Are you interested in mansard roofs and their construction without the involvement of specialists? I am ready to tell you how a sloping corrugated roof was built in my house. We will touch upon the choice of material, the structure of the truss system and the methods of installation of the main components. Let's get started.

What it is
A broken or mansard roof is a gable roof with a break in each slope, dividing it into sections with a different slope. Roofing material can be absolutely anything.
Typically, a mansard roof pie includes a layer of thermal insulation; insulation, coupled with a heat source, turns a cold attic into a living space - an attic.
Choice problems
Device
What is attractive about a house with a sloping roof against the background of a building with a traditional gable or hip (with littered gables) roof?
The maximum usable attic area with a minimum ridge height. The low height of the roof structure means savings in material and, accordingly, the minimum construction budget.
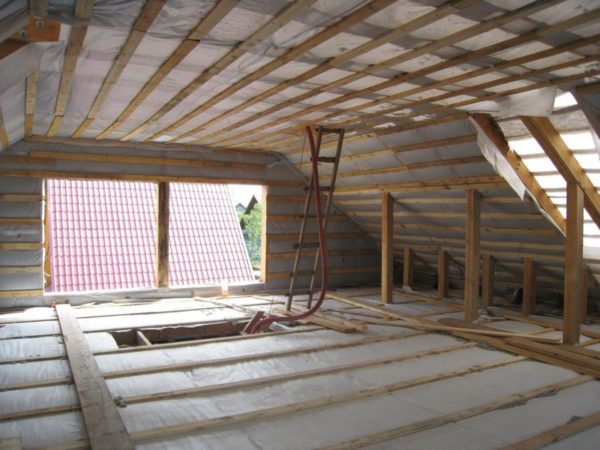

Roof
A few words about why I chose corrugated board. It attracts:
- Minimum price per square meter (at the beginning of 2017 - from 130 rubles for a galvanized sheet and from 150 rubles for a sheet with a polymer coating);
- Rigidity, which does not require the construction of a continuous crate. The step between the boards with a sheet thickness of 0.55 mm can be equal to 25-30 centimeters;

- Large leaf area and therefore - quick and easy installation;
Quick installation of the roof is attractive not only by saving time. In my case, the attic was erected over a fully finished residential floor, and the first rain with a missing roof would mean its flooding.
- Mechanical strength. This is important in light of the strong winter winds that are typical for Sevastopol, and sometimes large debris carried by the wind;
- Long service life (at least 30 years).
The profile sheet also has two disadvantages:
- Noise in the rain. It is really audible even through a layer of insulation, but does not interfere with life;
- Poor leak protection on overlaps perpendicular to the wave at small angles of roof slope. For a house with a sloping roof, it is irrelevant: the slope of the upper part of the slope is about 30 degrees to the horizon, the lower one is 60.
The structure of the truss system
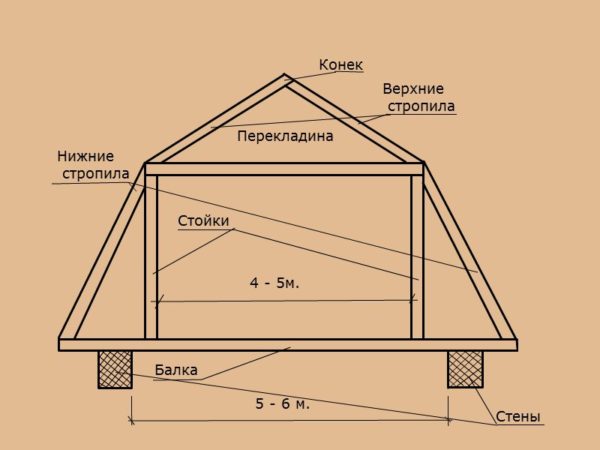
A few comments on the diagram:
- Racks always placed under the kink of the rafters and ensure their rigidity in relation to the side wind;
- Rigel (aka crossbar, or screed) can be shifted upward relative to the break. Its task is to pull the upper rafters together, providing resistance to snow load;
- Lower rafter legs they can rely both on floor beams and on a mauerlat (a beam laid on the main walls), on a monolithic or slab floor;
- Rafter section can be equal to 100x50 mm if the broken mansard roof has spans of no more than 3 meters. With a span of 3-4 meters, you need to use a bar 150x50 - 150x70 mm.
The entire rafter system of a sloping roof must be treated with an antiseptic. It will eliminate the decay of the tree and protect it from insects.
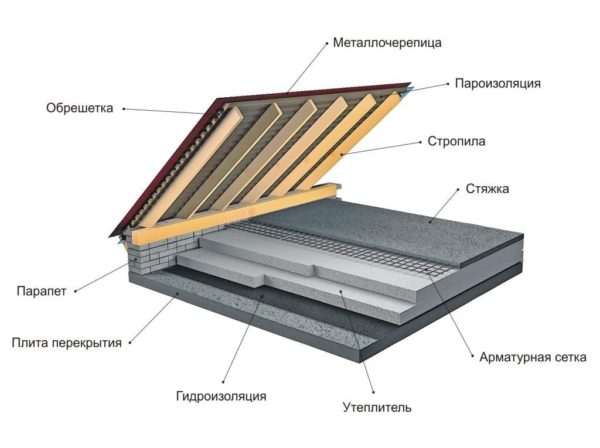
roofing pie
In my case, it has the following structure (bottom to top):
Connections
How to connect rafters with Mauerlat, crossbar and with each other?
My experience
In my case, the attic was built instead of a low cold attic on top of the slab. Here is how the main components of its design are arranged.
Mauerlat (lower harness): a beam measuring 100x50 mm is fixed with anchors to the floor surface. The second beam became a support for the racks and was laid directly under the break in the roof.

Lower rafter legs they are connected to the uprights with a common upper trim for them, on which the upper rafter legs rest.
Upper rafter legs are connected with studs to each other and to the crossbars. The upper legs and crossbar became the basis of the plasterboard suspended ceiling for interior decoration.

profiled sheet fixed to the crate with self-tapping screws with rubber press washers that ensure tightness. The ends of the overhangs above the gables are closed with U-shaped profiles. The lining of the overhangs is made with a profiled sheet.
drains: galvanized gutters laid along the junction of the lower roof slope to the walls of neighboring, higher houses (my house is a townhouse). Water is discharged into vertical drainpipes. The joints are sealed with bituminous mastic and silicone.

Daylight: each pediment is a panoramic window with an area of 13 squares. There are no windows in the roof: only the walls of neighboring houses would be visible through them.
Conclusion
I hope that my modest experience will help the reader in his own construction. To learn more about how a sloping roof works, the video attached to the article will help you. I look forward to your additions to it. Good luck, comrades!
Did the article help you?









