Recently, a flat roof has been increasingly used in private construction - its section is shown in the figure. This article discusses the main types of flat roofing, its construction and equipment for ventilation and drainage systems.
This is not just a constructive modern roof - a flat roof, which is widespread in recent times, also allows you to significantly increase the area available for operation. This type of roof, which has a rather small slope (from 2 to 5 °), can be used not only in the construction of residential buildings, but also to cover structures such as garages, terraces and various outbuildings.
Flat roofing materials manufactured using modern technologies provide a number of advantages:
- High reliability;
- Durability;
- Waterproof;
- Ease of installation;
- incombustibility;
- Serviceability, etc.
Flat roof construction elements are also highly reliable and durable.. When constructing a flat roof for a residential building, it is imperative to insulate it, otherwise, upon contact of the warm air coming from the premises and the cold surface of the roofing, condensation will form, appearing as spots on the ceiling.
In addition, moisture will accumulate in the structure, gradually destroying the roof.
Types, features and installation of flat roofs
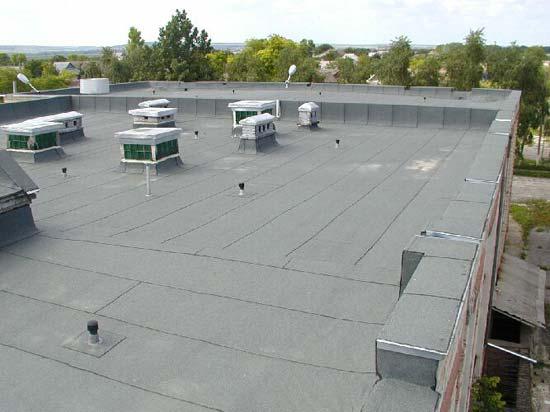

Flat roofs are divided into the following types:
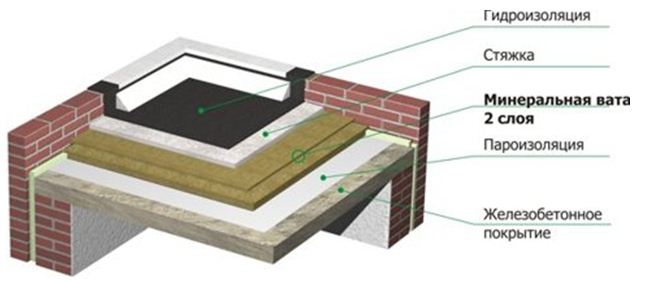
- Traditional, also called soft. Such a roof includes a carrier slab on which thermal insulation (usually in the form of mineral wool slabs) is laid over the vapor barrier layer.
The thermal insulation material is protected from precipitation by means of a waterproofing carpet, which is based on rolled bitumen-containing materials; - Inversion, which are a structurally improved version of traditional roofs;
- Operated, the base of which should be made rigid, which allows you to maintain the integrity of the waterproofing material.
As a base, a concrete screed can be used, providing the slope required for water flow, or corrugated board.
The insulation layer on such roofs experiences increased dynamic and static loads, respectively, it is necessary to choose a material with high compressive strength; - Unexploitedfor which the rigidity of the base for the installation of waterproofing and insulation is not required.
Access to a flat roof for its repair and maintenance is provided by building bridges or ladders that distribute loads evenly over the surface.
Such roofs of houses are cheaper, but also less durable than those in use.
The main advantages of a flat roof are:
- A slight slope significantly reduces the roof area, which reduces the cost of materials and roofing, as well as heating due to a smaller heat transfer area;
- Flat roof houses have additional usable areawhich can be used as a solarium, relaxation area, flower garden, small garden, etc.
The disadvantages of a flat roof include:
- The slightest mistake in the choice of material leads to the fact that the repair of a flat roof is required much earlier, and the overall life of the roof is reduced;
- During heavy snowfalls, a large amount of snow accumulates on the roof, which can cause leaks during the melting process.
In order for a flat roof to turn out to be as reliable and efficient as possible, it is first of all necessary to correctly develop and implement its design.
This requires:
- Choose the most reliable coverage;
- Buy quality building materials
- Attract to work performers with sufficient qualifications, capable of competently performing the installation of a flat roof.
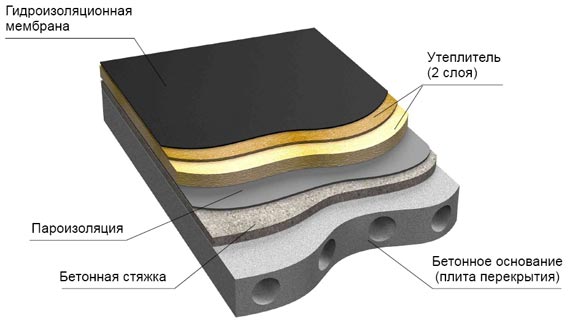
Traditional flat roofs include a base, on top of which a layer of vapor barrier is laid to protect the insulation from moisture penetrating from the premises.
The main nuances of building a flat roof are as follows:
- Vapor barrier is made in the form of a fiberglass-reinforced bitumen-polymer membrane or a vapor barrier film laid on top of the screed;
- Along the edges of the roof, the vapor barrier is wound vertically so that its height is greater than the height of the insulation, after which the seams are sealed;
- A heater is laid on top of the vapor barrier layer;
- A protective carpet made of waterproofing materials with a bituminous base is placed on top of the insulation.
Important: in the case of using expanded clay as an insulating material, a cement screed is made under it, on which the waterproofing carpet is laid in two layers.
When building a light roof, the design of which does not provide for loads, the waterproofing sheet is glued around the entire perimeter of the roof.
Ventilation

