A modern roof calculator is certainly a useful thing, it can save you many hours of and often obscure calculations. But no online calculator will give you a complete picture specifically for your roof, here you need to take into account a lot of specific parameters. All these subtleties will be discussed further.

The roof calculator will help you quickly calculate everything online. As for special software products, a good program is paid and rather complicated. While an online calculator you can simply bookmark and use as needed.
public data
Before you calculate the roof of the house, you need to decide which configuration of this roof suits you best.
A few words about popular types of roofs
It is better for amateurs not to take on the calculation of hip, semi-hip, tent and other structures that are complex in engineering terms, in this case the roof calculator will give only approximate parameters, you can only purchase material from them.
Terminology
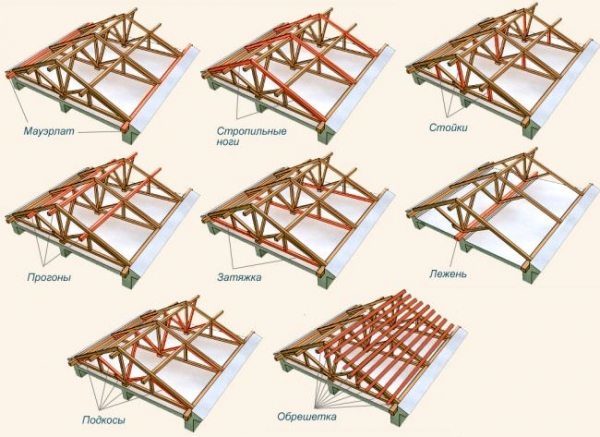
To calculate the roof in the interface of any online calculator, you need to enter the initial data, and for this you need to at least know the names of the main components and parts.
- rafters - load-bearing wooden beams on which the roofing cake is laid. The minimum section of the rafter leg is 50x150 mm. In the store you can buy a beam up to 6 m long, if you need more, then the beams will have to be increased. By the way, the price of rafter timber is the highest;
- Mauerlat - a wooden beam laid around the perimeter on top of the outer walls. Such a beam can be type-setting or solid, the Mauerlat section starts from 100x100 mm;
- puff - a horizontal crossbar that pulls together 2 adjacent rafter legs in a gable structure;
- Rack - a vertical bar that supports the most loaded roof nodes;
- Run - runs are lateral and ridge:
- The ridge run is installed either at the highest point between the rafters, or directly below this connection;
- The side purlins are also mounted horizontally, rest on the racks and serve as intermediate support for the rafter legs.
- Strut - this is a beam that supports the rafter system at a certain angle, often this angle is 45º;
- Sill - a bar that is mounted on the internal walls of the house and serves to support the racks;
- crate This is a wooden flooring for roofing. The minimum thickness of the batten boards is 25 mm.
The distance between the boards of the batten is called the step of the batten, this parameter is calculated depending on the type of roofing, for example, under the slate the step of the batten will be about 50 cm, and under the soft bituminous tiles you need to fill a solid flooring;
If you plan to mount a soft roof, then it is better and cheaper to use OSB sheets or waterproof plywood (thickness from 12 mm) as a crate.
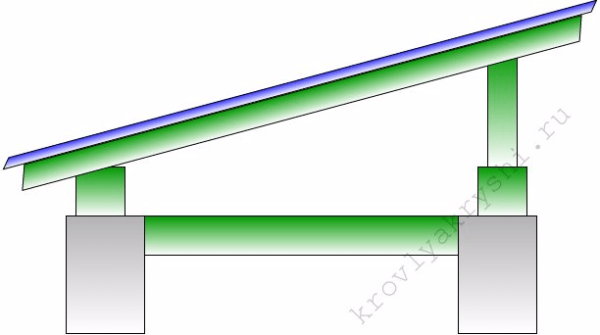
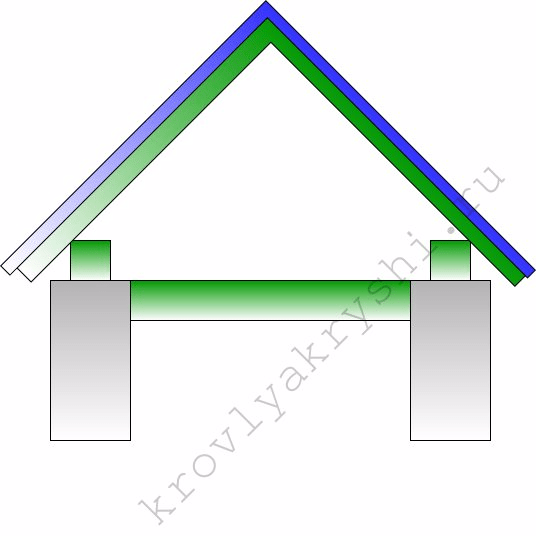
- Base Width - this is the distance between the opposite walls of the house, on which the rafter legs rest;
- lifting height - this is the distance from the floor beams (attic floor) to the roof ridge. It is from the height of the rise that the angle of inclination of the roof depends;
- Overhang - the distance from the wall of the house to the cut of the roof. The classical instruction, as well as GOST 24454-80, require that this distance be at least 50 cm.
What should be taken into account when calculating
Additional information includes the calculation of different types of roof loads. Loads are:
- variables (snow, wind);
- permanent (weight of roofing cake);
- atypical (earthquakes and subsidence).
Snow and wind
The “steeper” the roof, the less snow lingers on it. At the same time, the wind presses quite strongly on a steep roof, so you need to choose something in between.
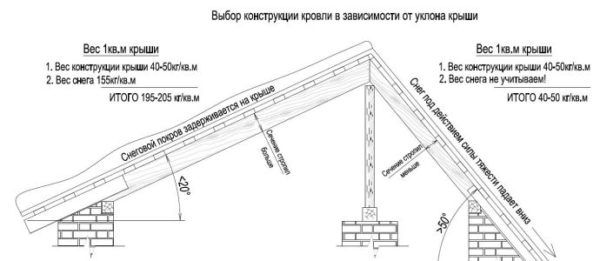
To determine the snow load, you need to multiply the weight of snow per 1 m² by the coefficient of the slope angle Sg * µ. The average snow cover mass varies by region, this information is easily found on the appropriate request or from tables.

