaves allows you to close or ennoble various boards protruding beyond the eaves, such as rafters and crate. The method of filing various elements of the cornice depends on the type of box made.
The simplest and most effective method of manufacturing a box is to mount a frame from a frontal (wind) bar and hemmed rails placed on the lower (inner) part of the rafters.
When using this method, the ends of the rafters can be cut both plumb, when their end is parallel to the wall, and perpendicular to the rafter axis, depending on the tastes of the developer.
Let us consider in more detail the option with parallel cutting of the ends of the rafters:
- To perform the work, you will need scaffolding, as well as a retractable ladder. Fastening will be done using a screwdriver and wood screws.
- First of all, the wind board is fastened, then the external hemmed, and, finally, the internal (wall). The cross section of all boards is 150x20 mm.
- For the manufacture of the box, untwisted even boards should be selected, on which there should not be bark and knots in large quantities. If it is planned to manufacture a box as a "hem", without using finishing materials, calibrated dry boards with a section of 50x20 mm should be used during work.
- After closing the front crate and rafters, the box is treated with special protective solutions. Optionally, you can also cover it with stain, as well as varnish, which will allow the hemming to last a long time and effectively.
Useful: a fairly high quality coating can be achieved by using a rather expensive, but effective ship varnish.
- To close the box, either light gray or white C10 corrugated board, or vinyl siding, which is lightweight and easy to install, is most often used.
- Hemming of parts of the eaves can also be carried out using a special material - soffits, which are perforated plates made of plastic or aluminum.
Their rather high cost is offset by high functionality and attractive appearance.
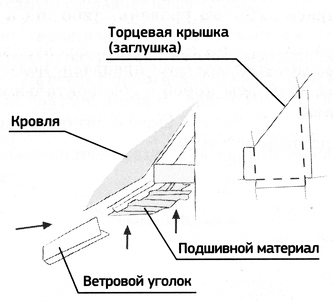
- Regardless of the material used for hemming the cornice strips, to close the frontal (wind) side of the box, you will have to use external corners, the color of which matches the color of the box itself.. The size of the corners is 50 mm, the edging must fit the size of the width of the wind part.
- To ennoble the sides, hand-cut covers are used from smooth sheets, the shape of which is selected in accordance with the shape of the end part of the box.
- The process of performing frontal hemming is much simpler. Two boards with a section of 150x20 mm are attached to the protruding crate, after which they are sewn up with a suitable material.
Installation of a cornice using filly

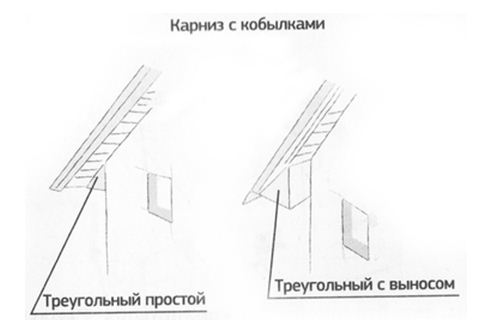
Hemming cornices using horizontal fillies is a more complex and time-consuming method.
Mares are boards with a section of 100x30 or 150x30 mm, or trimmings of rafters attached to the rafters so that their wide planes are perpendicular to the wall.
Important: when installing fillies, you should be guided either by brickwork or by level.
After the filly is installed, hemmed boards are attached to them, as a result of which a box is obtained, the lower plane of which is located horizontally. Further, the box can be decorated depending on tastes and overall style. house roofs.
When installing the cornice, it should be understood that the roof must necessarily breathe, which means that warm air enters the under-eaves part, after which it, passing through the rafters, the crate and the roofing material, goes outside. This provides effective ventilation that dries out the roof, extending its life.
In this regard, sealing of any elements of the ridge or cornice should not be allowed. When performing them, silicone or polyurethane foam are not used, with the exception of pipes, otherwise the process of decay will begin in a few years roofs.
There are several varieties of hemmed cornices with fillies. The simplest way is the usual triangular cornice, which, in addition to ease of installation, differs from other types of remote cornices in the absence of an unpleasant buzz during winter blizzards.
Consider the basic rules for its installation:
- The rafters should be cut flush with the outer walls, and the eaves should not hang over the wall. In the case of hanging the cornice at the junction of the wall and the rafters, a cornice board is nailed, equipped with a drain.
- The eaves extension is formed by lengthening the rafters with fillies, which are nailed directly to the legs of the rafters. This method is very popular due to a number of advantages, for example, guaranteed protection of the under-eaves space from wind-blown raindrops. Filly should form a gap that ensures the penetration of sufficient air to ventilate the roof.
- The removal of the cornice on the filly is left open from the bottom or closed with the help of planed and jointed hemmed boards of equal width, the thickness of which does not exceed 25 mm (hemmed cornice). The under-roof space is closed with boards from below perpendicular to the wall. A gap should also be left between the wall and the boards for ventilation of the roof.
- Strengthening the eaves extension is carried out using consoles with anchors made of metal or reinforced concrete, embedded in the wall. The filly in these places should be flush with the console. This method of designing the cornice is used when the hemmed cornice is moved to a distance exceeding the allowable for a wooden filly.
- The execution of the brick overhang is carried out on the walls of stone, the upper part of which is lined with brick, observing a gradual allowance of rows by a value not exceeding a third of the length of the brick (80 millimeters). The width of the cornice brick overhang should not be more than half the thickness of the wall.
The service life of the roof largely depends on the quality of the cornice overhang, during the installation of which filly plays a rather significant role. An illiterately executed cornice can cause the roof and its thermal insulation layer to get wet.
Did the article help you?