Traditional flat design roofs is not always reliable - a violation of the tightness of the vapor barrier layer leads to the penetration of moisture into the insulation.
A dense layer of waterproofing prevents its evaporation, as a result of which moisture accumulates in the insulation, reducing its thermal insulation performance and leading to the appearance of wet spots on the ceiling.
In addition, in winter, freezing water increases in volume, tearing off the waterproofing from the base. As a result of mechanical influences and temperature changes, cracks appear, leading to the leakage of the roof.
To avoid such problems, they make the so-called "breathing" roof.To do this, aerators are installed on it, which are devices made of plastic or metal pipes with umbrella caps.
Aerators are placed evenly throughout the roof at the highest points. Using the pressure difference created by air flows, aerators remove excess water vapor from the space under the roof, preventing the roof from bubbling and delamination of its coating.
Waterproofing

Waterproofing of flat roofs is usually carried out using membrane or polymer-bitumen materials, which are fused together with gas burners during installation. In addition, polymer-bitumen self-adhesive materials can be used for roofing.
Important: bituminous materials have a low lifespan and their use for roofing results in the need for repair and recoating every 3-4 years.
Most often, membrane synthetic materials are currently used, which have a number of advantages:
- High strength;
- fire safety;
- Resistance to aggressive environments, sunlight, natural and mechanical influences.
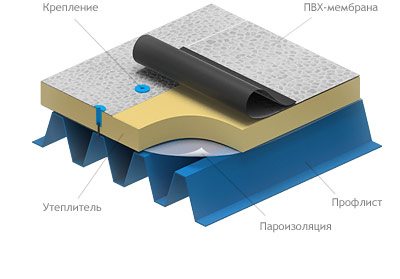
Such membranes are glued to the roof screed and lie freely on the base with a load in the form of ballast, or are attached by a complex method (mechanically, using glue).
Mechanical fastening is carried out by rolling the material over the flooring, gluing its sheets together, and subsequent fastening over the entire roof area. In this case, shrinkage and other movements of the building do not cause stress and damage to the web.
The low slope of a flat roof makes it easier to drain rainwater, but heavy rainfall can cause roof flooding.To avoid this, it is necessary to equip a drainage system, which can be unorganized or organized, including external and internal drainage systems.

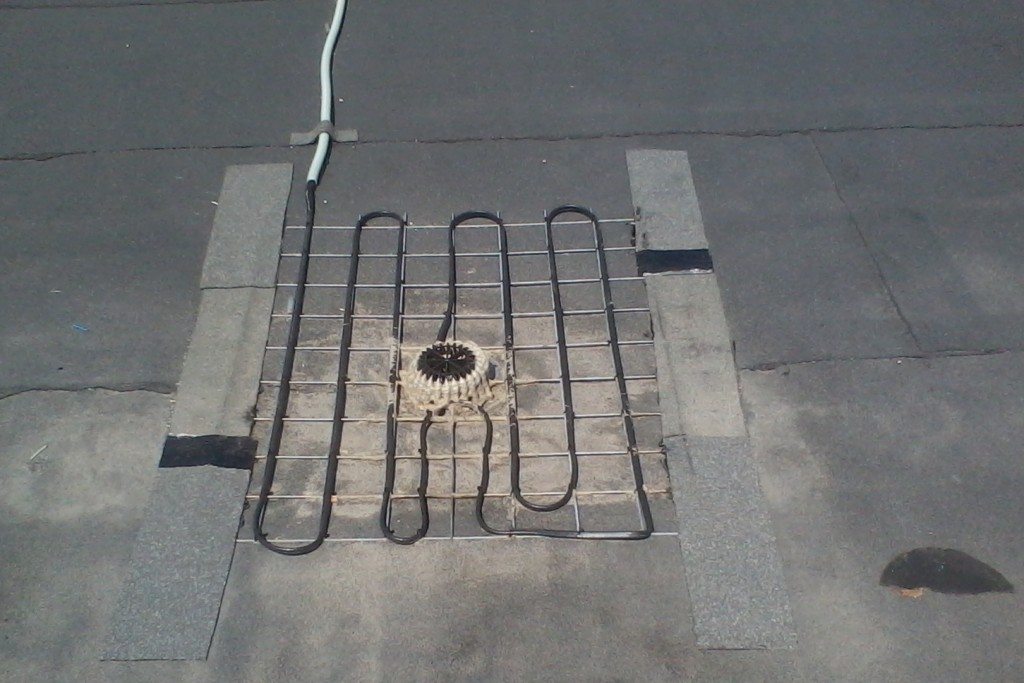
When organizing internal drainage, the roof surface is divided into zones so that 150-200 square meters fall on one riser; in the case of a smaller area, an additional riser is made. Funnels for a flat roof are placed at the slope points of the roof surface, also providing them with baskets for trapping debris.
Funnels are most often located in the center of the roof, and drain pipes are placed inside the building. To prevent freezing of water near the funnel around it, cable heating with an area of 1 square meter is performed.
That's all I wanted to talk about a flat roof. When choosing this type of roof during the construction of a country house, it is important to remember that its construction should be taken seriously so that it lasts a long time and effectively.
Did the article help you?