As for the coefficient, at the amateur level, 2 values \u200b\u200bare enough:
- For a roof with a slope of up to 25º, it is 1.0;
- From 25º to 60º the coefficient is 0.7;
- If the angle of inclination is more than 60º, then snow simply will not hold on this roof.
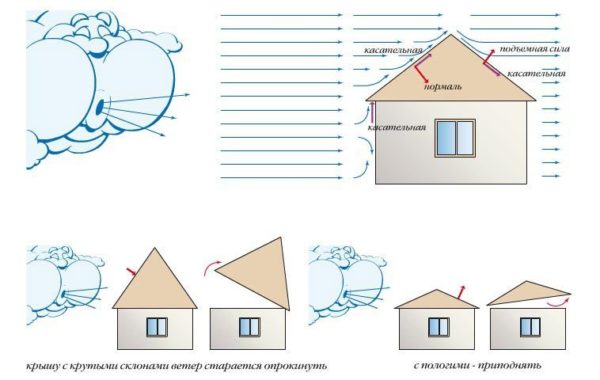
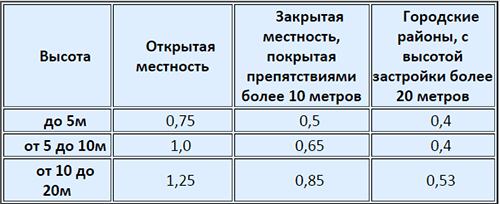
Wind load is calculated in the same way.The average level of wind load in the region must be multiplied by the coefficient responsible for the location and height of the house W0*k. Regional data is fixed, and the coefficient is taken from the table.
Roofing cake weight
The main constant load parameter is the weight of the roofing cake, it depends on it how many rows of lathing will have to be filled, with what step the rafter legs should be installed, and what section the rafters should be.
| roofing material | Average weight per 1 m² |
| Ceramic tiles | 40–60 kg |
| Cement-polymer tile | Up to 50 kg |
| Slate (asbestos-cement) | 12–15 kg |
| Soft bituminous tile | 8–12 kg |
| Composite slate | 4–6 kg |
| Metal sheet (metal tile, corrugated board, corrugated board) | Up to 5 kg |
The maximum for insulation is 10 kg / m² (basalt wool slabs with a thickness of 150 mm or more). Hydro and vapor barrier weighs about 2–3 kg / m², therefore, when building private houses, they are usually not taken into account.
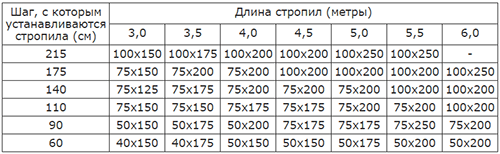
The cross section of the rafter beam is taken from the tables, so below is a table according to which this parameter is determined for central Russia.
Conclusion
Additional calculations are no less important than what the roof calculator will give you and they must be done. In the video in this article you will find information on working with some semi-professional programs. If you have any questions, write them in the comments, I will try to help.

Did the article help you?